Please refer to Physical Education Class 10 ICSE Football notes provided below. These revision notes have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination pattern for ICSE Class 10 Physical Education issued for the current academic year. Students should always revise these revision notes prior to their exams to properly prepare and understand all topics. After reading these notes also refer to Sample Papers for Class 10 ICSE Physical Education
ICSE Class 10 Physical Education Cricket Revision Notes
Students can refer to the quick revision notes prepared for Chapter Cricket in Class 10 ICSE. These notes will be really helpful for the students giving the Physical Education exam in ICSE Class 10. Our teachers have prepared these concept notes based on the latest ICSE syllabus and ICSE books issued for the current academic year. Please refer to Chapter wise notes for ICSE Class 10 Physical Education provided on our website.
Physical Education Class 10 ICSE Cricket Notes
➢ Introduction :
Football, which is now commonly known as soccer, is one of the most popular game in the world, as well as the most spectacular sport. The game is played by two opposing teams, with eleven members in each team including the goal keeper. It is played in a rectangular field of specific measurements, each team aiming to score a goal into the opponents goal mouth. The game is primarily played with feet and only the goalkeepers are allowed to touch and handle the ball with hands. The game is of ninety minutes with forty five minutes each half and the team that scores more goals within awarded time is declared as winner.
➢ World History :
Football is one of the most important games in the world. It has a vivid and interesting history in the world of sports. The evidence of the game is being alluded that Chinese used to play football in 2nd and 3rd century B.C. by the name of “Tsuchu” which means kicking the ball. Moreover, it was also played popularly by Greeks and Romans. The growth of ” modern football started in England. F.I.F.A. the governing body of football was established in 1904 with its headquarter in Zurich (Switzerland). The first F.I.F.A. world cup was started in the year 1930.
➢ Indian History :
Football in India was introduced by British soldiers in mid- nineteenth century and was spread in some parts of the country by forming regimental teams. Durand Cup which is India’s oldest tournament held (incidentally the third oldest in the world) was founded in 1888. A.I.F.F. the governing body of football in India was established in 1937. India participated in Olympics in 1948 and 1956. The years 1951-1962 were considered as golden era of Indian football as India won gold in 1951 and 1962 Asian Games. India qualified for 1950 F.I.F.A. World Cup but failed to participate due to fiscal problems. In 1956 Olympics, India was the first country from Asia to enter the semifinal of football. This achievement is considered as an apex position of Indian football.
➢ Governing Body :
Federation Internationale de Football Association (FIFA)
The Federation Internationale de Football Association (FIFA ) is the international governing body of association football, futsal and beach soccer. FIFA is responsible for the organization of Football’s major international tournaments, notably the World Cup which commenced in 1930 and the Women’s World Cup which commenced in 1991. FIFA was founded in 1904, with its headquarter in Zurich (Switzerland).
All India Football Federation (AIFF)
The All India Football Federation (AIFF) is the organization which manages the game of association football in India. It administers the running of Indian national football team and also controls the I League, India’s premier domestic club competition, in addition to various other competitions and teams. The AIFF was founded in 1937, gained FIFA affiliation in the year 1948 and A.F.C. affiliation in the year 1954. Currently it has its office at Dwarka, New Delhi.


➢ Football Field Markings
(i) Touch Line : Touch Line (length of the field) which is also known as side line is a line at the side of the football field. If the ball goes out of the touch line, the game will be restarted with throw-in.
(ii) Goal Line : Goal Line (width of the field) which is also known as end line is a line at the side of the goal posts.
If the ball goes out of the goal line touching the attacker then, the game will restart with goal kick and if the ball goes out touching the defender at the last moment before it crosses the goal line the game will restart with the corner kick.
(iii) Half way line : Half way line or a centre line is the line through the middle of the football field that divides the field into two equal halves.
(iv) Centre circle : It is a circle that is made in the centre of the football field, at the Centre line with radius of 9.15m from the centre mark that bounds the opponents from interfering the start of the game at the time of kick off.
(v) Centre mark : Centre Mark or the Centre spot is a mark or a spot in the centre of the football field, at the middle of the centre circle, where the ball is placed during kickoff.
(vi) Penalty box : Penalty Box, also called a Penalty Area is 16.5 m x 40.32 m area, at each end of the playing field.
The foul committed against attacking player inside that area is punishable with the penalty kick.
(vii)Penalty mark : It is a mark or a spot inside the penalty area at a distance of 11 m from the centre of the goal line.
(viii) Penalty arc : Penalty Arc is the semi-circle on the top of the penalty box with its radius of 9.15 m from penalty mark, where no player is allowed to be inside it, during penalty kick, except the penalty kicker and opponent’s goalkeeper.
(ix) Goal box : It is a small area of 5.5 m × 18.32 m within the penalty box, where goal kick is taken from area anywhere within a goal box.
(x) Corner arc : A semi-circle area with radius of 1 m, at each corner of the playing pitch is called Corner Arc. It is the area of the arc where the ball is to be placed during the corner kick.
➢ Fundamentals Skills of Football
(1) Kicking
(i) Kicking with inside of the foot
(ii) Kicking with inside of the instep
(iii) Kicking with full instep
(iv) Kicking with outside of instep
(v) Kicking with outside of the foot
(2) Receiving
(i) Receiving the ball with the inside of the foot
(ii) Receiving the ball with the full instep (stop volley)
(iii) Receiving the ball with the outside of the instep
(iv) Receiving with the sole of the foot
(v) Receiving with the heel
(vi) Receiving with the thigh
(vii) Receiving with the chest
(3) Heading
(i) Heading forward from a stationary position
(ii) Heading ball with side of the forehead
(iii) Heading from standing jump off both feet
(iv) Heading ball after a slight run and from a jump off one foot
(v) Heading sideways from stationary position
(vi) Heading ball from diving header
(4) Dribbling
(i) Dribbling with inside of the instep
(ii) Dribbling with full instep
(iii) Dribbling with the outside of instep
(5) Tackling
(i) Sliding tackle
(ii) Interception tackling
(iii) Sideways tackling
(6) Passing
(i) Short pass
(ii) Long pass
(iii) Through pass
Short description of some of the above mentioned fundamental skills:
(7) Kicking
(i) Kicking with inside of the foot : A technique of kicking that involves the part of the foot bordered by the base of the big toe, the heel bone and the inner ankle.
(ii) Kicking with inside of the instep : A kicking technique that involves the inner surface of the foot stretching from the base of big toe to the inner part of the ankle or more precisely the part of inner ankle.
(iii) Kicking with full instep : A technique of kicking that involves the part of foot extending from the base of the toes to the curve of ankle, in other words, the part which is covered by the laced part of the foot.
(iv) Kicking with outside of instep : A kicking technique that involves, the part of the foot extending from the outer edge of the full instep to the outer edge of the foot bordered by the base of small toe and stretches almost up to the outside of the ankle
(8) Receiving
(i) Receiving with the thigh : Receiving with the thigh involves, receiving the ball by resting on the standing leg which is bent at knee, while the other leg rising from the hip with the knee bent leading the thigh to be at angle of 50° to 60° to that of the shin, thigh blocking the ball.
(ii) Receiving with the chest : Technique which involves controlling the aerial ball by contacting the ball with the chest and allowing the ball to fall perpendicularly in front of him to attain a ball possession.
(9) Heading
Heading ball from diving header : A way of heading by which the player heads the ball finding that the only way to reach the ball is to fling himself in a dive to head it from off both feet or sometimes off one foot.
(10) Tackling
Interception tackling : The way of tackling by making a jump ahead of the attacker from behind to head or kick the ball away or take possession of it.
➢ Football Cards
The cards that are used in football are of size same as playing cards, which the referee holds up to indicate serious fouls or any unsporting behaviour of the players. The cards that are used in football are of two colors i.e. Yellow and Red cards.
(1) Yellow Cards
A player is cautioned and shown the yellow card if he/she commits any of the seven offences given below :
(i) Unsporting behaviour.
(ii) Dissent by words or action.
(iii) Persistent infringements of the laws of the game.
(iv) Delaying the restart of the play.
(v) Failure to respect the required distance when play is restarted with a corner kick, free kick or throw-in.
(vi) Entering or re-entering the field of play without the referee’s permission.
(vii) Deliberately leaving the field of play without the referee’s permission.
A substitute or substituted player is cautioned if he/she commits any of the following three offences :
(i) Unsporting behaviour
(ii) Dissent by word or action
(iii) Delaying the re-start of play
A player who receives two yellow cards is given red card and ejected.
(2) Red Card
A player substitute or substituted player is sent off if he commits any of the seven offences given below:
(i) Serious foul play
(ii) Violent conduct
(iii) Spitting at an opponent or any other person
(iv) Denying the opposing team a goal or an obvious goal scoring opportunity by deliberately handling the ball
(this does not apply to a goalkeeper within his own penalty area).
(v) Denying an obvious goal scoring opportunity to an opponent moving towards the player ’s goal by offences punishable by a free kick or a penalty kick.
(vi) Using offensive, insulting or abusive language and / or gesture
(vii) Receiving a second caution in the same match
Player shown a “red card” and sent off may not be replaced during that game (i.e. his team must play a player short for the rest of the game)
A player substitute or substituted player who has been sent off must leave the vicinity of the field of play and the technical area.
➢ Terminology Related to Football
(i) Kick off : The method of starting a game or restarting it after each goal, a player passes the ball forward to a teammate from the centre spot. The ball must move into the opponent’s half of the field.
(ii) Goal kick : Kick made from inside the goal area away from the goal. A goal kick is awarded to the defending team when a ball crosses the goal line that was last touched by a player of the attacking team.
(iii) Direct free kick : A free kick that is taken from of the areas outside the penalty box and can be kicked directly or in- directly to score a goal.
(iv) Indirect free kick : A free kick which cannot be scored directly and can be scored only if the ball touches the other player.
(v) Corner kick : A method of putting the ball into play after it has crossed the end line and was last touched by a member of the defending team. A kick is to be started from within corner arc.
(vi) Set play : It is a planned strategy that a team uses when a game is to be restarted with a free kick, penalty kick, corner kick, goal kick and throw-in.
(vii) Throw-in : It is a method of restarting play after the ball has travelled outside the touchline. The ball must be held with two hands and released directly over the head while both feet are touching the ground.
(viii)Penalty kick : A kick that is taken from a penalty mark in case a foul is committed by a defending player towards attacker inside the penalty box. A penalty kick is awarded to attacking team.
(ix) Hand ball : This term means deliberate handling of a ball by a player other than the goalkeeper in the Penalty Area. This is considered as a deliberate action by the player and is penalized normally if there is movement of the hand towards the ball.
(x) Passing : When a player kicks the ball to his teammate to keep the ball in possession and away from an opponent or to give the ball to a player who is in a better position to score.
(xi) Dribbling : Skill of advancing and controlling the ball close to the feet while playing.
(xii) Heading : The way of controlling, clearance or scoring the goal with the head.
(xiii) Receiving : The way of controlling the coming ball with the feet, head, chest, thigh etc.
(xiv) Shooting : When a player kicks the ball towards opponent’s net in an attempt to score a goal.
(xv) Foul : The violation of the rules. In response to a foul, a referee calls for a direct free kick, an indirect free kick or penalty kick in case a foul is committed within penalty box.
(xvi) Defender : A player who functions primarily in the defensive third of the field and whose major role is to repel attacks on the goal by the opposing team.
(xvii) Mid fielder : A Player who functions primarily in the central (neutral) third of the field and whose principal job is to link the defense and the attack through ball control and passing.
(xviii) Strikers : Players who function primarily in an attacking third of an opponent, to score a goal.
➢ Latest General Rules of Football
(i) Goal keeper can move on the goal line at the time of penalty kick; earlier the goal keeper was not allowed to do so until the execution of penalty kick.
(ii) Now the golden goal rule is not applied, instead of it, extra time of two halves (15minutes-15minutes) is given to the teams to decide the winner if the match remains draw in normal time of 45 minutes – 45 minutes and if the match still remains draw in extra time , the penalty shoot takes place.
New Amendments in the Rules of Football
(i) Where head covers are worn, they must—
(a) Be black or of the same main colour as the jersey (provided that the players of the same team wear the same colour)
(b) Be in keeping with the professional appearance of the players equipments
(c) Not be attached to the jersey
(d) Not pose any danger to the player wearing it or any other player (e.g. opening/closing mechanism around neck)
(e) Not have any parts extending out from the surface (protruding elements)
(ii) Now there can be 23 players instead of 18 players, out of these, 12 players are called substitute players i.e. 11 players and 12 substitutes whereas only 3 players can be substituted from 12 substitute players.
➢ Necessary Equipment

(i) Football fleets/football shoes
(ii) Stockings/ football socks
(iii) Shin guard
(iv) Jersey
(v) Shorts
(vi) Goalie apparel (jersey, shorts and pants)
(vii) Goal keeper gloves
(viii)Football
(ix) Supporters & cups
(x) Head gear
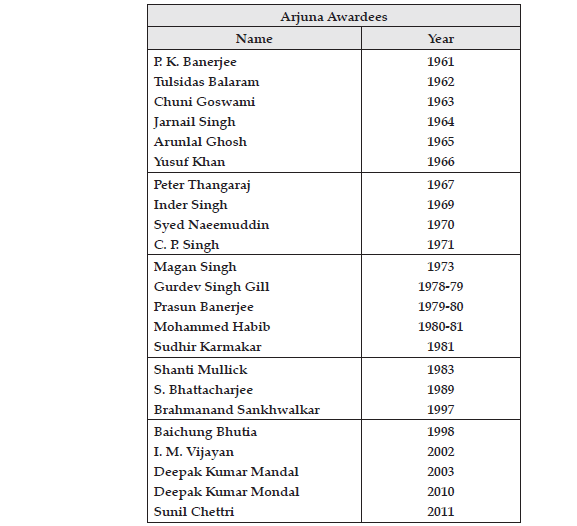
➢ Sports Award

➢ Tournaments and Venues
International Football Tournaments
(i) Soccer Champions League
(ii) UEFA Cup
(iii) UEFA European League
(iv) F.I.F.A. World Cup
(v) European Championship Men
(vi) European Championship Women
(vii) CONCACAF Champions League (viii)Dubai Cup
(ix) Confederations Cup
(x) Copa America
(xi) AFC Champion
➢ National Football Tournaments
(i) Indian Super League
(ii) I-League
(iii) I-League 2nd Division
(iv) Calcutta Football League
(v) Youth League
(vi) Federation Cup
(vii) Durand Cup
(viii)Santosh Trophy
(ix) Indian Super Cup
➢ National venues
(i) Salt Lake Stadium, Kolkata (West Bengal)
(ii) Jawaharlal Nehru Stadium, Kochi (Kerala)
(iii) Gurunanak Stadium, Ludhiana (Punjab)
(iv) Indira Gandhi Stadium, Guwahati (Assam)
(v) Kanchanjunga Stadium, Siliguri, (West Bengal)
➢ International venues
(i) Old Trafford, Manchester (England)
(ii) San Sairo, Milan (Italy)
(iii) Olyampiastadion, Berlin (Germany)
(iv) EstadioAzteea, Mexico City (Mexico)
(v) Millennium Stadium, Cardiff (Wales).
➢ Sports Personalities

➢ International Personalities
(i) Lionel Messi (Argentina and Barcelona)
(ii) Cristiano Ronaldo (Portugal and Real Madrid)
(iii) Luiz Suarez (Uruguay and Barcelona)
(iv) Andres Iniesta (Spain and Barcelona)
(v) Yaya Toure (Ivory Coast and Manchester City)
(vi) Gareth Bale (Wales and Real Madrid)
(vii) Phillip Lahm (Germany and Bayern Munich)
(viii)Arjen Robben (Netherland and Bayern Munich)
(ix) Robin Van Persie (Netherland and Manchester United)
(x) Zlatan lbrahimovic (Sweden and Paris saint German)



