Students of ICSE Class 10 should refer to Organic Chemistry ICSE Class 10 Chemistry board year questions and solutions. below which have come in past board exams. You should always go through questions that have come in previous years. This will help you to understand the pattern of questions in ICSE Class 10 Chemistry and prepare accordingly. This will help you to get better marks in ICSE Class 10 Board Exams
ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Organic Chemistry Board Exam Questions
Students should learn the important questions and answers given below for Chapter Organic Chemistry in Chemistry for ICSE Class 10. These board questions are expected to come in the upcoming exams. Students of ICSE Class 10th should go through the below board exams questions and answers which will help them to get more marks in exams.
Board Exam Questions Organic Chemistry ICSE Class 10 Chemistry
(a) The alkanes form an (1) ………………… series with the general formula (2) ………………….. . The alkanes are (3) …………………….. (4) ………………… which generally undergo (5) ……………………… reactions.
Answer
1. homologous
2. CnH2n+2
3. saturated
4. hydrocarbons
5. substitution
(b) Question. ……………… was the first organic compound prepared in laboratory.
Answer
Urea
Question. Organic compounds are generally insoluble in ………………… .
Answer
water
Question. The compounds of carbon and hydrogen are called ………….. .
Answer
hydrocarbons
Question. The hydrocarbon containing only single bonds are known as ………….. .
Answer
alkanes
Question. Alkanes are ………….. hydrocarbons.
Answer
saturated
Question. Alkanes are open-chain hydrocarbons in which the carbon atoms are joined by …………………… only.
Answer
single covalent bonds
Question. The four C—H bonds in the methane molecule are directed towards the corners of a regular …………………. .
Answer
tetrahedron
Question. Methane can be prepared by heating ………………… with solid ………………….. .
Answer
sodium acetate, sodium hydroxide
Question. When methane reacts with excess of chlorine, the product obtained is ………………. of the molecular formula …………….. .
Answer
carbon tetrachloride, CCl4
Question. Ethane is an …………………………………..
Answer
alkane
Question. Ethene reacts with chlorine to give…………… products.
Answer
substitution
Question. …………………………..does not react with hydrogen.
Answer
Ethane
Question. When methane is heated to a high temperature in the absence of oxygen, it yields …………….. and ……………. . This reaction is known as ………………. or ………………… .
Answer
carbon, hydrogen, pyrolysis, cracking
Question. The general formula CnH2n represents ………….. .
Answer
alkene
Question. Ethene is prepared by the …………… of ethyl alcohol by heating it with ……………….. .
Answer
dehydration, concentrated sulphuric acid
Question. Ethene reacts with chlorine to give …………………… the molecular formula of which is ………………………… .
Answer
ethene dichloride, CH2Cl2
Question. …………… has two carbon atoms joined by a triple covalent bond.
Answer
Ethyne
Question. Ethene and ethyne are……………….. hydrocarbons.
Answer
unsaturated
Question. …………… reacts with bromine to give two different addition products.
Answer
Ethyne
Question. Ethyne is prepared by the action of …………………….. on …………………. .
Answer
water, calcium carbide
Question. When ethyne is hydrogenated, the first product is ………………….. and the final product is …………………… .
Answer
ethene, ethane
Question. The conversion of ethene to ethane is an example of ……………………..
Answer
hydrogenation
Question. The catalyst used in the conversion of ethene to ethane is commonly ………………….
Answer
nickel
Question. The product formed when ethene gas reacts with water in the presence of sulphuric acid is…………
Answer
ethanol
Question. The product of the dehydration of ethyl alcohol is …………………….. .
Answer
ethene
Question. The conversion of ethanol to ethene is an example of …………………. .
Answer
dehydration
Question. Converting ethanol to ethene requires the use of ……………………….. .
Answer
concentrated sulphuric acid
Question. ………………….. is commonly called as wood spirit.
Answer
Methyl alcohol or methanol
Question. When acetaldehyde is oxidized with acidified potassium dichromate, it forms……
Answer
acetic acid
Question. Ethanoic acid reacts with ethanol in presence of concentrated H2SO4, so as to form a compound and water. The chemical reaction which takes place is called………
Answer
esterification
Question. The ability of carbon atom to link with other carbon atom is known as ………….. .
Answer
catenation
Question. Compounds represented by a single molecular formula but having different structural formulae are called ………….. and this phenomenon is known as …………. .
Answer
isomers, isomerism
Question. The name of the compound CH2Cl2 is …………………………. .
Answer
dichloromethane
Question. The compound formed when ethene reacts with hydrogen is………….
Answer
Ethane
Question. Conversion of ethene to ethane is an example of…
Answer
hydrogenation
Multiple Choice Questions
Question. The property of carbon of form chains and rings is called :
(a) Catenation
(b) Polymerisation
(c) Cracking
(d) Hydrogenation
Answer
A
Question. Two neighbours of a homologous series differ by :
(a) CH
(b) CH2
(c) CH3
(d) CH4
Answer
B
Question. Heating sodium acetate with soda lime produces :
(a) Methane
(b) Ethane
(c) Ethene
(d) Ethyne
Answer
A
Question. The number of C–H bonds in ethane molecule are :
(a) Four
(b) Six
(c) Eight
(d) Ten
Answer
B
Question. Halogenation of alkane can be carried out in :
(a) Dark
(b) Bright light
(c) UV light
(d) Diffused sunlight
Answer
D
Question. The unsaturated hydrocarbons undergo :
(a) a substitution reaction
(b) an oxidation reaction
(c) an addition reaction
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question. An organic compound undergoes addition reactions and gives a red colour precipitate with ammoniacal cuprous chloride. Therefore, the organic compound could be
(a) Ethane
(b) Ethene
(c) Ethyne
(d) Ethanol
Answer
C
Question. The I.U.P.A.C. name of acetylene is :
(a) Propane
(b) Propyne
(c) Ethene
(d) Ethyne
Answer
D
Question. Acetylene polymerises into benzene by joining :
(a) 3 molecules
(b) 2 molecules
(c) 4 molecules
(d) 6 molecules
Answer
A
Question. The organic compound mixed with ethanol to make it spurious is :
(a) Methanol
(b) Methanoic acid
(c) Methanal
(d) Ethanoic acid
Answer
A
Question. Dehydrohalogenation of X with alcoholic KOH produces ethene. X is :
(a) Ethyl chloride
(b) Methyl chloride
(c) Ethylene dichloride
(d) None
Answer
A
Question. The functional group present in acetic acid is :
(a) Ketonic C = O
(b) Hydroxyl —OH
(c) Aldehydic —CHO
(d) Carboxyl —COOH
Answer
D
Question. The resulting ester, when ethyl alcohol and acetic acid are mixed together :
(a) CH3COOCH3
(b) C2H5COOC2H5
(c) CH3COOC2H5
(d) C2H5COOCH3
Answer
C
Question. An acid used for removing ink stains :
(a) Acetic acid
(b) Oxalic acid
(c) Malic acid
(d) Formic acid
Answer
B
Question. Which compound is used as an antifreeze agent :
(a) Propene
(b) Acetylene
(c) Ethylene glycol
(d) Methanol
Answer
C
Question. Identify the statement which does not describe the property of alkenes :
(a) They are unsaturated hydrocarbons
(b) They decolourise bromine water
(c) They can undergo addition as well as substitution reactions
(d) They undergo combustion with oxygen forming carbon dioxide and water
Answer
C
Question. If the molecular formula of an organic compound is C10H18 it is :
(a) Alkene
(b) Alkane
(c) Alkyne
(d) Not a hydrocarbon
Answer
C
Give One Word/Chemical Term
Question. Name the organic compound which was first synthesized.
Answer
Urea
Question. A simplest hydrocarbon.
Answer
Methane
Question. The shape of methane molecule.
Answer
Tetrahedral
Question. An organic compound whose functional group is carboxyl.
Answer
Acetic acid
Question. The compound with –OH as the part of its structure.
Answer
Ethanol
Question. The compound with –COOH as the part of its structure.
Answer
Ethanoic acid
Question. The compounds having same molecular formula but different structural formula.
Answer
Isomer
Question. Homologue of homologous series with general formula CnH2n.
Answer
Ethene
Question. The next higher homologue of methyl alcohol.
Answer
Ethyl alcohol, C2H5OH
Question. The type of reactions alkenes undergo.
Answer
Addition reaction
Question. The type of reactions alkanes undergo.
Answer
Substitution reaction
Question. The hydrocarbon which contributes towards greenhouse effect.
Answer
Methane
Question. A reaction in which hydrogen of an alkane is replaced by a halogen.
Answer
A substitution reaction—halogenation
Question. Process by which ethene is obtained from ethanol.
Answer
Dehydration
Question. A hydrocarbon which on catalytic hydrogenation gives a saturated hydrocarbon.
Answer
Ethene
Question. The catalyst used during hydrogenation of alkene.
Answer
Nickel
Question. A white solid which on treatment with water liberate acetylene.
Answer
Calcium carbide
Question. The chemical name of the gas, which evolves in the marshy lands in the form of bubbles.
Answer
Methane gas
Question. The solution which detects the presence of unsaturation in the given hydrocarbon.
Answer
Bromine solution in carbon tetrachloride or Alkaline potassium permanganate
Question. An organic compound used as a thermometric liquid.
Answer
Ethanol
Question. Hydrocarbon, which increases the rate of fruit ripening.
Answer
Ethene
Question. A compound which is used in making denatured spirit.
Answer
Methyl alcohol
Question. A gas which forms explosive mixture with air.
Answer
Acetylene
Question. A solution used for storing biological specimens.
Answer
Formalin
Question. An unsaturated hydrocarbon used for welding purposes.
Answer
Ethyne
Question. Process by which ethane is obtained from ethene.
Answer
Hydrogenation
Question. A hydrocarbon which contributes towards the greenhouse effect.
Answer
Methane (CH4)
Question. Distinctive reaction that takes place when ethanol is treated with acetic acid.
Answer
Esterification
Question. The property of elements by virtue of which atoms of the element can link to each other in the form of a long chain or ring structure.
Answer
Catenation
Question. Reaction when an alkyl halide is treated with alcoholic potassium hydroxide.
Answer
Nickel or platinum
Question. The catalyst used in the conversion of ethyne to ethane.
Answer
Dehydrohalogenation
State the Observation
Question. Methane gas is burnt in air.
Answer
Methane gas burns in air with a blue flame and produces carbon dioxide and water. A large amount of heat energy is liberated during the reaction.
Question. A mixture of sodium acetate and soda lime is heated.
Answer
When a mixture of sodium acetate and soda lime is heated, colourless and odourless methane gas is liberated.
Question. When a mixture of acetylene with twice its volume of hydrogen is passed over nickel as catalyst at about 200°C.
Answer
When mixture of acetylene and hydrogen is heated at 200°C temperature, ethane is formed.

Question. Ethylene is heated at 400°C under very high pressure in traces of oxygen.
Answer
When ethylene is heated at 400°C under very high pressure in traces of oxygen, it polymerises to form polyethylene or polyethene

Question. A mixture of ethylene and hydrogen is passed over nickel at 150°C.
Answer
When a mixture of ethylene and hydrogen is passed over nickel at 150°C it forms ethane.

Question. Ethylene combines with hydrogen chloride.
Answer
Ethylene (unsaturated) combines with hydrogen chloride and results in the formation of an addition product chloroethane.

Question. Ethylene reacts with chlorine.
Answer
When ethylene is treated with chlorine, it combines and results in the formation of saturated 1, 2-dichloro ethane.

Question. Ethene is oxidized with alkaline KMnO4 solution.
Answer
Ethene gets oxidized with KMnO4 and produce glycol.

Question. Ethene is burnt in excess of oxygen.
Answer
A large amount of heat liberated with sooty flame is produced when, ethene is burnt in excess of oxygen.
H2C = CH2 + 3O2 ⎯→ 2CO2 + 2H2O + Heat
Question. Ethene reacts with bromine.
Answer
When ethene reacts with bromine, addition reaction takes place. A molecule of bromine is added to the molecule of ethene forming dibromoethane. The almond colour of bromine is discharged.
Question. Ethene is bubbled through a solution of bromine in tetrachloromethane (carbon tetrachloride).
Answer
Colour of bromine gets decolourised.
Question. Calcium carbide is boiled with water.
Answer
Calcium carbide is boiled with water to form acetylene and calcium hydroxide.
CaC2 + H2O ⎯→ CH ≡ CH + Ca(OH)2
Acetylene
Question. Acetylene is oxidized with alkaline KMnO4 solution.
Answer
Acetylene gets oxidized with alkaline KMnO4 solution to produce oxalic acid.

Question. Ethyne is bubbled through a solution of bromine in carbon tetrachloride.
Answer
Brown colour of bromine disappears due to the formation of ethylene tetrachloride
Question. Ethyl alcohol is heated at 300°C temperature, in presence of copper catalyst.
Answer
Ethyl alcohol is heated at 300°C temp. in presence of copper catalyst to form acetaldehyde.

Question. Ethanol is burnt in air.
Answer
Ethanol burns in air with a blue flame, producing carbon dioxide and water. During the reaction, large amount of heat energy is liberated.
Question. Acetic acid and ethyl alcohol react in the presence of sulphuric acid.
Answer
When acetic acid and ethyl alcohol react in the presence of sulphuric acid, esterification process takes place and ethyl acetate is formed.
Question. Sodium propionate is heated with soda lime.
Answer
Ethane is prepared by heating a dry mixture of sodium propionate and soda-lime.
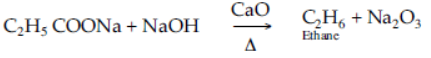
Define/Explain the Following
Catenation
Ans. The property of self-linking of carbon atoms through covalent bonds to form long, straight or branched chain and rings of different sizes is called catenation.
Hydrocarbons
Ans. Hydrocarbons are the compounds made up of only carbon and hydrogen e.g., CH4, C2H5.
Functional group
Ans. An atom of compounds of the same family in which each member differ from its adjacent.
Isomerism
Ans. Compounds having the same molecular formula, but different structural formula, are called ‘Isomers’ of one another and this phenomenon is called ‘Isomerism’.
Homologous series
Ans. A series of compounds of the same family in which each member differ from its adjacent member by one CH2 unit, is called homologous series.
Pyrolysis
Ans. The process of decomposition of an organic compound into elements on heating is called pyrolysis.
Fermentation
Ans. The process of slow decomposition of complex organic compounds into similar substances, in presence of enzymes is called fermentation.
Balancing/Writing the Chemical Equations
(a) 1. Monochloro ethane is hydrolysed with aqueous KOH.
Answer

2. A mixture of sodalime and sodium acetate is heated.
Answer

3. Ethanol under high pressure and low temperature is treated with acidified potassium dichromate.
Answer

4. Water is added to calcium carbide.
Answer

5. Ethanol reacts with sodium at room temperature.
Answer

6. Reaction between 1, 2-dibromoethane and alcoholic potassium hydroxide.
Answer

7. Preparation of ethane from sodium propionate.
Answer

8. Preparation of ethanol from monochloroethane and aq. sodium hydroxide.
Answer

9. A saturated hydrocarbon from iodomethane.
Answer

10. An unsaturated hydrocarbon from an alcohol.
Answer

11. An unsaturated hydrocarbon from calcium carbide.
Answer

12. An alcohol from ethyl bromide.
Answer

13. Reaction between ethyl alcohol and acetic acid.
Answer

14. Reaction of chlorine with excess of methane.
Answer

15. Addition of chlorine to ethene at ordinary temperature.
Answer

16. Burning of ethanol in air.
Answer

17. Preparation of ethane from sodium propionate.
Answer

18. Preparation of ethene from iodoethane.
Answer

IUPAC Naming/Writing the Structural Formula
Give the formula of the next higher homologue of :
| 1. Methanol | → | Ethanol — C2H5OH |
| 2. Ethane | → | Propane — C3H8 |
| 3. Ethene | → | Propene — C3H6 |
| 4. Ethyne | → | Propyne — C3H4 |
| 5. Propyl | → | Butyl — C4H9 |
| 6. Methanoic acid | → | Ethanoic acid — CH3COOH |
| 7. Propane | → | Butane — C4H10 |
| 8. Butene | → | Pentene — C5H10 |
| 9. Pentane | → | Hexane — C6H14 |
| 10. Methanal | → | Ethanal — CH3CHO |
Chemical Tests
1. Ethene and ethane.
Answer
Ethene gas decolourises bromine solution and potassium permanganate solution. But, ethane gas does not change the colour of these solutions.
2. Ethyne and ethane.
Answer
Ethyne gas forms a white precipitate with ammonical solution of silver nitrate and red ppt. with ammonical solution of copper(I) chloride. But, ethane does not respond to such tests.
3. Alkanes, alkenes and alkynes.
Answer

Reasoning Based Questions
Q. 1. Hydrocarbons are excellent fuels. Give reason.
Answer
Hydrocarbons are excellent fuels because they ignite easily at low temperature and liberate large amount of heat without producing harmful products.
Q. 2. Why alkanes are so inert ?
Answer
It is because in a molecule, a reactive site has one or more unshared pairs of electrons and a polar bond or an electron deficient atom. Alkanes have none of these, that is why they are so inert.
Q. 3. Why alkanes are insoluble in water ?
Answer
Alkanes are insoluble in water because alkanes are called hydrophobic hydrocarbons. They have phobia for water. These are insoluble because these cannot make hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
Q. 4. Methane is called as marsh gas. Why ?
Answer
Methane is called as marsh gas because methane is formed by the decomposition of plant and animal matter lying under water in marshy areas.
Q. 5. Methane does not undergo addition reactions, but ethene does. Why ?
Answer
Methane does not undergo addition reactions, but ethene does because methane is saturated hydrocarbon while ethene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon. Addition reactions are characteristic properties of unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Q. 6. Why it is dangerous to burn methane in an insufficient supply of air ?
Answer
It is dangerous to burn methane in an insufficient supply of air because it will form carbon monoxide which is poisonous for human beings as it cuts off the oxygen supply by forming carboxy haemoglobin in the blood.
Q. 7. Why light or heat is necessary for chlorination of alkanes ?
Answer
The Cl–Cl bond must be broken to form Cl radicals, before the chlorination of alkanes can commence. The breaking of bond requires energy which is supplied either by heat or light.
Q. 8. Ethene undergoes addition reactions with halogens whereas ethane undergoes substitution reactions. Why ?
Answer
Ethene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon so, it adds up a molecule of halogen to give a saturated compound, whereas, ethane is a saturated hydrocarbon compound and hence, can only undergo substitution reaction with halogen.
CH2 = CH2 + Cl2 ⎯→ CH2Cl—CH2Cl
Ethene addition product
(Unsaturated) (Saturated)
Q. 9. Alkynes are unsaturated hydrocarbons. Give reason.
Answer
Alkynes have triple bonds, so they are unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Q. 10. Why ethyne is more reactive than ethane ?
Answer
Ethyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon with a triple covalent bond. Ethane is a saturated hydrocarbon and hence is less reactive than ethyne.
Short Answer
Q. 1. The list of some organic compound is given below : Ethanol, ethane, methanol, methane, ethyne, and ethene. From the list above, name a compound :
(i) Formed by the dehydration of ethanol by concentrated sulphuric acid.
(ii) Which will give red precipitate with ammonical cuprous chloride solution.
(iii) Which forms methanoic acid on oxidation in the presence of copper at 200°C.
(iv) Which has vapour density 14 and turns alkaline potassium permanganate green.
(v) Which forms chloroform on halogenation in the presence of sunlight.
(vi) Which decolourises bromine solution in carbon tetrachloride.
Answer
(i) Ethene
(ii) Ethyne
(iii) Methane
(iv) Ethene
(v) Methane
(vi) Ethene
Q. 2. Name the functional group of each of CH3OH, CH3COOH, CH3CHO.
Answer
Alcoholic – OH group present in CH3OH.
Carboxylic – COOH group present in CH3COOH.
Aldehydic – CHO group present in CH3CHO.
Q. 3. The melting point of three members X, Y, and Z of a homologous series of hydrocarbons are –180°C, –140°C and –30°C respectively.
(i) Which one of the three would have the lowest number of carbon atoms in its molecule ? Justify your answer.
(ii) Which one of the three have the maximum number of carbon atoms in its molecule ? Justify your answer.
Answer
(i) The homologue with lower number of C-atoms in its molecule has lower melting point.
Therefore, compound X has the lowest number of carbon atoms in its molecule. It is clear from the given values of melting points in which – 180°C is lowest.
(ii) The homologue with maximum number of carbon atoms in its molecule has the highest melting point. Therefore, compound Z has the maximum number of carbon atoms in its molecules. It is clear from the given values of melting point in which 30°C is the highest of the three.
Q. 4. (i) Alkanes are called saturated hydrocarbons. Give a brief explanation, by taking the example of C2H6.
(ii) ‘Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons’. Illustrate it, by taking the example of ethene (C2H4).
(iii) A compound has number of H atoms just double that of C atoms. What types of hydrocarbon is it ?
Answer
(i) Alkane are called saturated hydrocarbons because tetra-valency of each carbon atom is satisfied by single covalent bond.

(ii) Ethene (C2H4) is an unsaturated hydrocarbon, commonly known as alkene. Ethene molecule contains two carbon atoms bonded by double bond.

Q. 5. (i) In the general formula CnH2n + 2, write the meaning of n and 2n + 2.
(ii) Write the formulae and names of the first four members of the alkane family.
(iii) Write the molecular formula of an alkane, which is composed of 16H atoms.
(iv) In a molecule of saturated hydrocarbon the number of C-atoms is 5, what is the number of H-atoms ?
Answer
(i) The number of alkane family represents the general formula CnH2n + 2. In this formula : n = number of carbon atoms in the same molecule of alkane.
2n + 2 = number of H-atoms in a molecule of alkane.
(ii) CH4 (methane), C2H6 (ethane), C3H8 (propane), C4H10 (butane).
(iii) C7H16 (Heptane). [·.· 2n + 2 = 16, 2n = 16 – 2, 2n = 14, n = 14/2 = 7].
(iv) According to general formula C4H2n + 2 when n = 5, C5H2 × 5 + 2 or C5H10+2 or C5H12.
Thus, the number of hydrogen atom is 12.
Q. 6. The molecules of alkene family are represented by a general formula CnH2n. Now answer the following :
(i) What do n and 2n signify ?
(ii) What is the lowest value which can be assigned to n ?
(iii) What is the molecular formula of alkene, when n = 4 ?
(iv) What is the structural formula of the first member of the alkene family ?
Answer
(i) n = Number of C-atoms in a molecule of alkene.
2n = Number of H-atoms in a molecule of alkene.
(ii) The lowest value of n is 2.
(iii) Butene (C4H8)
Q. 10. Indicate the type of reaction that occurs when :
(i) Ethane reacts with chlorine.
(ii) Ethene reacts with chlorine.
(iii) What type of reaction is common in C2H4 and C2H2 ?
(iv) What is formed when ethene reacts with steam at 300°C in the presence of phosphoric acid as catalyst ?
(v) Name a solid which on reaction with water forms :
(a) methane (b) ethyne (acetylene)
(vi) Give the names of each of the following compounds :
(a) CH3CH2CH2CH3
(b) CH2 = CH2
(c) CH ≡ CH
Answer
(i) Substitution reaction
(ii) Addition reaction
(iii) Addition reaction
(iv) Ethanol
(v) (a) Aluminium carbide, (b) Calcium carbide.
(vi) (a) Butane, (b) Ethylene (Ethene), (c) Acetylene (Ethyne).
Q. 11. (i) Experimentally, how can polychlorination of methane be minimized ?
(ii) What are the conditions required for the addition of hydrogen to ethene ?
(iii) Which catalyst is used for the addition of hydrogen to ethene at room temperature ?
(iv) Write the names of all the possible organic products in the reaction of methane with chlorine.
Answer
(i) If excess of methane over chlorine is used, the chance of chlorine reacting with methane is greatest than with any other of the formed chloromethane.
(ii) Addition of hydrogen to ethene occurs at 300°C in the presence of nickel (Ni) catalyst.
(iii) Palladium (Pd) or Platinum (Pt) are used as catalyst at room temperature for the addition of hydrogen.
(iv) The main products is methyl chloride (CH3Cl), (CH2Cl2) dichloro methane; (CHCl3)
trichloro methane, (CCl4) and tetra chloromethane.
Q. 14. (i) The alkenes having how many carbon atoms are in liquid state at normal temperature ?
(ii) The alkenes having how many carbon atoms are in solid state at normal temperature ?
Answer
(i) The alkenes having six to seventeen carbon atoms are in liquid state at normal temperature.
(ii) The alkenes having eighteen or more carbon atoms are in solid state at normal temperature.
Q. 19. (i) What word is used to describe these three compounds taken together ?
(ii) What is the special feature of the structure of :
(a) C2H4 (b) C2H2
(iii) What type of reaction is common in both of these compounds ?
(iv) How is acetylene filled in commercial gas cylinders ?
Answer
(i) Organic compounds .
(ii) (a) C2H4 contains a double bond between two carbon atoms.
(b) C2H2 contains a triple bond between two carbon atoms.
(iii) Addition reaction.
(iv) The commercial gas cylinders of acetylene contain a solution of acetylene in acetone. The cylinder contains a porous material into which the acetone and acetylene are absorbed.
The pressure in a freshly filled cylinder of acetylene is about 15 atmosphere.



