Students should refer to ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Question Paper solved Set H given below which will help them to prepare for the upcoming ICSE Chemistry exams. Students should read ICSE Chemistry Class 10 Books to make sure they are completely prepared and should also refer to ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Solutions to understand all questions and their answers.
ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Question Paper solved Set H
Answer to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately.
You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes.
This time is to be spent in reading the Question Paper.
The time given at the head of this paper is the time allowed for writing the answers.
Section I is compulsory. Attempt any four questions from Section II.
The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brackets [ ].
ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Question Paper solved Set H
SECTION – I (40 MARKS)
(Attempt all questions)
Question 1. (a) From the list given below, select the word(s) required to correctly complete the blanks (i) to (v) in the following passage : Note : Words chosen from the list are to be used only once. Write only the answers. Do not copy the passage. (reddish brown, ammonium, nitrogen dioxide, hydroxyl, dirty green, ammonia, acidic, alkaline) Nitrogen and hydrogen combine in the presence of a catalyst to give (i) …………….. gas. When the above mentioned gas is passed through water it forms a solution which will be (ii) …………….. in nature and the solution contains (iii) …………….. ions and (iv) …………….. ions. The above solution when added to iron (II) sulphate solution, given a (v) …………….. coloured precipitate of iron (II) hydroxide.
Ans.
(i) Ammonia
(ii) Alkaline
(iii) Ammonium
(iv) Hydroxyl
(v) Dirty green
(b) Select from the list given (A to E) one substance in each case which matches the description given in parts (i) to (v). (Note : Each substance is used only once in the answer.) (A) Nitroso Iron (II) sulphate (B) Iron (III) chloride (C) Chromium sulphate (D) Lead (II) chloride (E) Sodium chloride.
(i) A compound which is deliquescent.
(ii) A compound which is insoluble in cold water, but soluble in hot water.
(iii) The compound responsible for the brown ring during the brown ring test of nitrate ion.
(iv) A compound whose aqueous solution is neutral in nature.
(v) The compound which is responsible for the green coloration when sulphur dioxide is passed through acidified potassium dichromate solution. (5)
Ans. (i) Iron (II) chloride
(ii) Lead (II) chloride
(iii) Nitroso Iron (II) sulphate
(iv) Sodium chloride
(v) Chromium sulphate
(c) For part (c) (i) – (c) (x), select the correct answer from the choice A, B, C and D which are given. Write only the letter corresponding to the correct answer. (10)
(i) A particular solution contains molecules and ions of the solute so it is a :
(a) weak acid
(b) strong acid
(c) strong base
(d) salt solution
Ans. (a) weak acid
(ii) A compound which liberates reddish brown gas around the anode during electrolysis in its molten state is :
(a) Sodium chloride
(b) Copper (II) oxide
(c) Copper (II) sulphate
(d) Lead (II) bromide
Ans. (d) Lead (II) bromide
(iii) An organic compound undergoes addition reactions and gives a red colour precipitate with ammoniacal cuprous chloride. Therefore, the organic compound could be :
(a) Ethane
(b) Ethene
(c) Ethyne
(d) Ethanol
Ans. (c) Ethyne
(iv) An organic weak acid is :
(a) Formic acid
(b) Sulphuric acid
(c) Nitric acid
(d) Hydrochloric acid
Ans. (a) Formic acid
(v) During ionization metals lose electrons, this change can be called :
(a) Oxidation
(b) Reduction
(c) Redox
(d) Displacement
Ans. (a) Oxidation
(vi) Which one of the following in not true of metals :
(a) Metals are good conductors of electricity
(b) Metals are malleable and ductile
(c) Metals form non-polar covalent compounds
(d) Metal will have 1 or 2 or 3 electrons in their valence shell.
Ans. (c) Metals form non-polar covalent compounds
(vii) An example of a complex salt is :
(a) Zinc sulphate
(b) Sodium hydrogensulphate
(c) Iron (II) ammonium sulphate
(d) Tetrammine copper (II) sulphate
Ans. (d) Tetrammine copper (II) sulphate
(viii) Aqua regia is a mixture of :
(a) Dilute hydrochloric acid and concentrated nitric acid
(b) Concentrated hydrochloric acid and dilute nitric acid
(c) Concentrated hydrochloric acid (1 part) and concentrated nitric acid (3 parts)
(d) Concentrated hydrochloric acid (3 parts) and concentrated nitric acid (1 part)
Ans. (d) Concentrated hydrochloric acid (3 parts) and concentrated nitric acid (1 part)
(ix) The organic compound mixed with ethanol to make it spurious is :
(a) Methanol
(b) Methanoic acid
(c) Methanal
(d) Ethanoic acid
Ans. (a) Methanol
(x) The number of electrons present in the valence shell of a halogen is :
(a) 1
(b) 3
(c) 5
(d) 7
Ans. (d) 7
(d) State your observation for the following cases :
(i) Moist blue litmus is introduced into a gas jar of sulphur dioxide.
(ii) Dry red rose petals are placed in the jar of sulphur dioxide.
(iii) Paper soaked in potassium permanganate solution is introduced into a gas jar of sulphur dioxide.
(iv) Ammonia gas is burnt in an atmosphere of oxygen in the absence of a catalyst.
(v) Glass rod dipped in ammonium hydroxide is brought near the mouth of the concentrated hydrochloric acid bottle. (5)
Ans. (i) Moist blue litmus turns red and finally colourless as SO2 act as an acidic gas and then a bleaching agent.
(ii) The colour of red rose petals gets bleached because SO2 is a strong bleaching agent.
(iii) The pink colour of potassium permanganate paper turns colourless because of bleaching property of sulphur dioxide.
(iv) Greenish yellow flame is observed.
(v) Dense white fumes of ammonium chloride are observed.
(e) Match the column A with column B.

(f) Write the equation for each of the following reactions :
(i) Sulphur is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid
(ii) Zinc oxide is treated with sodium hydroxide solution.
(iii) Ammonium chloride is heated with sodium hydroxide.
(iv) Concentrated sulphuric acid is poured over sugar.
(v) Magnesium sulphate solution is mixed with barium chloride solution. (5)
Ans. (i) S + 2H2SO4 → 3SO2 + 2H2O
(ii) ZnO + 2NaOH → Na2ZnO2 + H2O
(iii) NH4Cl + NaOH → NaCl + NH3 + H2O
(iv) C12H22O11 + H2SO4 → 12C + 11H2O
(v) MgSO4 + BaCl2 → BaSO4 + MgCl2
(g) (i) LPG stands for liquefied petroleum gas. Varieties of LPG are marketed including a mixture of propane (60%) and butane (40%). If 10 litre of this mixture is burnt, find the total volume of carbon dioxide gas added to the atmosphere.
Combustion reaction can be represented as :
C3H8(g) + 502(g) ¾¾® 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g)
2C4H10(g) + 13O2(g) ¾¾® 8CO2(g) + 10H2O(g)
(ii) Calculate the percentage of nitrogen and oxygen in ammonium nitrate. (Relative molecular mass of ammonium nitrate is 80, H = 1, N = 14, O = 16). (5)
Ans. % of propane = 60%
% of butane = 40%
Total volume of the mixture = 10 litre
_ Propane = 60/100 × 10 = 6 litres
_ Butane = 40/100 × 10 = 4 litres
(i) Combustion of propane :

(ii) Combustion of butane :
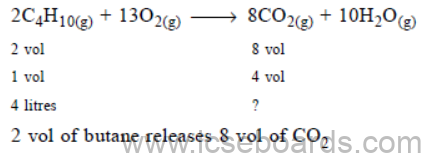
4 litres of butane releases 8/2 × 4 = 16 l
Total CO2 released O2 = 18 l + 16 l
= 34 litres of CO2 gas is added to atmosphere
(iii) NH4NO3
[14 + (4 × 1) + 14 + (16 × 3)]
[14 + 4 + 14 + 48] = 80
% of nitrogen = 28/80 × 100 = 35%
% of oxygen = 48/80 × 100 = 60%
% of hydrogen = 4/80 × 100 = 5%
35% of nitrogen, 60% of oxygen and 5% of hydrogen
ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Question Paper solved Set H
SECTION – II (40 MARKS)
(Attempt any four questions)
Question 2. (a) Give the equation for the following conversions A to E.

Ans.
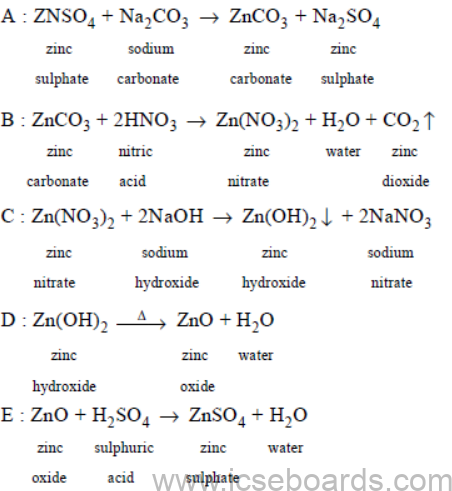
(b) The questions below are related to the manufacture of ammonia.
(i) Name the process.
(ii) In what ratio must the reactants be taken ?
(iii) Name the catalyst used.
(iv) Give the equation for the manufacture of ammonia.
(v) Ammonia can act as a reducing agent – write a relevant equation for such a reaction. (5)
Ans. (i) Habers process
(ii) N2 and H2 in the ratio (1 : 3)
(iii) Finely divided iron

Question 3.
(a) Draw the structural formula for each of the following :
(i) Ethanoic acid (ii) But-2-yne

(b) Mr. Ramu wants to electroplate his key chain with nickel to prevent rusting. For this electroplating :
(i) Name the electrolyte (ii) Name the cathode
(iii) Name the anode (iv) Give the reaction at the cathode
(v) Give the reaction at the anode. (5)
Ans. (i) Nickel sulphate
(ii) Key chain
(iii) Nickel electrode
(iv) At Cathode : Ni2+ + 2e– → Ni(s)
(v) At Anode : Ni (s) – 2e– → Ni2+
(c) Three different electrolytic cells A, B and C are connected in separate circuits. Electrolytic cell A contains sodium chloride solution. When the circuit is completed a bulb in the circuit glows brightly. Electrolytic cell B contains acetic acid solution and in this case the bulb in the circuit glows dimly. The electrolytic cell C contains sugar solution and the bulb does not glow. Give a reason for each of these observation.
Ans. Cell A : Strong electrolyte (NaCl) → Bulb glows brightly.
Cell B : Weak electrolyte (Acetic acid) → Bulb glows dimly.
Cell C : Non electrolyte (Sugar solution) → Bulb doesn’t glow.
Question 4.
(a) 4.5 moles of calcium carbonate are reacted with dilute hydrochloric acid.
(i) Write the equation for the reaction.
(ii) What is the mass of 4.5 moles of calcium carbonate ? (Relative molecular mass of calcium carbonate is 100).
(iii) What is the volume of carbon dioxide liberated at stp ?
(iv) What mass of calcium chloride is formed ? (Relative molecular mass of calcium chloride is 111).
(v) How many moles of HCl are used in this reaction ?

(ii) 1 mole of calcium carbonate weighs 100 g 4.5 moles of calcium carbonate weighs 100 × 4.5 = 450g
(iii) 1 mole of calcium carbonate liberates CO2 = 22.4l
4.5 moles of calcium carbonates liberates CO2 = 22.4 × 4.5 = 100.8 litres
(iv) CaCO3 + 2HCl ® CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
100g 111g
From 100g CaCO3; CaCl2 formed is 111g
From 1g of CaCO3; CaCl2 formed is 111 g /100
From 450g of CaCO3; CaCl2 formed is 111 /100× 450 = 499.5g of CaCl2
(v) 2 moles of HCl are used in this reaction.
(b) The diagram shows an apparatus for the laboratory preparation of hydrogen chloride.
(i) Identify A and B
(ii) Write the equation for the reaction.
(iii) How would you check whether or not the gas jar is filled with hydrogen chloride?
(iv) What does the method of collection tell you about the density of hydrogen chloride ?

Ans. (i) A → Sulphuric acid
B → Sodium chloride

(iii) In order to know that the jar is filled with the gas, bring a glass rod dipped in ammonium
hydroxide solution near its mouth. If dense white fumes of ammonium chloride are
produced, it indicates that the gas jar is full of HCl gas.
HCl + NH3 → NH4Cl(s)
(iv) The method used to collect HCl is “Upward displacement of air”. This clearly indicates that HCl gas is heavier than air.
Question 5. (a) Name the main constituent metal in the following alloys :
(i) Duralumin
(ii) Brass
(iii) Stainless steel
Ans.
(i) Aluminium
(ii) Zinc
(iii) Iron
(b) An element has an atomic number 16. State
(i) the period to which it belongs.
(ii) the number of valence electrons.
(iii) whether it is a metal or non-metal
Ans. Atomic no. (16) → 2/K , 8/L , 6/M
(i) 3 period (Because it has three shells)
(ii) 6 valence electrons (Valence electrons are present in outermost orbit)
(iii) Non metal (elements having 5, 6, or 7 valence electrons are non metals)
(c) Solution A is a sodium hydroxide solution. Solution B is a weak acid. Solution C is dilute sulphuric acid. Which solution will
(i) liberate sulphur dioxide from sodium sulphite.
(ii) give a white precipitate with zinc sulphate solution.
(iii) contain solute molecules and ions ? (3)
Ans.
(i) Solution C
(ii) Solution A
(iii) Solution B
(d) By the addition of only one solution how would you distinguish between dilute hydrochloric acid and dilute nitric acid ? (1)
Ans. HCl (dilute)
HNO3 (dilute) [To differentiate between HCl and HNO3 we can use AgNO3 solution]

By adding AgNO3, HCl gives white ppt whereas no such reaction takes place with HNO3.
Question 6.
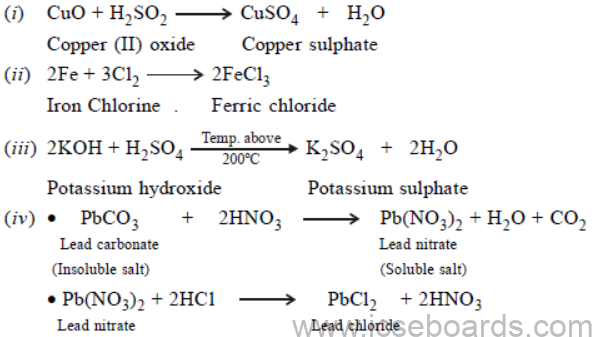
(a) Give the equation for the preparation of each of the following salts from the starting material given.
(i) Copper sulphate from copper (II) oxide.
(ii) Iron (III) chloride from iron.
(iii) Potassium sulphate from potassium hydroxide solution.
(iv) Lead chloride from lead carbonate (two equations).
Ans.
(b) Compound A is bubbled through bromine dissolved in carbon tetrachloride and the product is CH2Br – CH2Br.

(i) Draw the structural formula of A.
(ii) What type of reaction has A undergone ?
(iii) What is your observation ?
(iv) Name (not formula) the compound formed when steam reacts with A in the presence of phosphoric acid.
(v) What is the procedure for converting the product of (b) (iv) back to A ? (5)
Ans.


Question 7. (a) The diagram shows a simple arrangement of the fountain experiment :
(i) Name the two gases you have studied which can be used in this experiment.
(ii) What is the common property demonstrated by this experiment ? (3)

Ans. (i) · Hydrogen chloride gas (HCl)
· Ammonia (NH3)
(ii) Solubility of gases
(b) Define the following terms :
(i) Ionization potential
(ii) Electron affinity. (2)
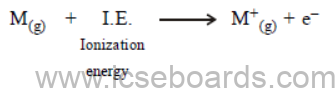
Ans. (i) Ionisation Energy : It is the minimum amount of energy required to remove the most loosely bond electron from an isolated, neutral gaseous atom :
(ii) Electron affinity : It is the amount of energy released when an isolated neutral gaseous atom of an element takes up an extra electron to form uninegative gaseous ions.

(c) The action of heat on the blue crystalline solid L gives a reddish brown gas M, a gas which re-lights a glowing splint and leaves a black residue. When gas N, which has a rotten egg smell, is passed through a solution of L a black precipitate is formed.
(i) Identify L, M and N (Name of formula)
(ii) Write the equation for the action of heat on L
(iii) Write the equation for the reaction between the solution of L and the gas N.
Ans.
