Students should refer to Genetics Some Basic Fundamentals ICSE Class 10 Biology Board Exam Questions provided below with solutions. These will help the students to understand the type of questions which have been asked in previous year examinations and the type of solutions which the student should give to get good marks. You should also refer to ICSE Class 10 Biology Sample papers for more practice. Read Genetics Some Basic Fundamentals ICSE Class 10 Biology solutions below
ICSE Class 10 Biology Genetics Some Basic Fundamentals Important Questions
Students should learn the important questions and answers given below for Chapter Genetics Some Basic Fundamentals in Biology for ICSE Class 10. These board questions are expected to come in the upcoming exams. Students of ICSE Class 10th should go through the Important questions and answers ICSE Class 10 Biology which will help them to get more marks in exams.
Genetics Some Basic Fundamentals ICSE Class 10 Biology Board Exam Questions
Genetics Some Basic Fundamentals ICSE Class 10 Biology
Question: What is a pedigree?
Ans. A pedigree is the representation of a family history for a few generations for a particular trait (character) in the form of a chart.
Question: What is Mendel’s Monohybrid ratio? Explain the same with an example.
Ans. Monohybrid ratio is the kind of ratio obtained in the progeny in F2 generation, by crossing for two different traits of a single character.
eg.1. Pure tall (TT) pea plants were crossed with dwarf plants and the progenies were obtained as follows:
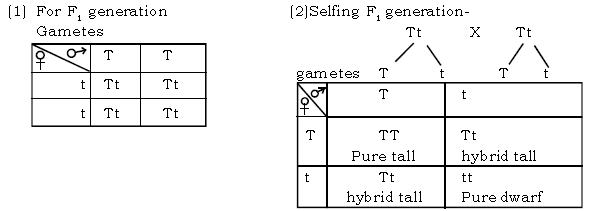
Thus the result is in the ratio 3 tall : 1 dwarf. The three tall may appear so phenotypically, but they are dissimilar genotypically. The phenotypic Monohybrid ratio is 3 tall : 1 dwarf genotypically, Monohybrid ratio is : 1 pure tall (TT): 2 hybrid tall (Tt) : 1 pure dwarf (tt). eg.2.

Phenotypic Ratio = 3 : 1 (3 red : 1 white)
Genotypic Ratio = 1 : 2 : 1 (1 pure red : 2 hybrid red : 1 pure white)
Question: Give general characteristics of chromosomes and its types.
Ans. a. Chromosomes are visible only when a cell is about to divide.
b. The chromosome number is constant for individuals of a species and every body cell has the same number. eg., Human cell has 46 chromosomes.
c. Chromosomes always occur in pairs derived one from each of the parents.
d. In human 1 to 22 pairs are identical and are called autosomes but the 23rd pair is different, known as sex – chromosome which are designated as X and Y. XX pair is found in female and XY pair is found in male.
e. Y – Chromosome of male is much smaller than the X.
f. On the chromosomes are a number of genes.
g. The lion, tiger and the domestic cat have the same number of chromosomes (38), yet each one is distinct from the other in body size, appearance, colour etc. These are the results of genes located on the chromosomes.
Question: Approximately, how many genes have been discovered in human?
Ans. Genes, so far discovered in human are 25,000 – 30,000.
Question: Which of the following in humans are established genetics traits?
a. The capacity to be a good cricketer x
b. Curly hair ✔
c. Left handedness ✔
d. Quality of voice ✔
e. Red green colour blindness ✔
Question: How is a gene related to heredity?
Ans. Genes are units of heredity that determine particular trait (eg. colour of hair, colour of the eye, blood group). Each gene is a segment of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) that carries instructions for making all or part of a specific protein.
Question: What is mutation? Give its types with one eg. each.
Ans. Mutation is a sudden change in one or more genes or change in the entire chromosome.
Accordingly there are two types of mutations : –
a) Gene mutation : – eg. sickle cell anemia – is a blood disease, where RBCs becomes sickle shaped.
b) Chromosomal mutation : eg. Down’s syndrome, also called Mongolism – A mental and physical disease where a person is born with one full extra – chromosome, in each cell (extra copy of chromosome 21).
Question: Name any two genetic diseases in human.
Ans. a) Haemophilia b) Colour blindness
Question: In short explain Y – linked inheritance.
Ans. The Y – linked inheritance is a trait (character) which occurs only in male as these traits are expressed by the genes present onb Y-chromosome for example: trait such as hairy pinna (hypertrichosis) are found in men only. Y – linked inheritance is direct, i.e. father to son.
Question: In a certain species of animals, black fur (B) is dominant over brown fur (b). Show possible ratio of genotype and phenotypes of the offspring.
Ans.
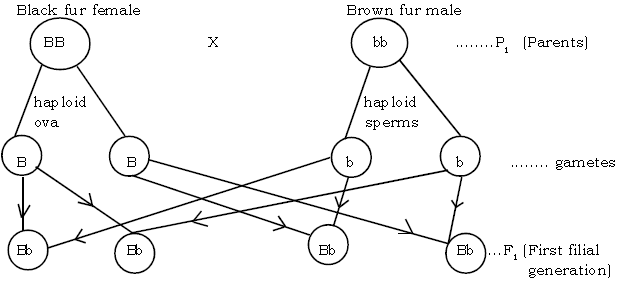
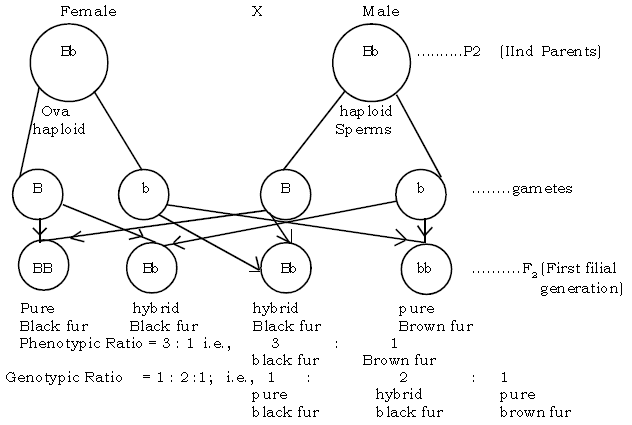
All have black fur in F1 generation. Therefore black fur is dominant over brown fur. On selfing the F1 generation, for F2 results (generation).
Question: Define the three laws of inheritance given by Mendel.
Ans. Mendel’s three laws of inheritance are as below : –
a) Law of Dominance b) Law of segregation
c) Law of independent assortment
a) Law of Dominance – Out of a pair of contrasting characters present together, only one is able to express itself (dominant) while the other remains suppressed (recessive).
b) Law of segregation/ Law of purity of gametes – The two members of a pair of factors separate during the formation of gametes.
c) Law of Independent Assortment : In crossing, if two or more traits (say height, colour etc) are involved, their factors (genes) assort independently, irrespective of their combinations present in the parents.
Question: Differentiate between : –
a) Genotype and phenotype
b) Character and trait.
Ans.

Question: Reasons for Experimenting with Garden Pea Plant.
Ans. 1. Large Variety : Pea plants have several distinct varieties, each with sharp contrasting characteristics, such as colour and shape of pods and seeds. The genes for the seven contrasting characters that Mendel used, appear on separate chromosomes.
2. Self pollinated : Pea plants are with bisexual flowers, a condition that favours self pollination. Also, the flower completely encloses the reproductive organs until fertilisation, which further ensures self-pollination. Self-fertilisation makes it easy to obtain pure lines for several generations. It could be cross-fertilised (crosspollinated).
3. Annual plant : The pea plant completes its life-cycle in one season. Therefore, it is possible to study several generations within a short span of time.
4. Produces large quantities of flowers and seeds : Each plant can produce a large number of seeds in a single generation. The flowers of pea plants are adequate in size and are easy to handle.
Question: “Like begets like”, this applies only to animals – True / False
Ans. False – “Like begets like,” means that the young ones look like their parents and this applies to plants also.
Question: Explain the inheritance of the character (trait) of free or attached ear lobes. Given below are pedigree charts of two families A and B.

(a) Family B has all children of one type, whereas family A has both types. Parents in which family, A or B are heterozygous.
Ans. Family A is heterozygous for this character.
(b) Which trait – free ear lobe or the attached ear lobe is dominant?
Ans. Free ear-lobe is dominant.
(c) What does a solid symbol and hollow symbol indicate in pedigree ?
Ans. Solid symbol indicates the character/trait being traced and the hollow symbol represent individuals without the trait.
(d) What is the difference indicated by : square and circle?
Ans. Square indicates male and circle indicates female.
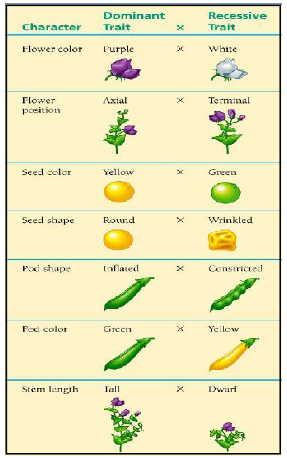
Question: List the features of Pisum sativum, with their dominant and recessive traits.
Ans. Pisum sativum (garden pea)
Question: Describe mechanism of sex determination in humans?
Ans. Sex Determination in Humans : In humans the mechanism of sex determination is of XX – XY type i.e., male is heterogametic. In human beings each cell contains 46 chromosomes. Of these, in male 44 are autosomes (A)while the remaining two which are dissimilar i.e., ‘XY’ are sex – chromosomes. In female there are 44 autosomes and ‘XX’ are sex chromosomes.
During gamete formation when meiosis (reduction division) takes place, the sex chromosomes separate and enter the different gametes. In male therefore, two types of sperm are produced, i.e., 50% sperms containing ‘X’ chromosome and another 50% sperms containing ‘Y’ chromosome. In female there are only one type of eggs, all containing ‘X’ chromosome.
During fertilization if the ‘X’ containing sperm fuses with egg, the child with ‘XX’ chromosome will be the female, whereas if the ‘Y’ containing sperm fuses with egg, the child with ‘XY’ chromosome is conceived and it will be a male child (as given below).
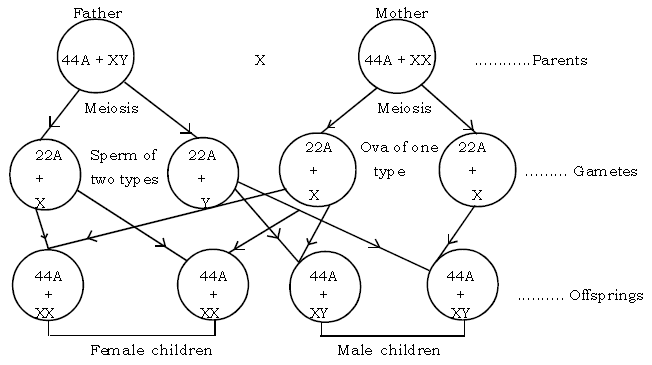
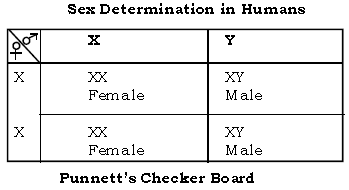
Thus it is evident that male parent and not the female is responsible for determination of sex of the child.
Question: Which of the following are homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive in regard to tongue rolling : – Rr, rr, RR.
Ans. RR – is homozygous dominant ,
Rr is heterozygous dominant.
rr – is homozygous recessive
Question: What is Albinism? Is it recessive or dominant trait?
Ans. Total absence of skin pigments is known as albinism. It is recessive character
Question: Give the chromosome number of different animals / plants.
Ans.
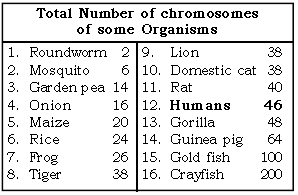
Question: A couple got four daughters in a row and no son. Does it mean that the husband does not produce Y- bearing sperms? Explain.
Ans. All eggs are alike each with one X- chromosome (haploid) but sperms are either with X- or Y-chromosome (50% of each kind). Which sperm fertilises the egg, determines whether the child will be a male or a female. It is a matter of chance. Thus it does not mean that the husband produces sperms with only X- chromosomes.
Question: Explain the sex – linked (X – chromosome linked) inheritance of colour – blindness (or haemophilia) in humans.
Case 1 : Normal female X colour blind male
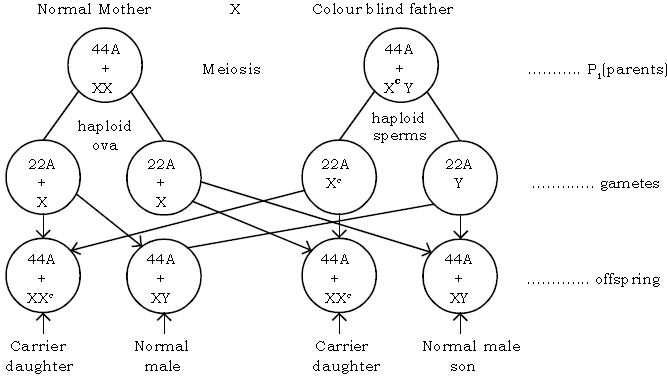
A Colour – blind person cannot distinguish between red and green colours. These colours appear gray to them. This X – linked gene for colourblindness is due to a recessive gene. The carrier females carry the gene for the disease but they are not diseased, i.e., recessive gene is not expressed phenotypically (outside expression).
Case 2 – If the carrier daughter marries a normal male :
The result are as below :
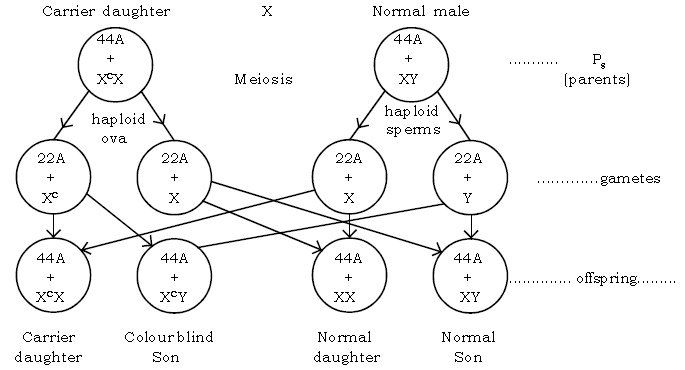
In Case 2 :50% sons will be colour blind and 50% with normal vision. So it is clear that the colour blind father transmits the disorder only to the grandson, through his carrier daughter in a zig – zag manner usually known as criss – cross inheritance.
Question: The entire human population shows variations – True / False
Ans. True – The human population shows variation because of genetic differences.
Question: Mutation and Cloning.
Ans. Mutation :
A mutation is a sudden change in one or more genes. It alters the hereditary material of an organism’s cells, thereby causing changes in certain traits. For the change to be visible, the mutation must be large.
A mutation can effect an individual gene or an entire chromosome.
a. A gene mutation is caused by slight chemical changes in DNA. Sickle cell anaemia is a blood disease caused by a mutation or minor change in the DNA of a gene that controls the production of a person’s red blood cells.
b. A chromosome mutation occurs if the number or arrangements of chromosome changes. Down’s syndrome, is a mental and physical disorder which occurs if a person is born with one extra chromosome number 21 (Trisomy 21) hence the total number of chromosome is 47. An organism can pass a mutation on to its offspring only if the mutation affects cells that produce eggs or sperm. Such a mutation is called a germinal mutation. The other type of mutation, called a somatic mutation, occurs in autosomes.

• Induced mutations are used in plant breeding to develop improved varieties.
• Induced mutation occur in a very high frequency.
Mutations can also be classified into two categories depending on which body cells they occur in.
(i) Somatic mutations, (ii) Germ mutations.

Cloning :
The exact copy of an individual is called a clone. In biological terms it represents a
group of genetically identical cells descended asexually from a single common ancestor.
Cloning is the process by which a genetic duplicate of an individual is created through asexual reproduction, as by stimulating a single cell or taking cuttings from a plant.
Scientists once thought that cloning an animal from an adult cell was impossible. A research team in Scotland discovered how to manipulate the genes needed to make a lamb from a single adult sheep cell. Dolly’s birth was heard all around the world. The first mammal, ever cloned from a single adult cell, she was living proof that scientists had solved one of the most challenging problems of cell biology.
Question: List any 4 characters in humans, mentioning which trait is dominant and recessive.
Ans.
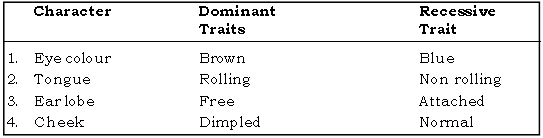
Question: Give some common heridity traits in human.
Ans. Showing dominant and recessive forms :
No. Trait Dominant Recessive
1. Eye Colour Brown Blue
2. Tongue Rolling Non – rolling
3. Hand Right handedness Left handedness
4. Ear – lobes Free attached
5. Cheek Dimpled Normal
6. Colour vision Normal Colour
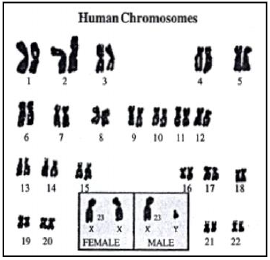
Question: Describe karyotype and different types of chromosomes-Allosomes/Autosomes.
Ans. Sex Chromosomes and Autosomes
• In human being there are two types of chromosomes : Autosomes and allosomes ( sex chromosomes) The chromosome pairs numbered 1-22 has identical chromosomes and these are categorised as autosomes. They are invovled in determining the somatic characters of an individual. The 23rd pair is different and its chromosomes are called sex chromosomes or allosomes. They determine the sex of the individual. Female allosomes are homologous (XX) where are the male allosomes are non-homologous (XY).
• The artificially arranging the chromosomes according to their size and shape on a chart is known as karyotype and the method is called karyotyping.
Question: If a carrier of haemophilic female (XXh) marries a haemophilic male (XhY). Work out the progeny in the following punnett square.
Ans.


Question: Define Mendel’s dihybrid ratio and explain the same with an example. (Genetics Some Basic Fundamentals ICSE Class 10 Biology)
Ans. In crossing, if two pairs of contrasting characters are concerned, the phenotypic ratio which one gets in F2 generation is called dihybrid ratio which is normally 9 : 3 : 3 : 1. For the dihybrid experiment, Mendel crossed a variety of pea pure plants having yellow colour and round seeds with another having green colour and wrinkled seeds. The F1 hybrids were all yellow and round indicating that yellow and round are dominant characters as only dominant character appear in F1 generation. When the hybrids F1 were selfed, they produced four types of offsprings in F2.

Question: Match the coloumns and rewrite correct matches.
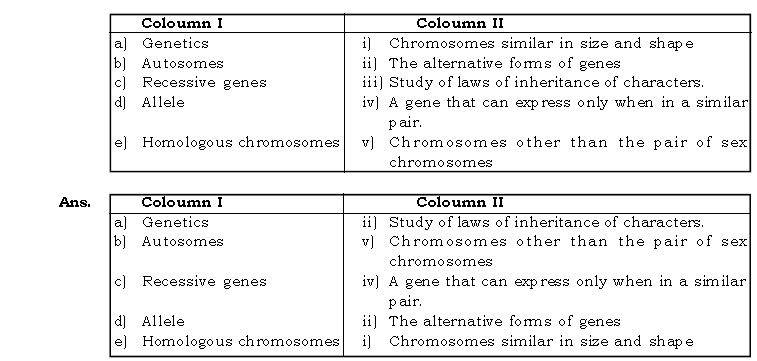
We hope you liked Genetics Some Basic Fundamentals ICSE Class 10 Biology Questions given above







