Students of ICSE Class 10 should refer to Metallurgy ICSE Class 10 Chemistry board year questions and solutions. below which have come in past board exams. You should always go through questions that have come in previous years. This will help you to understand the pattern of questions in ICSE Class 10 Chemistry and prepare accordingly. This will help you to get better marks in ICSE Class 10 Board Exams
ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Metallurgy Board Exam Questions
Students should learn the important questions and answers given below for Chapter Metallurgy in Chemistry for ICSE Class 10. These board questions are expected to come in the upcoming exams. Students of ICSE Class 10th should go through the below board exams questions and answers which will help them to get more marks in exams.
Board Exam Questions Metallurgy ICSE Class 10 Chemistry
(a)

Using the information above, complete the following :
Question. _________ is the metallic element.
Answer
Y
Question. Metal atoms tend to have a maximum of _______ electrons in the outermost energy level.
Answer
eight
Question. Non-metallic elements tend to form______oxides while metals tend to form______oxides.
Answer
acidic, basic
Question. Non-metallic elements tend to be ________ conductors of heat and electricity.
Answer
very poor
Question. Metals tend to _________ electrons and act as _________ agents in their reactions with elements and compounds
Answer
lose, reducing
(b) Fill in the blanks with a suitable word in the following paragraph :
In the smelting, the ore is heated (1) ……………………….. the melting point either along or with some (2) ………………………. . In calcination, the ore is heated (3) ……………….. the melting point and thus no (4) ………………… occurs in this process. Similar to calcination, (5)……………… involves heating at high temperature but chemical change occurs here. The (6) ……………….. is used only when ore or impurity is (7) ……………….. in nature.
Answer
(1) above (2) flux, (3) below, (4) chemical change, (5) roasting, (6) magnetic separation, (7)
magnetic.
(c) X is an element in the form of a powder. X, burns in oxygen and the product is soluble in water.
The solution is tested with litmus. Write down only the word, which will correctly complete each of the following sentences.
Question. If X is a metal, then the litmus will turn………….
Answer
blue,
Question. If X is a non-metal, then the litmus will turn…………..
Answer
red,
Question. If X is a reactive metal, then……….will be evolved when X reacts with dilute sulphuric acid.
Answer
hydrogen,
Question. If X is a metal it will form……..oxide, which will form………solution with water.
Answer
basic, alkaline
(d)
Question. The metal other than aluminium present both in magnalium and duralumin is………
Answer
magnesium
Question. The ore from which aluminium is extracted must first be treated with …………………. so that pure aluminium oxide can be obtained.
Answer
sodium hydroxide solution
Question. Aluminum is an important constituent metal in duralumin since it is…………
Answer
light
Question. In a thermetic mixture, aluminium…………iron (III) oxide.
Answer
reduces
Question. Pure aluminium oxide is dissolved in …………….. to make a conducting solution.
Answer
cryolite
Question. ………is a dark coloured crystalline solid.
Answer
Iodine
Question. The divalent metal whose oxide is reduced to metal by electrolysis of its fused salt is ………
Answer
magnesium
Question. Pine oil used in froth floatation process act as a …………
Answer
water repellant
Question. In dry cells, the zinc container acts as an …………
Answer
anode
Question. An …………… is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals or a metal and a ………….. .
Answer
alloy, non-metal.
Question. The properties of an alloy are not necessarily ……….. between those of its …………. . The M.P. of an alloy is always less than the melting point of its constituent ………… .
Answer
intermediate, constituents, metals.
Question. An alloy in which …………. is present as one of the constituents is called ……….. alloy.
Answer
iron, ferrous
Question. The alloy that contains lead is ……………………. .
Answer
solder
Question. The alloy of nickel and iron is known as…………
Answer
invar
Question. An alloy which is sonorous is………
Answer
bell metal
Question. An alloy used for making cases for cartridges is ………
Answer
brass
Question. The alloy used for making magnets is ………………….. .
Answer
alnico
Question. ………………….. is a ferrous alloy.
Answer
manganese steal
Question. Brass is an alloy of ………………………… .
Answer
Cu and Zn
Question. Bell metal is an alloy of ……………………… .
Answer
Cu and Sn
Question. Type metal is an alloy of ………………………….. .
Answer
Pb, Sn and Sb
Question. Addition of Tin to………lowers the melting point of alloy solder.
Answer
lead
Question. Alnico is a mixture of ……………….. .
Answer
Al, Ni and Co
Question. …………is used in machine parts due to its……………tensile strength.
Answer
steel, high
Question. The non-metallic component in stainless steel is ………
Answer
carbon
Question. Carbon content of steel is …………………… .
Answer
(0.5 to 1.5)%
Question. Stainless steel contains …………………… .
Answer
Cr, Ni and C
Multiple Choice Questions
Question. An element of an inorganic compound found in nature is known as :
(a) Mineral
(b) Ore
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following is not true of metals ?
(a) Metals are good conductors of electricity.
(b) Metals are malleable and ductile.
(c) Metals form non-polar covalent compounds.
(d) Metal will have 1 or 2 or 3 electrons in their valence shell.
Answer
C
Question. Which ore is metalloid ?
(a) C
(b) Germanium
(c) Si
(d) Tin
Answer
A
Question. A chemical process of extracting a metal from its ore is known as :
(a) Mineralogy
(b) Metallurgy
(c) Liquation
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. A mineral from which the metal is extracted economically is known as :
(a) Matrix
(b) Gangue
(c) Ore
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. An unwanted earthly material associated with tin ore as impurity is known as :
(a) Gangue
(b) Flux
(c) Froth
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. The process of heating the ore strongly in excess of air so that the volatile impurities are removed and the ore is changed to oxide is known as :
(a) Calcination
(b) Roasting
(c) Froth floatation
(d) Leaching
Answer
B
Question. Heating an ore in a limited supply of air or in the absence of air at a temperature just below its melting point is known as :
(a) Smelting
(b) Ore dressing
(c) Calcination
(d) Bessemerisation
Answer
C
Question. Smelting is carried out in :
(a) Blast furnace
(b) Muffle furnace
(c) Open Heat furnace
(d) Electric furnace
Answer
A
Question. The salt which is least likely to be found in minerals is :
(a) Chloride
(b) Sulphate
(c) Sulphite
(d) Nitrate
Answer
D
Question. The commonest method of extraction of metals from oxide ores involves :
(a) Reduction with carbon
(b) Reduction with aluminium
(c) Reduction with hydrogen
(d) Electrolytic method
Answer
A
Question. Froth floatation process for the concentration of ores is an illustration of the practical application of :
(a) Adsorption
(b) Absorption
(c) Sedimentation
(d) Coagulation.
Answer
B
Question. In the froth floatation process for the purification of ores, the ore particles float because :
(a) They are light
(b) Their surface is not easily wetted by water
(c) They bear electrostatic charge
(d) They are insoluble
Answer
B
Question. Froth floatation method may be used to increase the concentration of mineral in :
(a) Chalcopyrites
(b) Bauxite
(c) Haematite
(d) Calamine
Answer
A
Question. Sulphide ore is generally concentrated by :
(a) Roasting
(b) Froth floatation process
(c) Reduction by carbon
(d) Tempering
Answer
B
Question. The main ore used for the extraction of iron is :
(a) Haematite
(b) Calamine
(c) Bauxite
(d) Cryolite
Answer
A
Question. The process used to convert impure alumina to pure alumina is :
(a) Roasting
(b) Electrolytic refining
(c) Purification
(d) Baeyer’s Process
Answer
D
Question. The part of fluorspar (CaF2) which is added in small quantities in the electrolytic reduction of alumina dissolved in fused cryolite (Na3AIF6) is :
(a) As a catalyst
(b) To make the fused mixture very conducting
(c) To lower the temperature of the melt
(d) To decrease the rate of oxidation of carbon at the anode
Answer
C
Question. The electrolyte used for electroplating an article with silver is :
(a) Silver nitrate solution
(b) Silver cyanide solution
(c) Sodium argentocyanide solution
(d) Nickel sulphate solution
Answer
C
Question. Aluminium powder is used in thermite welding because :
(a) It is a strong reducing agent
(b) It is a strong oxidising agent
(c) It is corrosion resistant
(d) It is a good conductor of heat
Answer
A
Question. The metals zinc and tin are present in the alloy :
(a) Solder
(b) Brass
(c) Bronze
(d) Duralumin
Answer
C
Question. In electrolytic refining of metals the impure metal is made :
(a) Cathode
(b) Salt bridge
(c) Anode
(d) Electrode
Answer
C
Question. Stainless steel does not contain :
(a) Cr
(b) Al
(c) C
(d) Ni
Answer
B
Question. This is not an alloy of copper :
(a) Brass
(b) Bronze
(c) Solder
(d) Duralumin
Answer
D
Question. The two main metals in bronze are :
(a) Copper and zinc
(b) Copper and lead
(c) Copper and nickel
(d) Copper and tin
Answer
C
Give One Word/Chemical Term
(a) Name the metals which can be extracted from the following ores :
Ans.
1. Haematite → Iron
2. Malachite → Copper
3. Cinnabar → Mercury
4. Barytes → Barium
5. Cuprite → Copper
6. Bauxite → Aluminium
7. Galena → Lead
8. Zinc Blende → Zinc
9. Iron Pyrites → Iron
10. Epsom → Magnesium
11. Calamine → Zinc
12. Dolomite → Magnesium
(b) Name an ore which is : Ans
1. An oxide → Haematite (Fe2O3)
2. A hydrated oxide → Bauxite (Al2O3.2H2O)
3. A carbonate → Magnetite (MgCO3)
4. A sulphate → Gypsum (CaSO4.2H2O)
4. A sulphide → Galena (PbS)
6. A nitrate → Chile salt-peter (NaNO3)
5. A phosphate → Rock phosphate [Ca3(PO4)2]
8. A chloride → Horn silver (AgCl)
(c) Name the property of a metal by virtue of which it : Ans
1. Can be beaten into thin sheets → Malleability
2. Can be drawn into wires → Ductility
3. Possesses tensile strength → Tenacity
4. Is good conductor of heat → Thermal conductivity
5. Is good conductor of electricity → Electrical conductivity
6. Dissolves into another metal → Alloy formation
7. Is liberated at cathode → Electropositive nature
8. Can cut a non-metal → Hardness
9.Is heavier than a non-metal → Density
10. Acts as a reducing agent. → Donor of electrons
(d) Question. Name a metal which is found abundantly in the earth’s crust.
Answer
Aluminium
Question. Name two metals which have a high degree of malleability.
Answer
Silver and Aluminium
Question. Name any two metals which are both malleable and ductile.
Answer
Gold and Silver
Question. Name the metal which is a good conductor of both heat and electricity.
Answer
Aluminium
Question. Name a metal which can be cut even with a knife.
Answer
Sodium
Question. Name a metal which is not ductile, malleable and tenacious.
Answer
Arsenic
Question. Name a metal which is a poor conductor.
Answer
Bismuth
Question. A metal which exists in liquid state at room temperature.
Answer
Mercury
Question. Name the metal which floats in water.
Answer
Sodium
Question. Name the metal which is stored in kerosene oil.
Answer
Sodium
Question. Name a metal which has a low melting point.
Answer
Sodium
Question. Name a metal which has acidic oxide.
Answer
Antimony Oxide [Sb2O3]
Question. Name the metal that burns in air with a golden flame.
Answer
Sodium
Question. Name a metal which forms anions which are liberated at anode.
Answer
Manganese in the form of permanganate ions [MnO4–]
Question. The metal which combines directly with sulphur on heating.
Answer
Iron
Question. The burning metal which combines directly with nitrogen.
Answer
Magnesium
Question. The molten metal which gives white fumes while reacting with chlorine.
Answer
Sodium
Question. A metal which reacts reversibly with steam.
Answer
Iron
Question. Metal which is rendered passive on reaction with concentrated nitric acid.
Answer
Iron
Question. Name a metal which is used in accumulators or car batteries.
Answer
Lead
Question. Name a metal which is used for galvanizing iron.
Answer
Zinc
Question. Name a metal which is used as silver paper.
Answer
Aluminium
Question. Name a metal which is used in a torch cell.
Answer
Zinc
Question. Name a metal which is used in flashlight photography.
Answer
Magnesium
Question. Name a metal which is used in vapour lamps.
Answer
Sodium
Question. Name a non-metal which has shiny appearance.
Answer
Iodine
Question. Name a non-metal which is the hardest substance known.
Answer
Diamond
Question. Name a non-metal which has high melting and boiling points.
Answer
Carbon
Question. Name a non-metal which is a good conductor of heat and electricity.
Answer
Graphite
Question. Name a non-metal which forms alloys with metals.
Answer
Carbon
Question. Name a non-metal which is electropositive in nature.
Answer
Hydrogen
Question. Name a non-metal which forms a neutral oxide.
Answer
Hydrogen, (forms neutral oxide, water)
Question. Name a non-metallic element which forms both acidic and neutral oxides.
Answer
Carbon
Question. Name a non-metal which posses metallic lustre and sublimes on heating.
Answer
Iodine
Question. Name a non-metallic element which is a liquid at ordinary temperatures.
Answer
Bromine
Question. The non-metal, which forms two compounds, while reacting with chlorine.
Answer
Phosphorous
Question. The process of removal of gangue from ore.
Answer
Concentration
Question. Name the Sulphide ore of mercury.
Answer
Cinnabar
Question. The most common ore of aluminium.
Answer
Bauxite
Question. Name the process used for the enrichment of sulphide ore.
Answer
Froath floatation process
Question. The formula of slag.
Answer
CaSiO3
Question. The chemical name of slag.
Answer
Calcium silicate
Question. The major impurity associated with iron obtained from blast furnace.
Answer
Carbon
Question. The process of coating thin layer of zinc over the surface of iron.
Answer
Galvanization
Question. The process by which zinc is purified.
Answer
Distillation
Question. Gas obtained when zinc blende is roasted.
Answer
Sulphur dioxide
Question. Name one alloy each of aluminium and iron.
Answer
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron and duralium is an alloy of aluminium
Question. Name the alloy of zinc used in simple voltaic cells.
Answer
Amalgamated zinc
Question. The elements added to iron to form stainless steel.
Answer
Chromium (Cr) and Nickel (Ni)
Question. Name the metal which is alloyed with zinc to form brass.
Answer
Copper
Question. Name an element from which fencing wire is made.
Answer
Soft-iron
Question. Name the purest form of iron.
Answer
Wrought-iron
Question. Two elements, whose hydroxides are easily soluble in water and form alkaline solutions.
Answer
Sodium and Potassium
Question. One metal, which forms more than one type of positive ions.
Answer
Iron which forms Fe2+ and Fe3+
Question. One ion responsible for blue colour of an aqueous solution of copper sulphate.
Answer
Cupric ion (Cu2+)
Question. The alloy of steel with a minimum of 10·5% chromium content by mass.
Answer
Stainless steel
Question. Name the solution used to react with Bauxite as a first step in obtaining pure aluminium oxide in the Baeyer’s process.
Answer
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
Question. Name the compound added to pure alumina to lower the fusion temperature during the electrolytic reduction of alumina.
Answer
Cryolite
Question. The process of coating of iron with zinc.
Answer
Galvanisation
Question. An alloy of lead and tin that is used in electrical circuits.
Answer
Solder
Question. An ore of zinc containing its sulphide.
Answer
Zinc blende
Question. A metal oxide that can be reduced by hydrogen.
Answer
Copper oxide
State the Observation
Question. When powdered zinc is added to copper sulphate solution.
Answer
Zinc displaces reddish brown copper from copper sulphate solution and zinc sulphate is
formed. Zn + CuSO4 ⎯→ ZnSO4 + Cu
Question. When powdered copper is added to zinc sulphate solution.
Answer
No reaction takes place because copper is less reactive than zinc.
Question. When a rod of zinc metal is dipped into the solution of copper sulphate.
Answer
Zinc displaces copper from the solution of copper sulphate.
Question. When a zinc granule is added to copper sulphate solution.
Answer
A gelatinous white ppt. of zinc sulphate (ZnSO4) is formed and the blue coloured solution of copper sulphate decolourises because of its formation.
Question. When zinc nitrate crystals are strongly heated.
Answer
A precipitate of zinc oxide (ZnO) is formed with the evolution of NO2 and O2 gases. The precipitate (ZnO) formed is yellow when hot and white when cold.
A reddish brown gas (NO2) thus liberated has a pungent, irritating odour which turns potassium iodide paper brown.
A colourless and odourless gas (O2) thus liberated rekindles a glowing splinter.
Question. When a piece of calcium is dropped into a trough of water.
Answer
When a piece of calcium is dropped into water, a vigorous reaction takes place and a colourless, odourless gas hydrogen is evolved, which can be collected in a test tube and water becomes alkaline due to the formation of calcium hydroxide.
Ca + 2H2O ⎯→ Ca(OH)2 + H2↑
Question. When a piece of sodium is added to water.
Answer
When a small piece of sodium is dropped into water, producing hydrogen gas, which catches fire, the solution becomes alkaline due to the formation of sodium hydroxide.
2Na + 2H2O ⎯→ 2NaOH + H2↑
Question. When hydrogen is passed over a heated metallic oxide.
Answer
When hydrogen is passed over heated metallic oxide, it is oxidized into water (its corresponding oxide) and the metallic oxide is reduced to free metal.

Question. When a strip of copper is kept immersed in the solution of silver nitrate.
Answer
Copper is more reactive than silver. So it displaces silver from silver nitrate solution.
Question. Zinc metal is heated in air at 500°C.
Answer
Zinc metal is heated in air at 500°C, the metal burns with bluish-white flame and forms philosopher’s wool.

Question. Zinc metal is treated with ferric sulphate.
Answer
Zinc metal reduces ferric sulphate to ferrous sulphate. Zinc is a powerful reducing agent.

Question. What happens to the (a) aluminium oxide, (b) iron (III) oxide, when bauxite is treated with sodium hydroxide solution.
Answer
(a) Aluminium oxide dissolves in NaOH solution to form sodium meta-aluminate.
(b) The iron (III) oxide remains undissolved in the sodium.
Question. When iron filings are strongly heated.
Answer
When iron filings are strongly heated in the presence of atmospheric oxygen, iron is oxidized to form reddish brown ferric oxide.

Question. When a finely ground (powdered) mixture of iron filings and sulphur is heated.
Answer
When the mixture of iron filings and sulphur is heated, iron combines with sulphur to form a black powder of iron sulphide. During heating the mixture begins to glow, as it is an exothermic reaction.

Define/Explain the Following
Metal
Answer
A metal is an element which forms a positive ion by the loss of electrons. They are hard, malleable, ductile, lustrous, sonorous and also good conductors of heat and electricity.
Metalloids
Answer
Elements which exhibit the properties of both metals and non-metals, are called metalloids. They are also known as semimetals. For example, Arsenic, Antimony and Bismuth.
Metallurgy
Answer
The processes involved in the extraction of pure metals from their ore are collectively called metallurgy.
Ore
Answer
Those minerals from which, the metals are extracted commercially at a comparatively low cost and with minimum effort, are called ores of the metals
Gangue or Matrix
Answer
The unwanted impurities which are associated with ore are called gangue or matrix. e.g., stone, clay etc.
Slag
Answer
A fusible mass produced by the combination of flux and gangue is called slag.
Flux
Answer
A flux is a substance which is added to refine metals by combining with impurities to form a molten mixture that can be readily removed.
Roasting
Answer
The process of strongly heating the ore in excess of air is called roasting.
Calcination
Answer
Ans. The process of heating the ore in a limited supply of air, such that temperature is not sufficient to melt the ore is called calcination.
Alloy
Answer
. An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of either two or more metals or a metal and a nonmetal which are mixed together in definite proportion in their molten state.
Galvanized iron
Answer
Iron sheets with their surface covered with zinc coating either by electrolysis or by dipping them in molten zinc are known as galvanised iron sheets.
Passive iron
Answer
Iron dipped in conc. nitric acid and rendered unreactive due to the formation of the layer of ferric oxide, is known as passive iron.
Hardening of steel
Answer
When steel heated to a temperature of 750°C to 800°C and then suddenly plunged into cold water or cold oil, the process is called hardening of steel.
Tempering of steel
Answer
The process of heating the hardened steel to some fixed temperature and then cooling it slowly is called tempering or annealing of steel.
Case hardening of steel
Answer
The process of heating mould steel with powdered carbon in clay moulds, such that its upper surface becomes very hard, but inner surface remains soft and spongy is called case hardening of steel.
Amalgams
Answer
An alloy of mercury with, one or more other metals is called on amalgan, e.g., zinc amalgam, sodium amalgam, etc.
Balancing/Writing the Chemical Equations
(a) Write balanced chemical equation :
1. The reduction of metallic oxide inside the blast furnace.
Answer
1. Fe2O3 + 3CO ⎯→ 2Fe + 3O2
2. Formation of slag inside the blast furnace.
Answer
CaO + SiO2 ⎯→ CaSiO3
3. Heating of aluminium hydroxide.
Answer

4. Reaction of zinc with hot concentrated sodium hydroxide.
Answer
Zn + 2NaOH ⎯→ Na2ZnO2 + H2
5. Reduction of zinc oxide.
Answer
ZnO + C ⎯→ Zn + CO
6. Burning of aluminium in air.
Answer
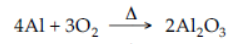
7. Reduction of ferric oxide by aluminium powder.
Answer
Fe2O3 + 2Al ⎯→ Al2O3 + 2Fe
8. Calamine is heated.
Answer

9. Zinc placed in ferrous sulphate solution.
Answer
Zn + FeSO4 ⎯→ ZnSO4 + Fe
10. Reduction of copper oxide by hydrogen
Answer
CuO + H2 ⎯→ Cu + H2O
11. Reduction of iron(III) oxide by carbon monoxide.
Answer
Fe2O3 + 3CO ⎯→ 2Fe + 3CO2
12. Reduction of lead(II) oxide by carbon.
Answer
PbO + C ⎯→ Pb + CO
13. Action of heat on aluminium hydroxide.
Answer

14. Zinc is treated with dilute sulphuric acid.
Answer
Zn + H2SO4 ⎯→ ZnSO4 + H2↑
(Dil.)
15. Action of copper sulphate solution on zinc.
Answer
Zn + CuSO4 ⎯→ ZnSO4 + Cu.
16. Action of steam on zinc.
Answer
Zn + H2O ⎯→ ZnO + H2↑
Steam Zinc oxide
(b) Complete and balance the following equations :

Ans.


IUPAC Naming/Writing the Structural Formula
Q. Give the chemical formulae of the following naturally occuring ores :
| 1. Cryolite | → | Na3AlF6 |
| 2. Galena | → | PbS |
| 3. Corundum | → | Al2O3 |
| 4. Dolomite | → | CaCO3.MgCO3 |
| 5. Zincite | → | ZnO |
| 6. Malachite | → | CuCO3.Cu(OH)2 |
| 7. Cinnabar | → | HgS |
| 8. Gypsum | → | CaSO4.2H2O |
| 9. Horn silver | → | AgCl |
| 10. Epsom salt | → | MgSO4. 7H2O |
| 11. Haematite | → | Fe2O3 |
| 12. Bauxite | → | Al2O3.2H2O |
Reasoning Based Questions
Q. 1. Why are metals called reducing agents ?
Answer
They tend to lose electrons and act as reducing agents.
Q. 2. Why are non-metals called oxidizing agents ?
Answer
They tend to gain electrons and act as oxidising agents.
Q. 3. Why iron is not found in free state in nature ?
Answer
Iron is quite reactive metal, it easily combines with other metals. Iron thus occurs in nature in the form of its compounds and not as a free element.
Q. 4. Iron liberates hydrogen from dilute sulphuric acid, while silver cannot. Why ?
Answer
In activity series of metal, iron occupies a higher position than hydrogen, while silver is placed below hydrogen, hence iron is more reactive than silver and is able to displace hydrogen from dilute sulphuric acid.
Fe + H2SO4 ⎯→ FeSO4 + H2↑
Q. 5. Zinc displaces lead from lead nitrate solution, while gold is unable to do so. Why ?
Answer
Zinc is above lead in the metal activity series. It is more reactive than lead while gold, a noble metal, lies far below lead in the activity series and it is less reactive or highly unreactive. Zinc reacts with lead nitrate solution to precipitate lead and zinc nitrate is formed. There is no reaction between gold and lead nitrate.
Pb(NO3)2 + Zn ⎯→ Zn(NO3)2 + Pb ↓
Lead nitrate Zinc nitrate Lead
Pb(NO3)2 + Au ⎯→ No reaction.
Lead nitrate
Q. 6. Why is sodium metal always stored under kerosene oil ?
Answer
Sodium is a very reactive metal and on exposure to moist air, the surface of sodium metal is tarnished due to the formation of sodium carbonate.
4Na + O2 ⎯→ 2Na2O.
Na2O + H2O ⎯→ 2NaOH
2NaOH + CO2 ⎯→ Na2CO3 + H2O
Sodium Carbonate
Q. 7. Why carbon can reduce copper(II) oxide to copper but not calcium oxide to calcium ?
Answer
Carbon can reduce copper(II) oxide to copper but not calcium oxide to calcium because carbon has greater affinity for oxygen than copper and less affinity for oxygen than calcium.
Q. 8. Aluminium is highly electropositive metal, in spite of it aluminium does not oxidise rapidly in air. Why ?
Answer
In moist air, a thin layer of aluminium oxide is formed on it quickly which protects aluminiumto oxidise. This is the reason why aluminium does not oxidise rapidly in air.
Q. 9. Why extraction of aluminium is difficult ?
Answer
Extraction of aluminium is difficult because :
(i) Pure aluminium oxide melts at 2050°C only. So, a large amount of energy is needed to maintain this high temperature.
(ii) A good amount of the aluminium vaporises at this temperature.
(iii) Fused alumina does not conduct electricity well.
Q. 10. During the extraction of aluminium, cryolite and fluorspar are added to alumina. Why ?
Answer
Cryolite and fluorspar are added to alumina :
(i) To lower the melting point of aluminium.
(ii) To make alumina a good conductor of electricity.
(iii) Cryolite acts as a solvent for alumina.
Short Questions
Q. 1. (i) Arrange Cu, Ca, Al, Fe, Mg, Pb, Na and Zn in the decreasing order, in which they appear in the activity series; putting down the most reactive metal first and least reactive in the last.
(ii) (a) Among the above metals, write the names of metals which will displace hydrogen from water or steam.
(b) Give two evidences to show that magnesium is more reactive than iron.
Answer
(i) The given metals are arranged in the activity series of metals as follows :
Na, Ca, Mg, Al, Zn, Fe, Pb (most reactive) and Cu (least reactive).
(ii) (a) (1) Sodium and calcium displace hydrogen from cold water.
2Na + 2H2O ⎯→ 2NaOH + H2↑
Ca + 2H2O ⎯→ Ca(OH)2 + H2↑
(2) Magnesium and zinc metals are less reactive as they react with boiling water to liberate hydrogen gas.
Mg + 2H2O ⎯→ Mg(OH)2 + H2↑
Zn + 2H2O ⎯→ Zn(OH)2 + H2↑
(3) Iron which is less reactive, reacts in red hot conditions with steam to liberate hydrogen gas.
3Fe + 4H2O ⎯→ Fe3O4 + 4H2↑
(4) Lead and copper almost fail to liberate hydrogen gas in any conditions, because they are not so reactive. They lie just above and below hydrogen in activity series of metals.
(b) (1) Magnesium reacts with boiling water to liberate hydrogen gas, while iron can do so with steam in red hot condition only.
(2) Magnesium can displace hydrogen from acids vigorously in cold but iron displaces hydrogen slowly.
Q. 2. (i) Na, Ca, Mg, Al, Zn, Fe, Pb and Cu, are well known metals.
(a) X, Y and Z are coded letters for three of the metals in the activity series of metals as given above.
Metal X, reacts violently with cold water and its hydroxide is not decomposed by heat.
Metal Y, has no reaction with water but its hydroxide decomposes, with slight warming, giving a black powder.
Metal Z, reacts vigorously with dilute hydrochloric acid but hardly at all with cold water. If it is heated in steam, a white solid A is formed and a colourless gas B is set free.
(1) which of the metals in the list is X ?
(2) which of the metals in the list is Y ?
(3) which of the metals in the list is Z ?
(4) write the name of the solid A and gas B.
(b) State whether the following are soluble or insoluble in water.
(1) The carbonate of X.
(2) The carbonate of Y.
(3) The hydroxide of Z.
(ii) A certain metal does not liberate hydrogen from dilute sulphuric acid but it displaces silver from aqueous silver nitrate solution. State the most likely place for the metal in the activity series.
(iii) What would you expect to happen, if aluminium metal is heated with iron(III) oxide ? Also write the equation.
Answer
(i) (a) (1) The metal X is sodium.
(2) The metal Y is copper.
(3) The metal Z is magnesium.
(4) The name of the solid A is magnesium hydroxide, while the gas B is hydrogen.
(b) (1) Soluble as sodium carbonate is soluble in water.
(2) Insoluble, as copper carbonate is insoluble in water.
(3) Soluble, as magnesium hydroxide is soluble in water.
(ii) The metal lies below hydrogen and above silver in the activity series of metals.
(iii) When aluminium metal is heated with iron(III) oxide with metallic iron, an enormous amount of heat is produced due to the exothermic nature of the reaction. Molten iron is
thus produced, which can be used in welding.
Fe2O3 + 2Al ⎯→ Al2O3 + 2Fe + Q.
Q. 3. (i) Arrange Ca, Pb, Fe, Na, Zn, Cu, and Al in the decreasing order of their reactivity.
(ii) Answer the following question related to above (i) sequence :
(a) Which of these is most likely to tarnish readily when exposed to the air ?
(b) Which of these is most likely to be found in free state in nature ?
(c) Which of these is most likely to react with cold water ?
Answer
(i) The decreasing order of the given metals is as follows :
[Most reactive] Na, Ca, Al, Zn, Fe, Pb, and Cu [Least reactive]
(ii) (a) Sodium [Na] (b) Copper [Cu]
(c) Sodium [Na] and calcium [Ca]
Q. 4. (i) From the metals copper, zinc, magnesium, sodium and iron, select the metal in each case which :
(a) Does not react with dil. hydrochloric acid.
(b) Has a hydroxide that reacts with both acids and alkalies.
(c) Does not react with cold water but reacts with steam when heated.
(d) Can form +2 and +3 ions.
(ii) Arrange the metals in decreasing order of reactivity.
Answer
(i) (a) Copper (b) Zinc
(c) Magnesium (d) Iron
(ii) Sodium > Magnesium > Iron > Zinc > Copper.
Q. 5. (i) Differentiate between :
(a) Slag and Flux. (b) Calcination and Roasting.
(ii) Compare the properties of a typical metal and a non-metal on the basis of the following :
(a) Electronic configuration
(b) Nature of the oxides
(c) Oxidising or reducing action
(d) Conductivity of heat and electricity.
(iii) What are the differences between a mineral and an ore ?
Answer

(a) Metals complete their octet by the loss of electrons whereas non-metals complete their octet by the gain of electrons.
Metals generally contain 1 to 3 valence electrons in their outermost shell whereas non-metals contain 4 to 7 valence electrons in their outermost shell.
(b) Metals form basic oxides whereas non-metals form acidic oxides.
(c) Metals are reducing agents whereas non-metals act as oxidising agents.
(d) Metals are generally good conductors of heat and electricity whereas non-metals are bad conductors of heat and electricity.
(iii) (a) The minerals contain a low percentage of metal, while the ores contain a large percentage of the metal.
(b) The metal cannot be extracted from mineral, on the other hand ores can be used for the extraction of metal.
Q. 6. (i) The ore zinc blende, is an important source of the metal zinc. What is the name of the zinc compound in zinc blende ?
(ii) What is the zinc compound obtained by roasting zinc blende ?
(iii) What is the type of chemical reaction carried out in order to obtain zinc ?
(iv) Are liquid zinc and liquid lead miscible or immiscible ?
(v) What is the name of the alloy formed between zinc and copper ?
Answer
(i) Zinc sulphide (ZnS).
(ii) Zinc blende is oxidized to zinc oxide by roasting in presence of excess air.
(iii) Reduction of zinc oxide.
(iv) Immiscible.
(v) Brass [7% of Cu, 30% of Zn].
Q. 7. The following questions refer to the extraction of aluminium and iron from their ores :
(i) Name the principal ore from which; (a) iron and (b) aluminium are extracted.
(ii) What is the most important chemical process in the extraction of any metal ? State how this essential step is carried out in the extraction of; (a) iron, (b) aluminium.
(iii) Iron and aluminium ores both, contain impurities. Explain briefly how these impurities are removed in each case.
(iv) What is the major impurity present in iron when it is removed from the blast furnace ?
Answer
(i) (a) Haematite (Fe2O3). (b) Bauxite (Al2O3).
(ii) Reduction of the oxide is an important step in extraction of metal.
In case of iron, Fe2O3 + 3CO ⎯→ 2Fe + 3CO2
Al2O3 cannot be easily reduced, hence it is subjected to electrolysis. Aluminium is collected at the cathode.
(iii) Iron ore contains impurities of silica and sand. These are removed by magnetic
separation. Bauxite and aluminium ore contains impurities of FeO and SiO2.
Bauxite containing FeO is calcinated at high temperature when FeO is oxidised to Fe2O3.
Calcinated ore is then treated with NaOH when Al2O3 is converted into soluble NaAlO2.Fe2O3
can thus be filtered off. Bauxite containing SiO2 is mixed with coke and heated to 1000°C in an
atmosphere of N2. Silica is reduced to Si which volatilises at the temperature of reaction.
Aluminium oxide is converted into AIN which is hydrolysed with water to obtain Al(OH)3.
(iv) Carbon is major impurity present in iron.
Q. 8. (i) What is bauxite ? Which metal is extracted from it ?
(ii) In the electrolysis of molten alumina, the carbon anode is gradually burnt away. Why ?
(iii) Describe modern method of aluminium extraction.
Answer
(i) Bauxite is hydrated aluminium oxide [Al2O3.2H2O] and aluminium metal is extracted from bauxite.
(ii) In the electrolysis of molten aluminium oxide, oxygen gas is liberated which gradually burns away carbon anode at a higher temperature to form carbon dioxide.
C + O2 ⎯→ CO2
(iii) In the modern method, pure alumina is dissolved in cryolite [Na3.AlF6], which makes it good conductor of electricity.
When an electric current is passed through electrolyte, the heat is also produced which keeps the mass in molten state and alumina gets reduced to free aluminium metal according to the following reactions :
Na3AlF6 ⎯→ 3NaF + AlF3
2AlF3 ⇌ 2Al3+ + 6F–
6F– + Al2O3 ⎯→ 2AlF3 + 3O2–
At cathode : 2Al3+ + 6e– ⎯→ 2Al
At anode : 3O2– – 6e– ⎯→ 3O
3O + 3O ⎯→ 3O2
Q. 9. The following questions are relevant to the extraction of aluminium :
(i) State the reason for addition of caustic alkali to bauxite ore during purification of bauxite.
(ii) Give a balanced chemical equation for the above reaction.
(iii) Alongwith cryolite and alumina, another substance is added to the electrolyte mixture.
Name the substance and give one reason for the addition.
Answer
(i) Caustic alkali dissolves aluminium oxide forming soluble sodium aluminate while impurities remains insoluble and ppt. as red mud.
(ii) Al2O3 · 2H2O + NaOH ⎯→ 2NaAlO2 + 3H2O
(iii) The name of substance is Fluorspar (CaF2) and it increases conductivity of the electrolyte.
Q. 10. ‘Alumina (aluminium oxide) has a very high melting point of over 2,000°C so that it cannot readily be liquiefied. However, conversion of alumina to aluminium and oxygen, by electrolysis, can occur when it is dissolved in some other substance.’
(i) Which solution is used to react with bauxite as a first step in obtaining pure aluminium oxide ?
(ii) The aluminium oxide for the electrolytic extraction of aluminium is obtained by heating aluminium hydroxide. Write the equation for this reaction.
(iii) Name the element which serves both as the anode and the cathode in the extraction of aluminium.
(iv) Write the equation for the reaction that occurs at the cathode during the extraction of aluminium by electrolysis.
(v) Give the equation for the reaction which occurs at the anode when aluminium is purified by electrolysis.
Answer
(i) Sodium hydroxide
(ii) 2Al(OH)3 Δ⎯→ Al2O3 + 3H2O



