Question 1. Define the following:
(i) Osmosis
(ii) Diffusion
(iii) Turgor pressure
(iv) Hypertonic solution
(v) Plasmolysis
Solution 1:
1. Osmosis:- Osmosis is defined as the passage of solvent molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration through semipermeable membrane it occurs simultaneously in response to a driving force.
2. Diffusion:- It is the process of transport of molecules from high concentration to the lower concentration regions, means. It occurs along the concentration gradient.
3. Turgor Pressure:- pressure applied from cytoplasm to the cell membrane inside cell is known as turgor pressure.
4. Hypertonic solution:- A solution whose osmotic concentration is more than that of another solution or cells sap is called hypotonic solution.
5. Plasmolysis:- plasmolysis is the shrinkage of the protoplast and its movement away from the cell wall due to the exosmosis when the cell is placed in a solution that has high solute concentration of hypertonic.
Question 2. What is the difference between diffusion and osmosis?
Solution 2:
| Diffusion | Osmosis |
| It is the transfer of a substance’s molecules from a high-concentration region to a low-concentration zone. | It is the process by which water molecules flow from an area of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration via a semi-permeable barrier. |
Question 3. What is the difference between endosmosis and exosmosis?
Solution 3:
| Endosmosis | Exosmosis |
| 1. Endosmosis is the process of water diffusion into a cell from the outside. | Exosmosis is the process of water diffusion from the inside to the exterior of a cell. |
| 2. When the cell is put in a hypotonic solution, this happens. | 2. When the cell is put in a hypertonic solution, this happens. |
Question 4. Define root pressure.
Solution 4:
It is a positive hydrostatic pressure develops in a root cortical cells which pushes the water into the xylem, upto a certain height. Maximum value of root pressure developed is 2b atmosphere which can help water raise up to 20 meters.
Question 5. What is permeability?
Solution 5:
Permeability is the ability of a membrane to allow passage of gases, liquid or solutes through it depends on nature of membrane and nature of molecules or ions passing through it.
Question 6. Which part of the root absorbs maximum water and why?
Solution 6:
Root hairs because the xylem is not fully formed in this region, the epidermis and endodermis are still permeable to water,
Question 7. What are the functions of root?
Solution 7:
1. Root has to absorb nutrition and water from the soil
2. It helps to store food materials.
3. Roots help to synthesize plant growth regulators.
4. It helps to anchor the plant in soil.
Question 8. Distinguish between the following:
(i) Filtration and diffusion
(ii) Turgor pressure and osmotic pressure
(iii) Hypotonic and hypertonic solutions
(iv) Osmosis and diffusion
(v) Flaccid condition and turgid condition
(vi) Plasmolysis and deplasmolysis
Solution 8:
(i) Filtration and diffusion
| Filtration | Diffusion |
| Filtration is the process of mechanically separating a liquid from the floating undissolved particles. | Diffusion is defined as the migration of a chemical from a high-concentration area to a low-concentration area. |
(ii) Turgor pressure and osmotic pressure
| Turgor Pressure | Osmotic Pressure |
| The turgor pressure of a turgid cell is the pressure exerted by the cell contents on the cell wall. | The osmotic pressure is the pressure at which water molecules prefer to penetrate a semipermeable barrier. |
(iii) Hypotonic and hypertonic solutions
| Hypotonic Solution | Hypertonic Solution |
| The fluid outside the cell has a lower solute concentration than the cell sap in this situation. | The fluid outside the cell has a greater solute content than the cell sap in this situation. |
(iv) Osmosis and diffusion
| Osmosis | Diffusion |
| It is the process by which water molecules flow from an area of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration via a semipermeable barrier. | It is the transfer of substance molecules from a higher concentration region to a lower concentration region. |
(v) Flaccid condition and turgid condition
| Flaccid Condition | Turgid Condition |
| Flaccid describes a cell that is undergoing plasmolysis. | Turgid describes a cell that has reached the point where it can no longer hold any more water, i.e. it is totally distended. |
(vi) Plasmolysis and deplasmolysis
| Plasmolysis | Deplasmolysis |
| When a cell is put in a hypertonic solution, water begins to osmosis out of the cell, causing protoplasm to decrease. Plasmolysis is the term for this phenomenon. | When a plasmolysis cell is put in a hypotonic solution or pure water, endosmosis occurs, and the protoplast of the cell resorbs the water and returns to its original location. Deplasmolysis is the term for this phenomenon. |
Question 9. What is the utility of plasmolysis?
Solution 9:
The effect of plasmolysis has also been commercially exploited. Bacteria do not survive in a highly salted pickle because they become plasmolysis and consequently that killed. Similarly high concentration of sugar in jam and jellies prevented the growth of bacteria etc.
The weeds or grasses can be eliminated by sprinkling the salt around their roots and then can watering them. The treatment causes plasmolysis in the root cells and the plant finally dies.
Question 10. Give an account of the importance of turgor pressure in a herbaceous plant.
Solution 10:
Turgor pressure is ultimately responsible for enlargement and extension of cell during the growth. It is also necessary for the cell’s proliferation. Stomata open and close in response to changes in turgor pressure.
Question 11. Mention two ways in which root hairs are suited for absorption of water from the soil?
Solution 11:
1. Water can pass through the epidermis and endodermis of root hairs.
2. The surface area of root hairs is tremendous.
Question 12. (i) How is root hair adapted for the absorption of water from the soil? (ii) What part is played by
(a) the cell wall?
(b) The cytoplasm in the uptake of water into the root hair?
(iii) What would happen to the root hair of a potted plant if the soil was watered with an extremely concentrated solution of sodium chloride?
Solution 12:
1. In the soil, the primary root and its many branches form a network. The root hairs become entangled in the soil particles and are in constant contact with the capillary water that surrounds them. Root hair epidermal cells feature vacuoles that store cell sap. The cell sap is generally more concentrated than the soil solution. As a result, endosmosis allows water to enter the root hair cells. The epidermal cell sap solution is diluted by this water. Water then enters the cortical cells via osmosis, travels to the endodermal cells, and finally to the pericycle cells. Water then reaches the xylem tissue through this layer. By osmosis, the water is absorbed and translocate up to the root’s xylem.

2. (a) The cell wall separates the two solutions – cell sap and soil solution – and is permeable, allowing water to enter by endosmosis into the root hair cells.
(b) The cytoplasm contains vacuoles containing cell sap or a mineral salt solution. Because the cell sap is more concentrated than the soil solution, it aids in endosmosis water absorption.
3. If the soil is watered with an excessively concentrated sodium chloride solution, osmosis causes the water to migrate out of the root hair, resulting in plasmolysis.
Question 13. The apparatus arranged alongside signifies an important process.
(i) Name the process.
(ii) Where does this process occur in plants?
(iii) What solution is placed inside the dialysis tubing?
(iv) What happens to the level of the solution in the capillary tube?

Solution 13:
1. The process is Osmosis
2. Process occur in Root hair
3. Sugar solution is placed inside the dialysis tubing
4. The level of the liquid in the capillary tube is raised up.
Question 14. Name the following:
(i) The pressure with which the molecules of a substance diffuse.
(ii) Two solutions having same concentrations.
(iii) The force developing in shoot responsible for most of the absorption of water.
(iv) The uptake of mineral ions against concentration gradient.
(v) Tissue concerned with upward conduction of water.
(vi) Condition of cell in which the cell contents are shrunken.
(vii) The inward movement of solvent molecules through the plasma membrane of cell.
(viii) The process by which raisins swell up when placed in a beaker of water.
(ix) Movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration.
Solution 14:
1. Osmotic pressure
2. Isotonic solutions
3. Cohesive force
4. Active absorption
5. Xylem
6. Plasmolysis
7. Endosmosis
8. Endosmosis
9. Diffusion
Question 15. Name the tissue concerned with upward conduction of water in plants.
Solution 15:
Tissue concerned with upward conduction of water in plants is Xylem
Question 16. Name the condition in which the cell contents are shrunken.
Solution 16:
Plasmolysis is the condition in which the cell contents are shrunken.
Question 17. Explain briefly why do not root hairs become flaccid when fertilizers are added to the moist soil around them?
Solution 17:
When fertilizers are introduced to the damp soil around them, the root hairs become flaccid because the fertilizers become hypertonic, causing plasmolysis in the root hair cells. The cell loses its turgidity and becomes flaccid.
Question 18. Name the process by which molecules distribute themselves evenly within the space they occupy ______ (Fill in the blank).
Solution 18:
Diffusion the process by which molecules distributes themselves evenly within the space they occupy.
Question 19. Name the term for the inward movement of solvent molecules through the plasma membrane of a cell.
Solution 19:
The term for the inward movement of solvent molecules through the plasma membrane of a cell Endosmosis.
Question 20. The diagram given below represents a plant cell after being placed in a strong sugar solution. Guidelines 1 to 5 indicate the following:
1. Strong sugar solution
2. Cell wall
3. Protoplasm
4. Large vacuole
5. Nucleus
Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow:
(i) What is the state of the cell shown in the diagram?
(ii) Name the structure which acts as a selectively permeable membrane.
(iii) If the cell had been placed in distilled water instead of strong sugar solution which feature would not have been present?
(iv) If the cell in the diagram possessed chloroplasts where would these be present?
(v) Name any one feature of this plant cell which is not present in animal cells.

Solution 20:
1. Plasmolysed cell
2. Plasma membrane
3. Large vacoule
4. The chloroplasts would be present in the shrunkenprotoplast.
5. Cell wall
Question 21. Explain why:
(i) Raisins swell up in water.
(ii) We gargle with saline solution in case of throat infection.
(iii) Bacteria and fungi do not grow in pickles, jams, jellies and squashes.
(iv) The leaves of wilted lettuce, if kept in cold water, become crisp.
Solution 21:
(i) When raisins are placed in water, they swell because the water is hypotonic in comparison to the raisins, allowing water to enter through endosmosis.
(ii) Hypertonic water is saline water. As a result, any infectious agent in the throat, such as bacteria, is plasmolyzed, curing the ailment.
(iii) Jam, jellies, and pickles are stored in a hypertonic sugar or salt solution in which bacteria and fungi undergo plasmolysis. As a result, bacteria and fungi are killed, and pickles, jams, and jellies are properly preserved.
(iv) In a hypotonic solution, the leaves of wilted lettuce grow crisp when kept in cold water because they absorb water by endosmosis.
Question 22. Define ascent of sap.
Solution 22:
The upward movement of water and minerals through the xylem in plants is called ascent of SAP.
Question 23. Why do plants die when salt is sprinkled over them?
Solution 23:
Plants die when they are sprayed with salt because their cells are plasmolyzed. Inside the plant cells, the salt renders the fluid hypertonic, causing cell shrinkage or exosmosis.
Question 24. Define root pressure. How would you demonstrate it experimentally?
Solution 24:
It is a positive hydrostatic pressure developed in the root cortical cells which pushes the water into the xylem up to the certain height maximum value of RP developed is 2 atmosphere when which can help water is up to 20 metres. Demonstration of Root pressure:
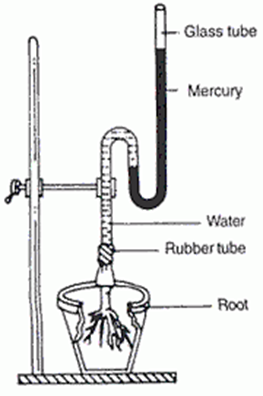
(a)Select a healthy, mature herbaceous plant.
(b) A sharp knife is used to cut the plant’s stem a few centimetres above the base and connect it to a manometer via a rubber tube.
(c) The mercury level in the manometer rises after a few hours.
(d) This is due to the pressure created by water ejected from the plant’s cut end as a result of root pressure caused by water entering the root cells.
Question 25. Give at least three uses of water to green plants.
Solution 25:
1. One of the raw ingredients for photosynthesis is water.
2. Seed germination necessitates the presence of water.
3. Water regulates stomata opening and shutting.
Question 26. What will happen if a concentrated solution of a fertilizer is given to the potted plants?
Solution 26:
When a concentrated fertiliser solution is applied to potted plants, the fertiliser reacts with the soil water to form a hypertonic solution, causing exosmosis.
Question 27. The figure shows a diagrammatic representation of the movement of certain substances inside the stem of a certain plant. Write five sentences on whatever you can explain about the processes or the arrangement of structures indicated in the diagram. Note: – Each sentence must include one or more of the following four words, and each word can be used several times. Xylem, phloem, roots, leaves.

Solution 27:
1. Water is absorbed by plants through their roots.
2. The plant’s stem and leaves receive water from the roots.
3. The xylem is not fully formed in root hairs, and the endodermis and epidermis are water permeable.
4. Water is absorbed by plants in all directions via xylem.
5. Phloem, on the other hand, is responsible for transporting food
Question 28. The diagram given below represents the results of an experiment conducted on two freshly taken leafy shoots of a herbaceous plant. The lower ends of the shoots dip in ordinary water.
(i) What is the aim of the experiment?
(ii) Some parts of the stem in both the shoots have been removed. Name the conducting tissue in shoot
(a) and in shoot (b) that has been removed.
(iii) What are the results of this experiment?

Solution 28:
1. The experiment’s goal is to demonstrate that xylem is responsible for water transmission in plants.
2. (a) Phloem has been taken from the shoot. (b) Xylem has been cut out of shoot.
3. The xylem has been destroyed in shoot (b), resulting in wilting leaves. The leaves in shoot (a) are turgid because the xylem has not been removed.
Question 29. Three plants (a), (b) and (c) were placed in beakers containing coloured water. The water in each beaker was covered with a layer of oil. The leaves were removed from plant (b), while plant (c) was exposed to strong light.
(i) In which plant, (a), (b) or (c) would the water move up the fastest?
(ii) In which plant (a), (b) or (c), would the water move up slowly?
(iii) Why was the water covered with a layer of oil?
(iv) What is being investigated by this experiment?

Solution 29:
1. The water would rise the fastest.
2. In the water would gradually rise.
3. To keep water from evaporating.
4. Water absorption by the roots
Question 30. Choose the correct answer:
(i) Osmosis involves diffusion of
(a) suspended particles from lower concentration to higher concentration.
(b) suspended particles from higher concentration to lower concentration.
(c) water from the more concentrated solution to the less concentrated solution.
(d) water from the less concentrated solution to the more concentrated solution.
Solution :
Water from the more concentrated solution to the less concentrated solution.
(ii) An example of a selective permeable membrane is
(a) cell wall
(b) mitochondrial membrane
(c) chloroplast membrane
(d) plasma lemma
Solution :
plasma lemma
(iii) Plasmolysis will occur when the cell is placed in a
(a) hypotonic solution
(b) isotonic solution
(c) hypertonic solution
(d) acidic solution
Solution :
hypertonic solution
(iv) Grapes when placed in a strong sugar solution shrink because of
(a) diffusion
(b) plasmolysis
(c) exosmosis
(d) endosmosis
Solution :
plasmolysis
(v) Cell turgidity is caused by:
(a) endosmosis
(b) exosmosis
(c) plasmolysis
(d) diffusion
Solution :
endosmosis
(vi) If a marine plant is transferred to fresh water, it bursts due to
(a) exosmosis
(b) endosmosis
(c) plasmolysis
(d) diffusion
Solution :
endosmosis
(vii) Which one is semi-permeable?
(a) Plasma lemma
(b) Cell wall
(c) Endoplasmic reticulum
(d) Golgi body
Solution :
Plasma lemma
(viii) Swelling of wooden doors during rains is caused by
(a) endosmosis
(b) imbibition
(c) capillarity
(d) osmosis
Solution :
imbibition
(ix) Meaning of ascent of sap is
(a) absorption of water from soil.
(b) alteration of water against gravitational force.
(c) reaching of water upwards against gravitational force.
(d) origin of cohesive force in water.
Solution :
reaching of water upwards against gravitational force
(x) Process of ascent of sap in plants occurs:
(a) by cortex
(b) by xylem
(c) by phloem
(d) by cambium
Solution :
by xylem
(xi) Which tissue makes passage for ascent of sap?
(a) Cortex
(b) Endodermis
(c) Phloem
(d) Xylem
Solution :
Xylem
(xii) Absorption of water from soil takes place by
(a) root cap region
(b) root hairs
(c) elongation zone
(d) maturation zone
Solution :
root hairs
(xiii) In ascent of sap water reaches upwards:
(a) In the form of a solid column.
(b) in the form of a fragile column.
(c) to some places in the form of solid and to some places in liquid form.
(d) none of the above.
Solution :
none of the above
(xiv) The water is translocate upwards from the roots through
(a) xylem
(b) phloem
(c) pith
(d) endodermis
Solution :
xylem
(xv) Exudation or bleeding is associated with
(a) capillarity
(b) imbibition
(c) hydrostatic pressure in the root
(d) pulsation in the innermost layer of cortex
Solution :
hydrostatic pressure in the root
(xvi) Wilting of plants occurs when:
(a) phloem is blocked.
(b) xylem is blocked.
(c) a few old roots are removed.
(d) both xylem and phloem are blocked.
Solution :
xylem is blocked




