Students of ICSE Class 10 should refer to Agro Based Industry ICSE Class 10 Geography previous year questions and solutions. below which have come in past board exams. You should always go through questions that have come in previous years. This will help you to understand the pattern of questions in ICSE Class 10 Geography and prepare accordingly. This will help you to get better marks in ICSE Class 10 Board Exams
ICSE Class 10 Geography Agro Based Industry Last Year Questions
Students should learn the important questions and answers given below for Chapter Agro Based Industry in Geography for ICSE Class 10. These board questions are expected to come in the upcoming exams. Students of ICSE Class 10th should go through the board exams questions and answers for ICSE Class 10 Geography which will help them to get more marks in exams.
Board Exam Questions Agro Based Industry ICSE Class 10 Geography
Short Answer Type Questions
Question: Classify industries on the basis of the nature of products.
Answer: On the basis of the nature of products, the industries re classified into-
(i) Heavy Industries- Ship building, machinery manufacturing, iron and steel.
(ii) Light Industries- Sewing Machines, cycles, electronic goods.
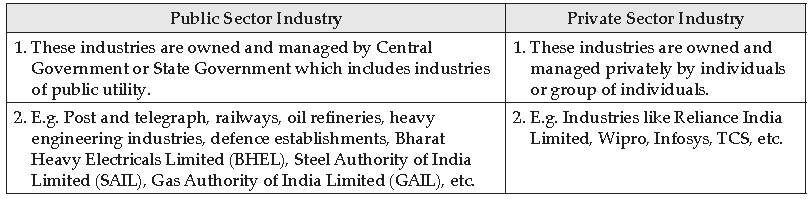
Question: What is the difference between a public sector industry and one which is in the private sector? Give an example of an industry in each of the two sectors.
Answer:
Question: Mention two ways in which the agro-based industries have affected the economy of India.
Answer: (i) Agro-based industries provide agricultural raw materials to the industries.
(ii) These industries are good foreign exchange earner.
Question: With the help of an example each, differentiate between Basic and Consumer Industries.
Answer:

Question: Give two reasons to explain why cottage industries are important for Indian economy?
Answer: (i) It provides employment to a large number of people.
(ii) It is a subsidiary occupation since agriculture alone cannot support livelihood to all rural people.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question: State four geographical factors which should be kept in mind while setting up an agro-based industry.
Answer: (i) Industry should be set up close to the availability of the raw material.
(ii) Nearness to the market.
(iii) Proper transportation infrastructure for transporting the raw materials to the industry.
(iv) Cheap and regular supply of power.
Question: What is the need for rapid industrialisation in India?
Answer: (i) India is an agricultural country and through industrialisation the development of agriculture can be initiated.
(ii) Only agriculture cannot generate employment and thus establishment of industries can generate employment opportunities on a large scale.
(iii) The development of industries producing capital goods i.e. machines, equipment etc. enables a country to produce a variety of goods in large quantities and at low costs and make for technological progress.
(iv) Through industrialisation infrastructures like railways, roadways, dams, etc. can be constructed which can enhance the future growth of Indian economy.
(v) Industrialisation is a necessity for country’s security because only through industrial development self-reliance in defence can be achieved where she can produce her own defence materials.
(vi) Expansion of industries in the backward regions of India is needed to counter the regional imbalance.
Question: What is a cottage industry? Why are cottage industries very important to our country?
Answer: Cottage industries are organised by individuals with private resources and with the help of their family members and their skills e.g. weaving, handloom, carpet industry, etc. Cottage industries are important because :
(i) It provides employment to a large number of people.
(ii) It is a subsidiary occupation since agriculture alone cannot support livelihood to all rural people.
Agro Based Industries Sugar Cotton and Silk
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question: Why is the cotton textile industry called an agrobased industry?
Answer: Cotton textile industry is called an agro-based industry because it requires cotton as its raw material which is an agricultural product.
Question: Name the state that produces the most silk products.
Answer: Karnataka.
Question: State one of the main problems of the silk industry.
Answer: (i) Competition from artificial silk which is cheap and of better quality.
(ii) Import of cheap and alternative textiles from China and other Asian countries.
(iii) Use of outdated manufacturing technology, primitive and unscientific ‘reeling’ and ‘weaving’ techniques, etc.
(iv) The price fluctuation of raw silk affects the weavers and the industry.
(v) Lack of new technologies and modern power looms is affecting the growth of production.
Question: Cotton grows widely in Maharashtra. Give a geographical reason.
Answer: Cotton grows widely in Maharashtra due to ideal climatic conditions, i.e. 21°C to 30°C of temperature,
50 to 75 cm of rain and black soil.
Question: Name a centre of the silk industry in India.
Answer: Bangalore
Short Answer Type Questions
Question: Give two reasons why Ahmedabad in Gujarat is famous for cotton-textile industry.
Answer: (i) Regular supply or proximity to raw material.
(ii) Favourable climatic conditions.
(iii) Good network of road and rail transportation within the country and sea routes for the international market.
(iv) Location of major ports facilitates the export and import facilities.
(v) Availability of cheap and skilled labours.
Question: Differentiate between Mineral-based industry and Agro-based industry giving one example for each.
Answer:

Question: ‘Though Uttar Pradesh has the largest number of sugar mills yet Maharashtra is the largest producer of sugar.’ Give any two reasons to justify the statement.
OR
Mention two reasons why the sugar industry has developed in Maharashtra.
Answer: (i) The maritime climate of Maharashtra which is free from loo and frost.
(ii) The availability of black soil which is well drained and more fertile than alluvial soil.
(iii) Excellent transport facilities in Maharashtra has given it an advantageous position in relation to
export markets.
(iv) The sugar factories are located close to the sugarcane farms which prevent the loss of sucrose content due to minimum transportation time.
(v) The farmers have new machinery and crushing devices which ensures high yield.
Question: Mention two problems of the Cotton Textile Industry in India.
OR
State three main problems of the Cotton Textile Industry in India.
Answer: Fluctuation in availability of raw material as it is agricultural based / outdated machines / frequent power cut.
Question: Give two reasons for the importance of the jute industry in the Ganga-Brahmaputra delta region.
Answer: Availability of raw material as it is a jute producing area / Plenty of clean water for retting / availability of labour and transport facility
Question: (i) Why is the cotton textile industry called an agro-based industry?
(ii) Give an important reason for it being more widespread than the jute industry.
Answer: (i) As it requires cotton, an agricultural product as its raw material.
(ii) It is more widespread than the jute textile industry because cotton is grown all over the country/ whereas jute is cultivated mainly in the east of India/ there continues to be a great demand for cotton all over the country/hence mills are set up everywhere; whereas the demand for jute is declining as it is facing stiff competition from synthetic material like nylon and plastic/ India being a tropical country more demand for cotton fabrics/ affordable by mass
Question: (i) State one important point of similarity between the woollen industry and the silk industry.
(ii) Name the state that produces the most woollen and silk products respectively.
Answer: (i) One important point of similarity between the woolen and silk industry is that both use animal products as raw materials/ both are small-scale/cottage industries.
(ii) Woollen industry- Punjab ; Silk Industry- Karnataka
Question: Name two textile industries using any animal furs. Name an important State where these industries are located.
Answer: Wool – Jammu & Kashmir / Punjab / Haryana / Himachal Pradesh / Uttar Pradesh Silk – Karnataka / Andhra Pradesh / Tamil Nadu / West Bengal / Bihar / Jharkhand / Assam.
Question: Give two reasons for each of the following:
(i) Kolkata is an important cotton manufacturing centre even though West Bengal is not a leading producer of cotton.
(ii) The wool industry is not as well developed as compared to the cotton industry in India.
Answer: Any two of the following:
(i) Water from the Ganga and her distributaries Power from DVC Kolkata is a port Well connected by road and rail
Labour is easily available from West Bengal, Odisha, Jharkhand.
(ii) India is a tropical country, so the demand for wool is not as much as for cotton. Woollen goods are not as profitable as cotton, so more investment in the cotton industry. Woollen goods are not as affordable as cotton The sheep do not have a thick or good quality fleece Competition from synthetic material.
Question: Name any two large sugar producing states, one each in North and South India.
Answer: Uttar Pradesh in North India and Tamil Nadu in South India.
Question: Name an agro-based industry based in the following industrial centres:
(i) Ahmedabad
(ii) Mysuru
Answer: (i) Cotton in Ahmedabad
(ii) Silk in Mysuru
Question: Give geographical reasons for the following:
(i) It is necessary to crush sugarcane within 24 hours of harvesting.
(ii) Sericulture flourished in Karnataka.
Answer: (i) It is so because after harvesting the sucrose content in the cane begins to decrease.
(ii) Favourable climatic conditions with temperatures between 16°C and 32°C which is ideal for rearing the silkworms.
Question: Name and define two important by-products of the sugar industry.
Answer: Molasses- It is thick, dark brown juice obtained from raw sugar during the refining process.
Bagasse- It is the dry pulpy residue left after the extraction of juice from sugarcane.
Question: What is Sericulture? Name any two types of silk.
Answer: The rearing of silk worms for the production of silk is known as Sericulture. The two types of silk are- Mulberry and Tasar.
Question: Why is the silk industry considered as a small scale industry? Name the two types of silk produced in india.
Answer: The silk industry considered as a small scale industry because-
(a) Low capital investment i.e. less than one crore.
(b) It is a farm based and labour intensive industry and requires less machinery. Two types of silk produced in India- Mulberry and Tasar.
Question: Name two important silk weaving centres in Karnataka.
Ans. Bengaluru (Bengalore) and Mysuru (Mysore).
Question: Give two reasons for the importance of the silk industry in India.
Answer: (i) The Indian silk industry is an integral part of Indian Textile Industry and is one of the largest
producers of silk in the world.
(ii) The silk industry in India employs 60 lakh workers.
Question: State two reasons for the concentration of the sugar industry in Uttar Pradesh.
Answer: Two reasons for the concentration of the sugar industry in Uttar Pradesh-
(i) Availability of fertile alluvial soil in the Ganga- Yamuna doab area.
(ii) Provides cheap labour as it is densely populated.
Question: The Khadi and Handloom Sectors of Textile Industry cannot be ignored. Give two reasons to
justifying this statement.
Answer: (i) Handloom industry is one of the oldest industries of India providing employment to millions of skilled and unskilled people.
(ii) The handloom industry is mainly located in small town and rural areas and thus preserve our heritage and culture.
(iii) They earn valuable foreign exchange.
Question: State two economic advantages of the Handloom Industry.
Answer: Two economic advantages of the Handloom Industry-
(i) It provides employment.
(ii) It earns foreign exchange
Long Answer Type Questions
Question: (i) Explain the term Sericulture.
(ii) Why is Karnataka famous for silk industry? Give two reasons.
OR
State two factors which favour the silk industry in Karnataka.
Answer: (i) The rearing of silk worms for the production of
silk is known as Sericulture.
(ii) Karnataka is famous for silk industry because-
1. It has favourable climate for rearing silkworms.
2. The state-owned Channapatna has a capacity of numerous spindles.
3. There are nurseries, silk farms and licensed seed distributors.
4. The decentralized sector has many power looms and handlooms.
Question: Give the geographic term for each of the following:
(i) Non-Mulberry silk produced in Madhya Pradesh.
(ii) Rejected cane after crushing.
(iii) The rearing of silk worms to obtain silk.
Answer: (i) Tasar Silk
(ii) Bagasse
(iii) Sericulture
Question:. With reference to the cotton textile industry, answer the following questions:
(i) Give two reasons why Mumbai is an important cotton textile industry.
(ii) Mention two more important centres of cotton textile industry in India.
Answer: (i) (a) Regular supply or proximity to raw material.
(b) Favourable climatic conditions specially the humid climate.
(c) Good network of road and rail transportation within the country and sea routes for the international market.
(d) Location of major ports facilitates the export and import facilities.
(e) Availability of cheap and skilled labours.
(f) Mumbai is a centre of financial and commercial resources.
(g) Electricity is supplied by the Tata Hydroelectricity system in the Western Ghats to Mumbai. [Any two points]
(ii) Ahmedabad and Coimbatore.
Question: With reference to the silk industry, answer the following:
(i) Why is Karnataka the largest producer of Mulberry silk?
(ii) Mention two varieties of non-mulberry silk produced in India.
(iii) Name one silk weaving centre each in U.P. and in Tamil Nadu.
Answer: (i) Climatic condition of Karnataka is suitable for mulberry tree and so sericulture can be practiced.
(ii) Tassar, Eri, Muga
(iii) Uttar Pradesh – Mirzapur / Pratapgarh / Shahjahanpur Tamil Nadu – Coimbatore / Salem / Tanjavur / Tirunelveli
Question: (i) Give two reasons why the woollen industry is not a flourishing industry in India.
(ii) Name two centres for this industry.
Answer: (i) India is a tropical country and so demand of woollen is low / Poor quality of indigenous wool / Woollens are expensive so less demand / Winter is severe only in north so there is small market.
(ii) Amritsar, Ludhiana, Dhariwal.
Question: (i) State two major problems faced by the sugar industry.
OR
State three problems of the sugar industry in India.
(ii) Name two by-products of the sugar industry.
Answer: (i) Problems of the sugar industry: poor quality of cane/out-dated machinery/fluctuating supply
of raw material/low profit margins as prices are fixed by the govt./inadequate use of byproducts,
increasing production costs/mills are located far from fields, leading to loss of sucrose/ the seasonal nature of the industry, increasing production costs/small size of farms/inadequate use of fertilizers.
(ii) By- products- bagasse, molasses, pressmud
Question: (i) State one of the main problems of the silk industry.
(ii) Name two products of the jute industry, other than rope and gunny bags.
(iii) Why are synthetic fibres popular?
Answer: (i) Introduction of artificial silk which is more durable / Easy to maintain / crease proof / cheaper to produce /Need for modern power looms for increase in production/ No systematic testing and grading of silk/ changes in price of raw silk affect both growers and the industry.
(ii) Two products of the jute industry- carpets/ wall- hangings/pot holders fabrics/sandals/ hand-bags. [Any two points]
(iii) As they are cheaper/are more durable /are moth resistant/ not dependent on agriculture for raw
materials / Chemicals are easily available.
Question: Mention three problems of the jute textile industry in India.
Answer: Any three of the following: Agro-based industry, therefore the supply fluctuates Unproductive workers Outdated machinery and methods of processing jute Competition from synthetic materials Competition from countries like Bangladesh.
Question: Mention three factors that have helped the sugar industry flourish in the peninsular region rather
than in the northern regions of India.
Answer: Any three of the following: Sugarcane grows better in the south because it is a tropical crop and because of the black soil and more scientific methods of cultivation. The sugar mills are near the plantations, so there is no loss of sucrose.
This also lowers the transport costs.
The sugar industry is better managed in the south.
The factories are near the centres of consumption.
Question: In what way does the cotton industry contribute to the economy of India? Mention any three relevant factors.
Answer: The cotton textile industry contributes nearly 30% of the value of exports and employs more than 55 million people.
2. The industry is one of the largest foreign exchange earner commodities of India.
3. It contributes about 14% to the industrial production, 4% to the GDP and 14.42% to the country’s export earnings.
Question: With reference to the cotton textile industry:
(i) Which is the country’s most important manufacturing centre?
(ii) State two geographical reasons for its importance.
Answer: (i) Maharashtra and Gujarat.
(ii) (a) Regular supply or proximity to raw material.
(b) Favourable climatic conditions specially the humid climate.
(c) Good network of road and rail transportation within the country and sea routes for the international market.
(d) Location of major ports facilitates the export and import facilities.
(e) Availability of cheap and skilled labours.
Question: (i) Mention two reasons for the importance of the cotton textile industry.
(ii) Mention one reason for its poor performance.
Answer: (i) Two reasons for the importance of the cotton textile industry-
1. The cotton textile industry contributes nearly 30% of the value of exports and employs more than 55 million people.
2. The industry is one of the largest foreign exchange earner commodities of India.
(ii) One reason for its poor performance-
1. Many factories are old, obsolete and sick industrial units and thus faces low productivity
Question: Give geographical reasons for the following:
(i) Kolkata has many cotton mills though cotton is not grown in West Bengal.
(ii) Karnataka is an important centre for silk.
(iii) India produces very little cane-sugar though it is one of the largest producers of sugarcane in the world.
Answer: (i) Kolkata has many cotton mills though cotton is not grown in West Bengal because-
(a) Kolkata is located very close to coal mines.
(b) It has abundant capital supply.
(c) There is availability of cheap labour, humid climate, plenty of soft water.
(d) It has port facility and excellent means of transport and communication.
(ii) (a) Karnataka has favourable climatic conditions with temperature ranging from 16°C to 32°C.
(b) Sericulture provides employment to a large number of people. [Any one point]
(iii) (a) The sugarcane produced in India is of poor quality with low sucrose content.
(b) In rural areas, instead of sugar, gurand khandsari are in more demand.
Question: Name any two by-products of the sugar industry. Give two uses of each.
Answer: Two by-products of Sugarcane– Molasses- It is used in the production of citric acid, chemicals, synthetic rubber and as fuel for mills. Bagasse- It is used as a biofuel and in the manufacture of pulp and building materials. Pressmud- It is used for making wax, carbon paper and shoe polish.
Question: Explain two factors affecting the development of the cotton textile in India.
Answer: (i) Regular supply or proximity to raw material.
(ii) Favourable climatic conditions specially the humid climate.
Question. Name an agro-based industry based in the following industrial centres:
(a) Ahmedabad (b) Mysore
Answer: (a) Ahmedabad – Cotton (b) Mysore – Silk
Question. Sugar industry in North India and Sugar industry in Peninsular India.
Answer:

Question. Give three important reasons which have made Maharashtra the leading producer of sugar in India.
Answer: (i) The black soil here is more fertile than the alluvial soil of the northern India. Besides this, the black soil is well drained.
(ii) The cane is of superior quality with higher yield.
(iii) The excellent transport facilities, especially in the state of Maharashtra in relation to export markets have placed it in a very advantageous position for the further expansion of the sugarcane industry.
Question. Classify the industries on the basis of the source of raw materials.
Answer: (i) Agro based : These industries procure raw materials from agriculture.(ii) Mineral based : These industries depend on minerals for their raw
materials.
(iii) Forest based : These industries procure raw materials from forest products. Eg.: Paper, Shellac etc.
(iv) Animal based : These industries depend upon other living beings for their raw materials. Eg.: Silk, woollen, dairy, leather etc.
Question. Public Sector and Private Sector industries.
Answer:

Question. What is sericulture? Name any two types of silk.
Answer: The rearing of silkworms for silk production is known as Sericulture. Types of silk are mulberry, eri, tasar and muga.
Question. Why Uttar Pradesh has been relegated to the second place in terms of sugar production?
Answer: Uttar Pradesh has been relegated to second position because of old mills, management and labour problems and shorter crushing period.
Question. Name the by-products of the sugar industry. Give the industrial use of each.
Answer: (i) Molasses is used in the alcohol industry for the distillation of liquor (rum), power alcohol, etc. It is also used in the production of certain
chemicals and synthetic rubber.
(ii) Press mud is utilised for making wax, carbon paper and shoe polish.
Question. Basic and Secondary industries.
Answer:

Question. How and why does the government take decision to encourage new industries to be set up ? OR Why does government try to control the location of industries ?
Answer: (i) The government has a very significant role in the industrialisation process especially in the developing and under developed countries.
(ii) The big industries which require large infrastructure and capital are set up by the government.
(iii) The government makes rules and regulations for running the industries and also provides the basic facilities like land, water, electricity.
(iv) Further, it is the government which makes policies and taken decisions to protect and encourage indigenous industries.
Question. Classify the industries on the basis of ownership and management.
Answer: (i) Private sector : They are owned and managed by individuals or firms. Eg.: Tata Iron and Steel at Jamshedpur, Infosys, Wipro etc.
(ii) Public sector : These are completely owned and managed by the state or central govt., or by their agencies. For eg.: Railways, Postal service, BHEL, GAIL, Indian Oil Corporation etc.
(iii) Joint sector : These are owned & managed jointly by government individuals and firms. The government may hold 26% or more of stake, while the private promoters hold 25% and the rest is by general public by means of share capital. Eg.: Maruti Udyog Ltd, TELCO, Automobile Corporation of Goa Ltd., etc.
(iv) Co-operative sector : These industrial units are run with the active cooperation of a large number of individuals or firms. Eg.: The Sugar cooperatives
in Maharashtra, Anand Co-operative Society in Gujarat etc.
Question. Name the major sugar producing centres in Andhra Pradesh.
Answer: Kakinada, Chittor, West Godavari, East Godavari and Vijayawada.
Question. Heavy and Light industries.
Answer:

Question. Name the major sugar producing centres in Karnataka.
Answer: Mandya, Shimoga, Belgaum, Bijapur and Bellary.
Question. Classify the small scale industries on the basis of location and market.
Answer: (i) Village industries : Based in villages. Cater the local needs. Raw materials are procured locally. Eg.: Pottery, handloom, carpentry, blacksmithy etc.
(ii) Cottage industries : They are run by the household members. Locally available resources are used. Eg. Carpet making in Kashmir, Woollen clothing in the North-East. Products need not be sold in local market alone.
Question. Give reasons for sick mills and how they can be revived ?
Answer: Reason for sickness :
(i) Uncertainty of raw material.
(ii) Low productivity of machines and labour.
(iii) Lack of modernisation.
(iv) Management problems.
Revival :
(i) This sick units require heavy financial investments for replacement and modernization purposes.
(ii) Many of these sick units have been taken over by the government.
Question. Mineral-based and Agro-based industries.
Answer:

Question. What are the reasons for higher output of sugar in Tamil Nadu?
Answer: Tamil Nadu has higher sugar output due to :
(i) Higher sucrose content of sugarcane.
(ii) Longer crushing season.
(iii) Higher per hecrare yield of sugarcane.
Question. Why is the sugar industry highly dispersed in India?
Answer: Sugar industry is highly dispersed in India since sugarcane is grown throughout the country.
Question. Classify industries on the basis of the nature of products. Give one example of each.
Answer: (i) Basic Industries : Iron and steel industry and petroleum industry.
(ii) Secondary or Consumer Industries : Textile, sugar, paper making, etc.
(iii) Tertiary Industries : Railways, transport, banking, post and telegraph, etc.
Question. Classify the industries on the basis of the quantity and cost of raw materials and the nature of products.
Answer: (i) Heavy industries : The quantity and the cost of their raw materials is greater, more scientific knowledge and sophisticated machinery. Finished product is heavy and bulky. Cost of transport is more.
(ii) Light industries : They require lesser and cheaper raw materials, lesser labour, less capital investment and less sophisticated machinery
as compared to heavy industries. Finished product is lighter. Transport cost is less.
Question. Which industry has a tendency to migrate towards the south? Why?
Answer: Sugar industry has a tendency migrate towords the south. The reason are:
(i) The yield per hectare is high due to tropical climatic conditions.
(ii) The crushing season is longer than northern India.
(iii) Most of the mills are new and are well equipped with modern machines.
Question. Mention any two important by-products of the sugar industry.
Answer: Molasses, Press Mud, Bagasse are important by-products of the sugar industry.
Question. Large-scale and Small-scale industries.
Answer:




