ICSE Class 10 students can refer to ICSE Class 10 Study of Compounds Nitric Acid Notes given below which have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and guidelines issued by ICSE Board. All chapter wise revision notes for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry have been prepared by teachers have strong understanding of Chemistry. Read the notes prior to the exams to get better marks in exams
Study of Compounds Nitric Acid ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Revision Notes
Students can refer to the quick revision notes prepared for Chapter Study of Compounds Nitric Acid in Class 10 ICSE. These notes will be really helpful for the students giving the Chemistry exam in ICSE Class 10. Our teachers have prepared these concept notes based on the latest ICSE syllabus and ICSE books issued for the current academic year.
Revision Notes ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Study of Compounds Nitric Acid
Please refer to the detailed notes below
Nitric Acid

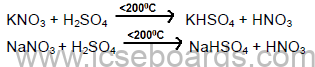
Laboratory Preparation of Nitric Acid
Reactions:
Properties of Nitric Acid
(A)Physical Properties
• Pure acid (98% conc.) is colourless, suffocating and sour to taste.
• It is heavier than water, with a specific gravity of 1.54.
• Boiling point is 86°C, and freezing point is −42°C
(B) Chemical Properties
• Pure nitric acid is colourless, unstable and decomposes slightly even at room temperature and in the
presence of sunlight.
4HNO3 → 4NO2 + 2H2O + O2
• Nitric acid is a very strong monobasic acid and ionises almost completely in aqueous solution.

• Nitric acid neutralises alkalis to form salt and water.
CaO + 2HNO3 → Ca (NO3)2 + H2O
CuO + 2HNO3 → Cu (NO3)2 + H2O
NaOH + HNO3 → NaNO3 + H2O
• Nitric acid reacts with carbonates and bicarbonates to produce salt, water and carbon dioxide.
Na2CO3 + 2HNO3 → 2NaNO3 + H2O + CO2
NaHCO3 + HNO3 → NaNO3 + H2O + CO2
• Nitric acid oxidises carbon, sulphur and phosphorus to their highest oxides or oxy-acids such as
carbon dioxide, sulphuric acid and phosphoric acid.
C + 4HNO3 → 2H2O + 4NO2 + CO2
S + 6HNO3 → H2SO4 + 2H2O + 6NO2
P4 + 20HNO3 → 4H3PO4 + 4H2O + 20NO2
Uses of Nitric Acid
• To etch designs on copper and brassware because it acts as a solvent for several metals except the
noble metals.
• To purify gold with impurities of Cu, Ag and Zn which dissolve in nitric acid.
• It acts as a rocket fuel oxidant.
• In preparation of fertilisers such as Ca(NO3)2 and NH4NO3.
• In the preparation of aqua regia, which dissolves noble metals.



