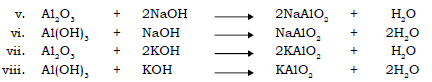Students of ICSE Class 10 should refer to Analytical Chemistry ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Questions below which have come in past board exams. You should always go through questions that have come in previous years. This will help you to understand the pattern of questions in ICSE Class 10 Chemistry and prepare accordingly. This will help you to get better marks in ICSE Class 10 Board Exams
ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Important Questions Analytical Chemistry
Analytical Chemistry is an important chapter in ICSE Class 10 Chemistry. Our faculty has prepared the following ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Questions and answers based on the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Please refer to the solved questions below and also see links provided for other chapters.
Analytical Chemistry ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Questions
Analytical Chemistry ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Questions
I. DO WE KNOW?
Analytical chemistry is the branch of chemistry which deals with experimental study by qualitative and quantitative means. It includes the identification of unknown salt solution by chemical tests. Use of sodium and ammonium hydroxides on salt solution is involved in the chemical tests and study of observation of the colour and solubility of precipitates is made.
1. Define the following terms :
i) Alkalis : A basic hydroxide which is soluble in water is known as alkali
E.g. sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide.
The solution of an alkali in water contains hydroxide ions

ii) Salt : A salt is a compound containing a cation other than H+ ion and anion other than OH– ion. A salt is generally coloured if its cation or anion is coloured.
iii) Precipitate : A solid insoluble substance formed by the reaction between solutions is called a precipitate.
iv) Precipitation : It is a process of formation of precipitate (insoluble solid) on mixing solutions.
v) Analysis : Determination of the chemical components in a given sample is called Analysis.
vi) Qualitative analysis : Qualitative analysis is the analysis which involves the identification of the unknown substance.
vii) Reagent : A Reagent is a substance that reacts with another substance used for its identification.
A. Colour of salts
2.a. Write the probable colour of the following salts.
1. Iron (III) chloride
2. Potassium nitrate
3. Ferrous sulphate
4. Aluminium acetate
5. Calcium carbonate
6. Cupric sulphate
7. Potassium permanganate
8. Nickel sulphate
9. Potassium chromate
10. Chromium sulphate
Ans. 1. Yellow/brown
2. Colourless/ white
3. Green
4. Colourless / white
5. Colourless / white
6. Blue
7. Pink
8. Green
9. Yellow
10. Green.
2.b. Match the colour of the solution in column ‘A’ with the probable ions in Column ‘B’.
Column ‘A’ Column ‘B’
1. Yellow coloured solution (a) Cr2O72-
2. Orange coloured solution (b) Co2+
3. Green coloured solution (c) Fe3+
4. Pink coloured solution (d) Ni2+
5. Blue coloured solution (e) Mn2+
Ans : (i) (c) Fe3+ (ii) (a) Cr2O72- (iii) (d) Ni2+ (iv) (e) Mn2+ (v) (b) Co2+
3. State the action of NaOH on salt solution with the balanced chemical equation for each.
Ans. Action of sodium hydroxide on solutions of soluble salt of metals.


4. State the action of ammonium hydroxide on various salt solutions and give balanced equations for each reactions.
Ans. Action of ammonium hydroxide on solutions of soluble salts of metals.

5. State the action of hot concentrated sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide on metals like zinc, lead and aluminium. Give balanced equations for the same.
Ans. The metals like Zn, Pb and Al react with hot concentrated NaOH and KOH to give the corresponding salt and liberate hydrogen.

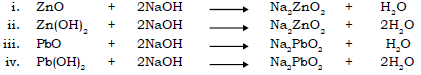
6. State the action of alkali on oxides and hydroxides of certain metals like Zn, Pb and Al.
Ans. Oxides and hydroxides of certain metals e.g. Zn, Al and Pb are amphoteric in nature i.e. they react with acids and with alkali to give salt and water. On reaction with strong alkalis, these oxides behave as weak base and give salt and water.
Action of alkalis on oxides and hydroxides of certain metals :

ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS
1. Name the following.
1. Any one salt that can be used to distinguish between NaOH and NH4OH solution.
Ans. Calcium nitrate or lead nitrate or copper sulphate
2. A metal hydroxide which is sparingly soluble in caustic soda solution.
Ans. Calcium hydroxide
3. A metallic oxide soluble in excess caustic soda solution.
Ans. Lead oxide or aluminium oxide or zinc oxide.
4. A metal that evolves a gas which burns with a pop sound when boiled with alkali solutions.
Ans. Aluminium or zinc or lead.
5. A coloured metallic oxide which dissolves in alkalis to yield colourless solutions.
Ans. Lead oxide
6. A compound containing zinc in the anion.
Ans. Sodium zincate or potassium zincate.
2. State the correct answer from the brackets :
1. Salts of elements are generally coloured. ________________________
[Normal/Transition]
Answer
Transition
2. The hydroxide which is soluble in excess of NaOH ________________________
[Zn(OH)2/Fe(OH)3/Fe(OH)2]
Answer
Zn(OH)2
3. The salt which will not react with NH4OH solution ______________________
(ZnCl2/CuCl2/NH4Cl/FeCl2)
Answer
NH4Cl
4. To distinguish soluble salts of zinc and lead ____________________________
[NaOH/NH4OH]
Answer
NH4OH
5. Oxides and hydroxides of certain metals i.e. ________________________ are amphoteric in nature.
[iron/zinc/copper]
Answer
zinc
6. Amphoteric oxides react with __________________________ to give the respective salt and water.
[acids/alkali/acids and alkali]
Answer
acids and alkali
7. Metals like Zn, Al and Pb react with hot concentrated alkalis to give the corresponding soluble salt and liberate ________________________ gas.
[H2/SO2/CO2]
Answer
H2
3. Identify the cations in each of the following case :
a) NaOH soln when added to the soln ‘A’ gives reddish brown ppt.
Answer
Fe3+
b) NH4OH soln when added to the soln ‘B’ gives gelatinous white ppt which dissolves in excess.
Answer
Zn2+
c) NaOH soln when added to soln ‘C’ gives pale blue ppt which is insoluble in excess.
Answer
Cu2+
d) NH4OH soln when added to soln ‘D’ gives dirty green ppt which changes to reddish brown after sometime.
Answer
Fe2+
e) NaOH soln when added to soln ‘E’ gives white ppt which dissolves in excess to give colouless soln.
Answer
Pb2+
4. (a) Chemical equations.
1) Iron (II) sulphate to iron (II) hydroxide.

2) Iron (III) chloride to iron (III) hydroxide.
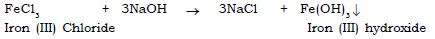
3) Lead nitrate to sodium plumbite.

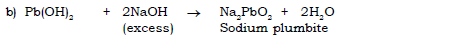
4) Zinc hydroxide to tetramine zinc hydroxide.
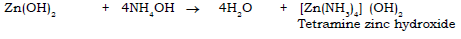
5) Zinc sulphate to sodium zincate.
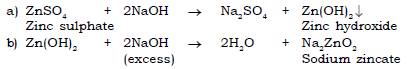
6) Aluminium hydroxide to potassium aluminate.

7) Zinc to sodium zincate.

(b) Complete and balance the following equation:
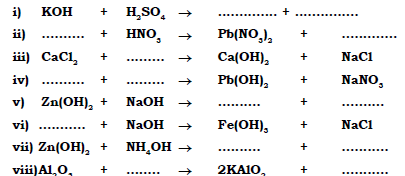
Ans.
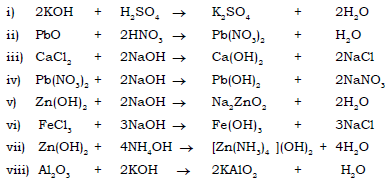
5. Match the salts in column ‘A’ with the colour of the precipitate’s formed in column ‘B’ on reacting with NaOH.
‘A’ ‘B’
1. FeSO4 (a) White
2. MgSO4 (b) Gelatinous white
3. Ca(NO3)2 (c) Dull White
4. Pb(NO3)2 (d) Dirty green
5. ZnSO4 (e) Chalky white
Ans. 1. (d) Dirty green
2. (c) Dull White
3. (a) White
4. (e) Chalky white
5. (b) Gelatinous white
6. What do you observe when.
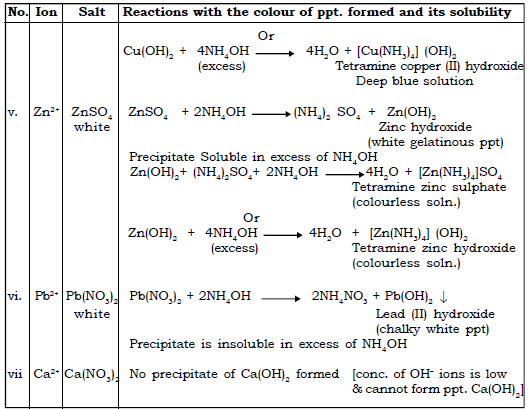
(a) Ammonium hydroxide is added to copper sulphate solution first a little then in excess.
Ans. On adding Ammonium hydroxide drop by drop, a pale blue ppt is formed which dissolves in excess of Ammonium hydroxide to give deep blue solution or inky blue solution.
(b) Sodium hydroxide soln is added to zinc sulphate solution first a little then in excess.
Ans. A white ppt is formed which is soluble in excess of NaOH to give a colourless solution
(c) Calcium nitrate is added to sodium hydroxide solution.
Ans. A white ppt is formed which is slightly soluble in excess.
(d) Sodium hydroxide is added to Iron (III) sulphate solution first a little then in excess.
Ans. A reddish brown ppt is formed which is insoluble in excess.
(e) Freshly precipitated aluminium hydroxide reacts with caustic soda solution.
Ans. A colourless gas is evolved which burns with a pop sound of a pale blue flame.
(f) Caustic soda is added to FeCl3 solution first little then in excess.
Ans. Reddish brown precipitate is observed which is insoluble in excess.
7. Distinguish between.
(i) Using sodium hydroxide solution, how would you distinguish :
a) Zinc chloride and calcium nitrate solution.
b) Iron (II) chloride from iron (III) chloride.
c) Lead hydroxide from magnesium hydroxide.
Ans.


(ii) How does Ammonium hydroxide help in distinguish between :
a) Zinc nitrate and lead nitrate
b) Lead hydroxide and zinc hydroxide
Ans.

(c) You are proivded with two reagent bottles marked A and B. One of which contains NH4OH solution and the other contains NaOH solution. How will you identify them by a chemical test?
Ans. (i) Add calcium nitrate solution to both reagents. If a white precipitate is observed, the reagent is sodium hydroxide. If precipitate is not observed the solution contains NH4OH OR
(ii) Add lead nitrate solution to both reagents. If the white precipitate formed is soluble on adding excess of the reagent it is NaOH. If the precipitate is insoluble, the reagent is NH4OH OR
(iii) Add copper sulphate solution to both reagents. If the pale blue precipitate formed is soluble in excess of reagent it is NH4OH. If the precipitate is insoluble, the reagent is NaOH.
8. When ammonium hydroxide is added to solution B. it gives an inky blue solution. What is the cation present in solution B? What is the probable colour of solution B?
Ans. The cation present in B is Cu2+
The colour of solution B is blue.
9. On adding dilute ammonia solution to a colourless solution of a salt, a white gelatinous precipitate appears. This precipitate however dissolves on addition of excess of ammonia solution. Identify (choose from Na, Al,Zn, Pb, Fe)
(a) Which metal salt solution was used ?
(b) What is the formula of the white gelatinous precipitate obtained ?
Ans. a) Zinc salt was used
b) Zn(OH)2
10. Give reason for each:
a) A solution of ferrous chloride in water, which is light green, changes into reddish brown colour when exposed to air for some time.
b) Green-coloured crystals of ferrous sulphate turn brown when exposed to air for a long duration of time.
Ans. a) The light green colour of the solution of ferrous chloride in water changes to reddish brown colour when exposed to air for some time due to the oxidation of ferrous ions (Fe2+) to ferric ions (Fe3+). The reddish brown colour is of ferric chloride.
b) Green-coloured crystals of ferrous sulphate turn brown when exposed to air for a long duration of time due to the oxidation of ferrous ions(Fe2+) to ferric ions (Fe3+). The brown -coloured crystals are of ferric sulphate.
11. a) What are amphoteric Oxides?
b) How do these oxides react with NaOH? Give the equation zinc oxide with NaOH.
c) Ammonium hydroxide does not give a precipitate with Ca2+ salt
Ans: a) Amphoteric oxides are those oxides which react with both acids as well as alkalis to give salt and water.
b) Oxides of amphoteric metals like Zn, Pb, Al, etc., react with strong alkalis like NaOH to form complex salts and water.

c) Ammonium hydroxide is a weak alkali; it dissociates partially and thus yeilds less OH– ions in its solution and hence cannot precipitate Ca(OH)2 from its salt.
III. EQUATION SUMMARY
A. Reactions with sodium hydroxide :


B. Reactions with Ammonium hydroxide :

C. Action of alkalis on certain metals : NaOH & KOH [Hot & Conc.]

D. Action of alkali on oxides and hydroxide of certain metals :