Students should refer to Pollution ICSE Class 10 Biology notes provided below designed based on the latest syllabus and examination pattern issued by ICSE. These revision notes are really useful and will help you to learn all the important and difficult topics. These notes will also be very useful if you use them to revise just before your Biology Exams. Refer to more ICSE Class 10 Biology Notes for better preparation.
ICSE Class 10 Biology Pollution Revision Notes
Students can refer to the quick revision notes prepared for Chapter Pollution in Class 10 ICSE. These notes will be really helpful for the students giving the Biology exam in ICSE Class 10. Our teachers have prepared these concept notes based on the latest ICSE syllabus and ICSE books issued for the current academic year. Please refer to Chapter wise notes for ICSE Class 10 Biology provided on our website.
Pollution ICSE Class 10 Biology
TOPIC-1
Pollution and its Types
Quick Review
➢ Pollution is the undesirable change in the physical, chemical and biological characteristics of our environment, which occurs largely due to human activities is called pollution. Substances that is responsible for pollution are called pollutants. These are classified into two main types:
➢ Biodegradable pollutants : These pollutants are degraded by decomposers e.g., food, kitchen waste etc.
➢ Non-biodegradable pollutants : These pollutants are not degraded or decomposed by decomposers e.g., DDT, BHC.
➢ Pollution of the surrounding environment is the most serious ecological crisis that humans are man is facing today and the reason behind this are :
➢ Increase in population.
➢ Industrial development.
➢ Based on the component of environment being affected, pollution can be categorized into the following main types :
➢ Air pollution.
➢ Water pollution.
➢ Soil pollution.
➢ Noise pollution.
➢ Air pollution : Release of harmful substances into atmosphere which are harmful to mankind and other organisms is called the air pollution. Air pollutants are the following main types-
➢ Particulate pollutants : These constitute harmful particles such as dust particles, metallic particles, smoke, mining, stone drilling, wearing of rubber tyres, etc which remain suspended in the air.
➢ Gaseous pollutants : These constitute the harmful gases such as CO2, H2S, CO, SO2, NO2, etc that are given out from a variety of sources.
➢ Air pollution can be caused by either of the following sources – Natural resources and Man-made sources.
➢ Natural sources include volcanic eruptions, fumes from forest fires, dust from storms, pollen etc.
➢ Man-made sources include excessive use of automobiles, garbage, industrial brick kilns, etc.
Some of the man-made sources of air pollution are described below:
➢ Vehicular Air Pollution : Pollutants produced by vehicle exhausts include CO, NO2, SO2, hydrocarbon and volatile organic compounds etc. The main cause of vehicular pollution is the rapidly growing number of vehicles. This type of pollution can be easily controlled by use of lead free petrol, use of CNG over petrol, efficient engine, good quality automobiles etc.
➢ Industrial air pollution : Factories pollute the air through fossil fuel emission. These emissions include CO2, CH4 and nitrous oxides. Combustion creates these toxic pollutants. Industries should not be allowed to operate in highly populated areas. Instead, they should be established at least a few kilometers away from the same. A broad zone of trees and shrubs should be planted around the industrial area.
➢ Burning Garbage : Garbage from homes and kitchen wastes include items such as vegetables and fruit peels, polythene bags. These wastes are either used in making manures for agriculture purposes or should be burnt in enclosure. On burning garbage harmful gases such as CO2 etc. are released which causes air pollution.
➢ Brick kilns : Brick kilns are fire heated enclosures used for making bricks that are used in construction purposes. The waste produced by these enclosures are large quantity of ash and broken small pieces of bricks, which cause air pollution.
➢ Water pollution is defined as any change in water quality that makes it unsuitable for use by humans and other living organisms.
➢ The major sources of water pollution are given below :
➢ Sewage : Discharge of untreated and partially treated sewage into the rivers, canals, tanks etc, cause very serious pollution. They cause spreading of water born diseases like dysentery, typhoid, cholera, jaundice etc.
➢ Household detergents : Detergents and soaps used for household purposes, i.e. for washing clothes and utensils and for bathing release dirty water that is also a cause of water pollution.
➢ Industrial effluents : Discharge of untreated wastes (wastes from breweries, dyeing, textiles, paper, pharmaceutical industries etc.) of various industries into near by river or lake cause serious water pollution.
➢ Oil spills : Spills from oil wells and refineries and washing of tankers during loading and unloading cause a lot of pollution. The spills are always in danger of catching fire. Oil spills spread over the surface of water kill plankton and smear others which happen to come on the surface. There is reduced oxygenation of underlying water. As a result, many aquatic life forms such as fishes, etc are killed.
➢ Thermal pollution : Water used for oil refineries, nuclear power plants and other thermal power plants are released into the nearby streams. The water released by industries is warmer than the normal water of streams. Due to this temperature changes, the aquatic life forms and aquatic plants get affected.
➢ Soil pollution is defined as any undesirable change in the soil profile affecting its productivity. Water and air pollution can spread to long distances but soil pollution is largely localized.
➢ The major sources of soil pollution are given below :
➢ Industrial wastes : Various industries release certain solid wastes in addition to gaseous air pollutants and other chemicals. The solid wastes is thrown out in the form of fly ash, metallic ash, chemical residues, etc. which gets settled on the surface of soil, thus pollutes it.
➢ Urban and domestic wastes : Solid wastes is also produce from homes, shops, restaurants, etc. These include plastic bottles, polythene bags, bulbs, kitchen wastes, etc. which is collected and disposed off by municipal workers into nearby areas rather than disposing it properly to avoid pollution.
➢ Biomedical wastes : Wastes produced by hospitals, clinics, laboratories, etc are also one of the major cause of soil pollution. Numerous items such as syringes, needles, unused and discarded tablets, research material, wound dressings, etc are discarded and disposed off carelessly in the municipal garbage, due to which soil gets polluted.
➢ Chemical fertilizers : Chemical fertilizers that are used for increasing crop yield are proved to be harmful in excess amount.
➢ Pesticides such as DDT which are used to kill pests and other insects in agricultural farms and fields, also act as major pollutants responsible for soil production.
➢ Noise pollution is defined as unwanted sound of generally 80 db or more, which is unpleasant and which affects the receiver directly is called noise pollution.
➢ Major sources of noise pollution includes high intensity sound produced by trains, heavy machines, jet crafts, automobiles, loudspeakers at road side and in residential areas.
➢ Noise pollution has harmful effects on human beings such as it interferes in communication, lowers the efficiency of work, disturb sleep thus leading to nervous irritability and sometimes damage ear drums.
➢ Noise pollution can be minimized by following methods –
➢ Misuse of loudspeakers should be checked.
➢ Good quality silencer should be used in automobiles.
➢ Growing a green belt area around residential area.
➢ Radiation is the form of energy which consists of high energy particles such as photons, X-rays, etc. Radiations are used in laboratory equipments in the field of medicines and other researches. Sources of radiations are mainly X-rays and radioactive rays released from nuclear power plants. X-rays contain a huge amount of energy particles which may damage the body cells.
➢ Nuclear radiations leaked out of nuclear power plants are also major cause of radioactive pollution. The chief radioactive pollutant during explosion in Japan and Chernobyl was Iodine-131, which was responsible for haemorrhaging and even cancers. It also raises the risk of thyroid cancer. Thus, radioactive material should be discarded and dispose off carefully, so as to avoid the serious damage, to environment and mankind.
TOPIC-2
Effects of Pollution
Quick Review
• Pollution affects the life of organisms thereby, influencing the whole environment and climate ultimately.
• Effects of pollution on human beings and other organisms is described below :
•Effect of Air Pollution :
• Lead damages of kidney, liver, brain, muscles, reproductive system etc.
• Hydrocarbons cause eye irritation, coughing, sneezing. Benzene causes leukemia.
• Carbon monoxide binds with haemoglobin and causes (CO) poisoning, headache, nausea, muscular weakness etc.
• N2O, NO2 causes eye irritation, blood congestion, lungs swelling etc.
• PAN (Peroxy Acetyl Nitrate) causes eye irritation and respiratory problems.
•Effects of Water Pollution :
• Pollution of water may cause many water born diseases such as typhoid, dysentery, etc.
• Aquatic animals and sea birds may be killed due to oil spills.
• Discharge of excessive nutrients through sewage into the static water leads to death of aquatic life. The organic matter increases growth of algae that consumes a lot of O2. This decreases the O2 content causing problem for water organisms. This phenomena is known as eutrophication.
•Effects of Soil Pollution :
• Soil pollution may lead to loss of soil fertility.
• Accumulation of pesticides in increasing concentration in the body of living beings through food chain results in biomagnification or biological magnification.
• Non-target organisms are killed in the soil.
• Effects of Radiations :
• Radiation may cause cancer and mutation in reproductive cells.
• Overdoses of radiation may be lethal and may even cause death.
• Effects of Pollution on Climate and Environment
• Pollution may adversely affect the climate and environment in many ways.
The three major ways are as follows :
1. Acid Rain : Acid rain is rainfall and other form of precipitation pH less than 5. It consists of acidic gases like sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, volatile organic carbons and hydrogen chlorides. Acid rain is harmful to the environment in many ways as follows :
• It damages plants by direct effect on foliage and growing points. Chlorosis, necrosis, defoliation and die back.
• It causes leaching of essential minerals of soil and toxic mineral left will kill the plants. 50% natural forests have been destroyed by acid rain in Germany, Sweden, Poland etc.
• Acid in the rain reacts with the calcium of statues, sculpture and ancient monuments and damage them.
• Fine particles of sulphates and nitrates are also harmful for humans.
2. Green House Effect and Global Warming – The world is experiencing green house effect or rise in atmospheric temperature due to increase in concentration of green house gases. Concentration of CO2 has increased from 280 ppm in 1800 to 360 ppm in 2000. If the trends continues, CO2 concentration is likely to double in the next few years as the rate of fossil fuel consumption is rising by 6% annually.
• Global warming is the phenomenon of gradual increase in the average temperature of the surface of the earth. This occurs due to the following reasons –
• Release of more CO2 due to burning of fossil fuels.
• Less utilization of CO2 in photosynthesis due to decreases in vegetation cover by deforestation.
• Effects of global warming
• melting of glaciers and ice caps.
• rise of water levels in oceans.
• submerge of several islands.
• developing different rain pattern.
3. Ozone Layer Depletion : Ozone is a triatomic molecule (O3) of oxygen found in the upper atmosphere. In the stratosphere, it helps in absorbing harmful UV radiations coming from the sun. The absorption of UV radiations is directly proportional to thickness of ozone shield. The O3 shield is thin near equator, therefore in this region maximum UV radiations reach earth. Global average O3 layer thickness is declining, because of escape of CFCs, CH4 and N2O into stratosphere which damage O3 layer. Ozone depletion is particularly marked over the Antarctic region. This led to formation of a large area of thinned ozone layer, called as Ozone hole. A 5% loss of O3 shield results in increase of 10% UV radiations which reach the earth.
These have following effects on human beings :
• of the steps that we should follow to control or to remove pollution are as follow :
• Diesel buses should be replaced by CNG buses.
• Use of unleaded petrol in cars and two wheelers.
• The plants which can fix carbon monoxide should be grown.
• By switching off the engines of the vehicles at traffic signals, when it is not in use.
• Organic wastes should be composed to produce bio-gas.
• Recycling of paper, plastic, metal and glass is the effective measure to control soil pollution.
• Use of pesticides should be checked.
• Electrostatic precipitators and filters should be used in chimneys to lessen industrial pollution.
• Control of Air Pollution (Vehicular Standards)
Euro/Bharat Stage
According to this standard, all transport vehicles carry a fitness certificate that is renewed each year after the first two years of new vehicle’s registration. On Oct. 6, 2003 the National Auto Fuel Policy has been announced for introducing Euro 2-4 emission and fuel regulations. Accordingly a standard that is Bharat Stage III Euro 3 for nationwide is envisaged.
Pollution is the addition of any substance in the environment which contributes to the deterioration or contamination of the environment, making it less favourable for organisms.
A pollutant is any substance which causes pollution.
Nature of Pollutants

Types of Pollution
Air Pollution
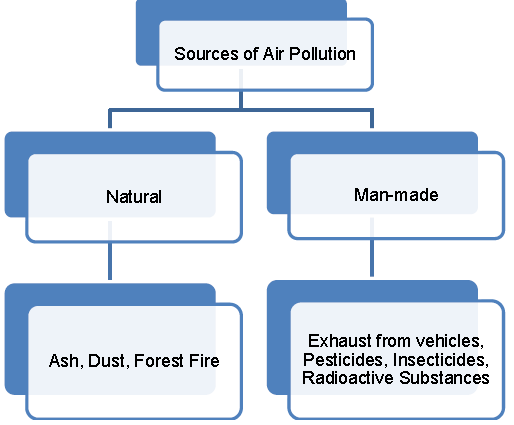
Types of Air Pollution

Some Major Gaseous Pollutants
1. Carbon Monoxide (CO)
• Sources: Exhaust from vehicles and burning of farm wastes, dry leaves and domestic and industrial wastes.
• Harmful Effects:
➢ It combines with haemoglobin and forms an irreversible product carboxyhaemolglobin. Thus, oxygen is prevented from circulating in the blood.
➢ This creates problems such as headache, nausea and anaemia. Continuous presence of CO inside the body may cause death.
2. Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2)
• Sources: Lightning and high temperature in the combustion chamber of automobile engines.
• Harmful Effects:
➢ Presence of NO2 in the air causes irritation of eyes.
➢ Causes acid rain.
3. Sulphur Dioxide (SO2) and Sulphur Trioxide (SO3)
• Sources: Fossil fuels and heating sulphide ores in excess air.
• Harmful Effects:
➢ Form smog.
➢ High concentrations cause severe lung ailments and even death.
4. Hydrogen Sulphide (H2S)
• Sources: Burning of coal, petrol refineries, volcano eruptions
• Harmful Effects:
➢ Causes nausea, sore throat and irritation of the eyes.
Effects of Air Pollution

Under the Euro/Bharat title, certain norms have been laid down on the emission levels given out by all automobiles.
Water Pollution
Water pollution is any change in the water quality which makes it unsuitable for use by humans and by other living organisms.
Source of Water Pollution
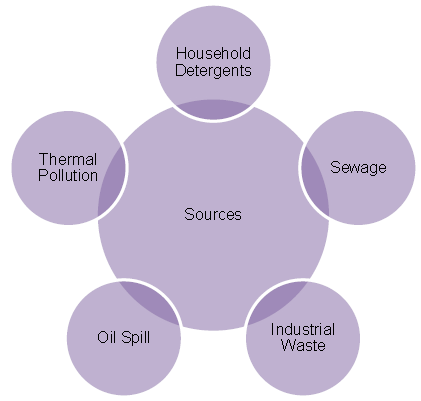
Effects of Water Pollution
• Brain and nerve damage due to industrial effluents.
• Water borne diseases such as cholera, dysentery, jaundice etc.
• Insects breeding in stagnant water result in malaria, dengue, fever and yellow fever.
• Intestinal parasitism leading to anaemia and weakness.
• Nitrates and phosphates help plants to grow. However, if these nutrients accumulate in water, algae use them as a source of food and multiply rapidly. The lake soon becomes choked by a green slimy mass of green algae. This process is called eutrophication.
• The process by which the harmful and toxic substances enter the food chain and get concentrated in the body of living organisms at each successive trophic level is called biomagnification.
Soil Pollution
The contamination of soil by pollutants which reduces its productivity is called soil pollution.
Sources of Soil Pollution
When soil loses its plant cover, it becomes exposed to wind and rain. It gets blown or washed away rapidly. This condition is known as soil erosion
Effects of Soil Pollution
• Soil pollution mainly lowers soil fertility.
• Fertilisers and pesticides used may enter the food chain which can cause tremendous harm to the organisms of each trophic level.
Radioactive Pollution
Radiation is a form of energy consisting of high-energy particles.
Sources of Radioactive Pollution
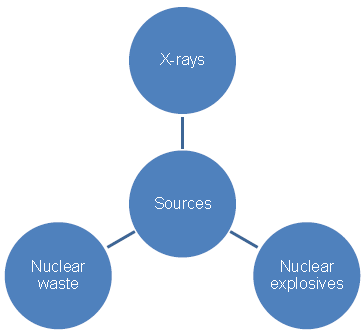
Types of Radiations
• Alpha Radiation (α): Penetrates the surface of the skin.
• Beta Radiation (β): Usually emitted during nuclear tests. Bears more penetrating strength than α-radiations.
• Gamma Radiation (γ): Used in the treatment of cancer. The penetrating power is the strongest
Effects of Radioactive Pollution
Radioactive rays are harmful to living organisms.
• Destroy living tissues and blood cells.
• Affect the functioning of the cell membrane and cell enzymes.
• Bring about gene mutation.
• May cause cancer such as leukaemia.
• Can cause deformities in the foetus.
Noise Pollution
Noise is any disturbing sound.
Sources of Noise Pollution
• Industrial machines
• Workshops
• Trains and automobiles
• Jet aircrafts
• Loud conversation
• Sounds of radio and television
• Loudspeakers
• Firecrackers
Effects of Noise Pollution
• Prolonged exposure to high-decibel noise damages the ear and brings about permanent hearing impairment.
• Noise pollution can lead to high blood pressure (hypertension), constant headache and lack of concentration.
• It interrupts the thought process, resulting in low efficiency at work.
• It disturbs sleep which causes irritability and nervous disorders.
Measures to Minimise Noise Pollution
• Prohibiting the blowing of horns.
• Use of loud speakers should be banned.
• Airports should be located away from residential areas.
• People should restrain themselves from lighting firecrackers.
Abatement of Pollution
• Use of unleaded petrol and CNG in automobiles.
• Installation of tall chimneys in factories. Tall chimneys must have filters and electrostatic precipitators.
• Treating industrial effluents before discharging them into water bodies.
• Recycling of plastic, glass and metal materials and incineration of non-recyclable materials.
• Planting trees along roadsides and on mountain slopes to reduce soil erosion.
Vehicular Standards
• Introduced in 2000, the Bharat norms are emission control standards that are based on the European regulations (Euro norms).
• It has been upgraded to BS II, BS III and now BS IV norms.
• They set limits for release of air pollutants from equipment using internal combustion engines, including vehicles.
• The Supreme Court recently ordered that only vehicles with engines compliant with BS IV standards must be sold from April 1, 2017.
Clean India Movement
• Swachh Bharat Abhiyan is a Swachh Bharat mission led by the government of India to make India a clean India. This campaign was launched officially by the government of India on 145th birthday anniversary of the great person, Mahatma Gandhi on 2nd of October, 2014.
• The mission has targeted aims like eliminating the open defecation, converting insanitary toilets into pour flush toilets, eradicating manual scavenging, complete disposal and reuse of solid and liquid wastes, etc.



