Students should refer to Photosynthesis ICSE Class 10 Biology Board Exam Questions provided below with solutions. These will help the students to understand the type of questions which have been asked in previous year examinations and the type of solutions which the student should give to get good marks. You should also refer to ICSE Class 10 Biology Sample papers for more practice
ICSE Class 10 Biology Photosynthesis Important Questions
Students should learn the important questions and answers given below for Chapter Photosynthesis in Biology for ICSE Class 10. These board questions are expected to come in the upcoming exams. Students of ICSE Class 10th should go through the Important questions and answers ICSE Class 10 Biology which will help them to get more marks in exams.
Photosynthesis Unit of Life ICSE Class 10 Biology Board Exam Questions
Photosynthesis ICSE Class 10 Biology
Question. a. Explain the ‘law of limiting factors’.
Ans. When a physiological process is controlled by more than one factor than the rate of the process is governed by that factor which is in least amount. For photosynthesis
• light intensity, CO2 concentration and temperatures are the limiting factors.
b. Explain the following graph based on law of limiting factors.

Ans. As the light intensity increases, the rate of photosynthesis increases. But at pt x, even when the light intensity increase, the rate of photosynthesis stabilizes as CO2 becomes a limiting factor. It the conc. of CO2 is increased from 0.02% to 0.05% the rate of photosynthesis again rises.
Question. State any 4 adaptations in a leaf to carry out photosynthesis efficiently.
Ans. A leaf may have the following adaptations –
1. Large and expanded leaf lamina provides a large surface area for maximum exposure and absorption of sunlight.
2. Thin leaves ensure easy penetration of light energy and also reduces the distance between cells facilitating rapid transport.
3. More concentration of chloroplast in palisade layers below the upper epidermis helps to trap more solar energy for the process.
4. Extensive network of veins to ensure rapid transportation of materials in and out of the cells of the leaves.
Question. a. Draw a neat and labeled diagram of the stomatal apparatus as seen during the
(i) day time, (ii) night time
Ans.

b. Explain the mechanism which bring about closure of stomata at night.
Ans. At night, no photosynthesis occurs. The osmotic pressure within the guard cells falls. The cells lose water due to
exosmosis and turn flaccid. As a result the inner walls straighten to close the stomata.
c. Explain the mechanism which brings about the opening of the stomata during the day time.
Ans. • Guard cells contain chloroplast.
• During the daytime guard cells begin photosynthesis and glucose is produced. This increases the osmotic pressure within the guard cells, thus water is drawn in from the adjoining cells due to endosmosis.
• Guard cells become turgid and bulge outwards due to their thin outer walls and stomatal pore opens wide.
Question. How do the following external factors affect the rate of photosynthesis in a plant?
a. Light Intensity b. CO2 Concentration c. Temperature d. Water content in the soil
Ans: a. Photosynthesis increases with light intensity up to a certain limit and then stabilizes as some other factor must have become limiting at this point.
b. As the rate of CO2 concentration increases, the rate of photosynthesis increases as it is a raw material for the process, unless some other factor becomes limiting.
c. With increase in temperature, the rate of photosynthesis rises up to an optimum of 350C after which the rate falls and stops at 400C.
d. Scarcity of water due to reduced absorption from the soil or due to excessive loss through transpiration reduces rate of photosynthesis due to partial closure of stomata.
Question. Adjoining figure is the diagrammatic representation of three dimensional structure of a plant cell organelle. Study the diagram and answer the questions.

a. Name the physiological process taking place is this organelle. Give the overall chemical equation for the reaction.
Ans. Photosynthesis

b. Name the cell organelle.
Ans. Chloroplast
c. State the function of parts marked 1 and 2
Ans. No. Part No. Function
1. Granum 1. site for light reaction
2. Stroma 2. site for dark reaction.
d. Label the parts marked by guidelines.
Ans. 1. Thylakoids
2. Stroma
3. Double membrane
4. Granum (pile of thylakoids)
Question. a. What is the source of the raw materials for the plant ?
Ans. Land plants absorb CO2 from the atmosphere Aquatic plants absorb CO2 that is dissolved in water Land plants absorb H2O from the soil by the roots. Aquatic plants absorb H2O from their surroundings.
b. Name the raw materials for photosynthesis.
Ans. The raw materials are carbon dioxide and water
c. What is the source of O2 liberated during photosynthesis ?
Ans. The source of O2 is water
d. Give the overall chemical equation for photosynthesis
Ans.

Question. At the end of photosynthesis glucose is produced and oxygen is released as a by-product.
a. Why is the plant leaf tested for the presence of starch ?
Ans. As soon as glucose is produced it is converted to insoluble starch and stored temporarily inthe mesophyll cells of the leaf. Therefore the leaf is tested for the presence of starch.
b. What is the result of a starch test if the leaf has photosynthesised ?
Ans. A leaf which has photosynthesised has starch in it. It turns blue black after the starch test is performed on it.
c. Enumerate the steps for starch test.
Ans. i. The leaf is removed from the plant and dipped in boiling water to kill the cells.
ii. The leaf is then boiled in methylated spirit over a water bath to remove the chlorophyll.
iii. The decolorized leaf is dipped in hot water to soften it.
iv. It is put on a white tile and a drop of iodine is put on it.
Question. An experiment was set up as shown in the figure given along side.

a. How will you test this gas ?
Ans. A glowing splinter bursts into flame which shows the presence of oxygen.
b. Name one water plant that can be used for this experiment.
Ans. Hydrilla
c. What happens when a pinch of sodium bicarbonate is added to the water in the beaker.
Ans. The rate of photosynthesis will increase and the rate of bubling also increases.
d. Identify the gas collected.
Ans. Oxygen.
e. What is the aim of the experiment ?
Ans. To show that oxygen is produced during photosynthesis.
Question. Light phase and dark phase are the two stages of photosynthesis.
a. Name the scientist who discovered the reactions of dark reaction.
Ans. Melvin Calvin and Benson discovered the reaction of this phase.
b. Why is the dark reaction called so?
Ans. Dark reaction is called so as it is independent of light energy.
c. Why is it termed light phase of photosynthesis ?
Ans. It is termed the light phase as it is dependent on the light energy. The events of this phase require light energy to take place.
d. What is the site of dark reaction ?
Ans. It is the stroma of chloroplast in the cell
e. State another name for the light phase.
Ans. It is also called the photo-chemical phase
f. What is the site of light reaction ?
Ans. The site of light reaction in the cell is the grana of the chloroplast.
Question. Dark phase is the biosynthetic phase.
a) What is the first stable intermediate compound formed during dark reaction?
Ans. PGA (3 – phosphoglyceric acid) is the first stable intermediate product formed.
b) What is the carbohydrate formed at the end of dark reaction ?
Ans. A simple carbohydrate glucose is formed
c) Does dark reaction occur after the light reaction ?
Ans. No dark reaction does not require light and occurs simultaneously with light reaction
d) What is the source of energy for dark reaction ?
Ans. ATP and NADPH2 formed during light reaction are used up during dark reaction.
e) What is the site of dark reaction ?
Ans. The site of dark reaction is the stroma of chloroplast
Question: Draw a neat and labelled diagram of the chloroplast.

Question. Give biological reasons for each of the following:
a. The grass growing in the shade turns yellow after a few days.
Ans The chloroplast contains a green pigment chlorophyll which imparts green colour to the grass leaves. The formation of new chlorophyll requires light. If the grass is devoid of sunlight new chlorophyll is not formed and the old chlorophyll disintegrates, therefore the grass turns yellow in colour.
b. A tiger owes its existence to green plants.
Ans: Plants are autotrophs and thus the primary producer. They form the base of any food chain

c. Life on this planet is possible due to green plants.
Ans. For life one needs
a) Food b) Oxygen
Green plants during the process of photosynthesis prepare both i.e.
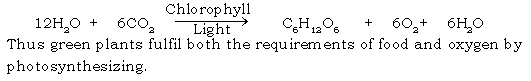
d. Oxygen given out during photosynthesis comes from water.
Ans. During photosynthesis the water molecule splits into its ions.

Question. Shown below is an experimental set up used to perform an experiment to show one of the conditions necessary for Photosynthesis : Study the set up and answer the questions.

a. What will be the result of starch test on a leaf from set up A and set up B ?
Ans. When tested with iodine, leaf of set A show starch test while leaf B of set B will not show starch test since NaOH absorbs all the CO2 and no photosynthesis takes place
b. What is the role of NaOH placed inside the bell jar ?
Ans. NaOH absorbs CO2 and keeps the bell jar free from the CO2.
c. What is the aim of the experiment ?
Ans. To show that CO2 is necessary for photosynthesis
d. What is the role of set up A ?
Ans. Set up A shows all the conditions necessary for photosynthesis and it is a ‘control’.
e. Give a balanced equation for the process of photosynthesis.
Ans.
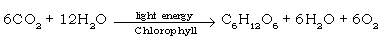
Question. A plant with variegated leaves was kept in the darkness after which it was placed in the sunlight for few hours. One of the leaves was then plucked and an outline of the leaf making the green and non green parts was drawn. It was then tested for starch. Using the above information answer the following questions.
a. What change is seen on the leaf after the starch test ?
Ans. The green area turns blue black due to the presence of starch. The non – green area turns brown due to the absence of starch
b. Name the chemical used for testing the presence of starch.
Ans. Iodine solution.
c. Name a plant with variegated leaves.
Ans. Coleus, Geranium, and Croton.
d. State the aim of the experiment ?
Ans. To show that chlorophyll is necessary for photosynthesis.
e. Why is the leaf boiled in water and alcohol before testing for the presence of starch?
Ans. The leaf is boiled in water and alcohol to remove the chlorophyll pigments.
f. What is the purpose of keeping the leaf in the darkness first ?
Ans. The purpose of keeping the leaf in the darkness first is to de-starch the leaf.
Question. Observe the diagram given below and answer the questions :
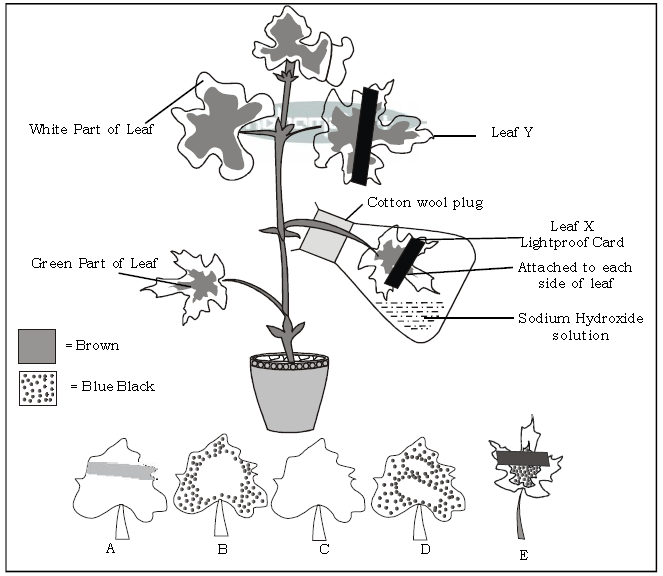
a. What is the function of NaOH in the flask ?
Ans. NaOH absorbs CO2 thereby making the flask CO2 free.
b. Name 2 factors, shown here, on which photosynthesis depends.
Ans. CO2 and sunlight
c. Select the correct leaf shown in the diagram and fill in the blanks:
1. After starch test, leaf X would look like
Ans. Leaf X would like ‘C’
2. After starch test, leaf Y would look like
Ans. Leaf Y would like ‘E’
d. Why was the plant initially kept in the darkness for 24 hrs ?
Ans. The plant is initially kept in the darkness for 24 hrs. to destarch the leaf.
Question. A twig of a plant was kept inside a flask as shown is the diagram and it was kept in sunlight for a few hours.

a. What is the special condition inside the flask ?
Ans. KOH is kept inside the flask to absorb the carbon dioxide.
b. What is the aim of the experiment ?
Ans. To prove that carbon dioxide is necessary for photosynthesis.
c What control would you set up for this experiment ?
Ans. Take another flask and place a leaf in it as shown above, without KOH.
d. What test would you do on the leaf inside the flask ? Give the steps of the test.
Ans. Starch test.
Step I : Dip the the leaf in boiling water for a minute to kill the cells.
Step II : Boil the leaf in methylated spirit to remove chlorophyll.
Step III : Put the leaf in normal water to make it soft.
Step IV : Put iodine solution on the leaf. It turns starch blue black
Question. An experiment was set up to test a certain aspect of photosynthesis. Study the diagram and answer the question.
Ans.
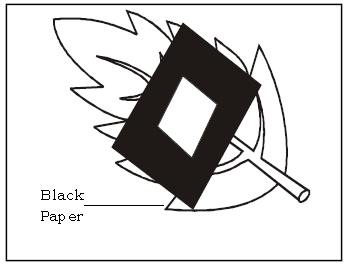
a. What is aim of the experiment?
Ans. To show that sunlight is necessary for photosynthesis
b. Name the solution used to test for starch.
Ans. Iodine solution
c. Why was a part of the leaf covered with black paper?
Ans. A part of the leaf is covered with black paper to prevent the entry of sunlight
Question. Note the relatioship between the first two words and suggest the suitable word / words for the fourth place.
1. Water plant : Hydrilla : : Plant with variegated leaves: __________
Ans.
Coleus / Croton
2. Plants : Autotrophs : : Animals: _________
Ans.
Heterotrophs
3. Haemoglobin : Iron : : Chlorophyll : _________
Ans.
Magnesium
4. Respiration : Oxygen : : Photosynthesis : __________
Ans.
Carbon dioxide
5. Xylem : Transportation of water : : Phloem: _________
Ans.
Translocation of food
6. Catabolism : Respiration : : Anabolism: __________
Ans.
Photosynthesis
7. Light reaction : grana : : Dark reaction : _________
Ans.
Stroma
8. Light phase : Hill reaction : : Dark phase : _________
Ans.
Biosynthetic phase
9. Light phase : Photochemical : : Dark phase : __________
Ans.
Biosynthetic
10. Mitochondrion : Respiration : : Chloroplast: __________
Ans.
Photosynthesis
Question. Choose the most appropriate answer :
1. Light reaction takes place in the __________
a. grana of chloroplast
b. stroma of chloroplast
c. cytoplasm of cell
d. mitochondria
Ans.
grana of chloroplast
2. The first intermediary stable product of photosynthesis is ___________
a. Glucose
b. PGA
c. Ribulose diphosphate
d. Starch
Ans.
PGA
3. The end product of photosynthesis is ___________
a. Glucose
b. Starch
c. cellulose
d. PGA.
Ans.
Glucose
4. The mode of nutrition in green plants is called ___________
a. Heterotrophic
b. Holozoic
c. Autotrophic
d. Saprophytic
Ans.
Autotrophic
5. Mineral needed for synthesis of chlorophyll is __________
a. Iron
b. Calcium
c. sodium
d. Magnesium
Ans.
Magnesium
6. The assimilatory powers for dark reaction are __________
a. ATP and O2
b. ATP and NADPH2
c. ATP and H2O
d. O2 and CO2
Ans.
ATP and NADPH2
7. The rate of photosynthesis in not affected by ___________
a. CO2, concentration
b. light intensity
c. temperature
d. Wind velocity
Ans.
Wind velocity
8. Which of the following pigment is not present in Chlorophyll _________
a. Chlorophyll – a
b. Chlorophyll – a
c. Xanthophyll
d. Haemocyanin
Ans.
Haemocyanin
9 . If the rate of respiration becomes more than rate of photosynthesis, plant will___________
a. continue to live, but will not store food
b. grow more vigorously
c. stop growing and eventually will die
d. be killed instantly.
Ans.
stop growing and eventually will die
10. The raw materials for photosynthesis are __________
a. H2O, CO2 and Solar energy
b. CO2, O2 and Solar energy
c. CO2 starch and Solar energy
d. CO2, O2 and water.
Ans.
H2O, CO2 and Solar energy
11. Events of dark phase were discovered by ___________
a. Hill
b. Watson and Crick
c. Calvin
d. Robert Brown
Ans.
Calvin
12. Number of water molecules needed to produce one molecule of glucose during photosynthesis _________
a. six
b. twelve
c. eighteen
d. four
Ans.
twelve
13. In flowering plants food is transported in the form of __________
a. Starch
b. Glucose
c. Glycogen
d. Cellulose
Ans.
Glucose
14. Starting point of a food chain is always a plant called ___________
a. Consumer
b. Producer
c. Scavengar
d. Herbivore.
Ans.
Producer
15. The function of light energy in photosynthesis is __________
a. Reduce CO2
b. split water molecule
c. synthesise glucose
d. Activate chlorophyll.
Ans.
Activate chlorophyll
16. Which of the following reactions occurs during photosynthesis____________
a. CO2 is reduced and water is oxidised
b. H2O is reduced and CO2 is oxidised
c. Both CO2 and H2O are reduced
d. Both CO2 and H2O are oxidised.
Ans.
CO2 is reduced and water is oxidised
17. A plant which does not have variegated leaves _____________
a. Hydrilla
b. Coleus
c. Geranium
d. Croton
Ans.
Hydrilla
18. An internal factor which affects the rate of photosynthesis __________
a. Light intensity
b. Chlorophyll
c. CO2 concentration
d. Temperature
Ans.
chlorophyll
19. Chemical used to absorb CO2 from inside a flask ____________
a. Calcium chloride
b. Potassium hydroxide
c. Pyrogallic Acid
d. Iodine solution
Ans.
Potassium hydroxide
20. Chlorophyll in the leaf is required for __________
a. Imparting green colour
b. storing starch
c. trapping light energy
d. splitting of water molecule.
Ans.
trapping light energy
Question. Fill in the blanks :
a. ___________ is an important mineral constituent of chlorophyll.
Ans.
Magnesium
b. light of one particular wavelength is called __________ light.
Ans.
monochromatic
c. In regard to photosynthesis _______________ is the source of oxygen.
Ans.
Water
d. Maximum photosynthesis occurs in _____________ light.
Ans.
Red
e. _____________ traps the solar energy of particular wavelength.
Ans.
chlorophyll
f. Starch can be tested with ______________ .
Ans.
Iodine solution
g. In photosynthesis radiant energy is converted to _______________ energy.
Ans.
Chemical
h. KOH solution absorbs __________ .
Ans.
Carbon dioxide
i. Methylated spirit is a solvent for _____________.
Ans.
chlorophyll
j. In photosynthesis _____________ is reduced and ___________ is oxidised.
Ans.
Carbon dioxide, water
k. The tissue that translocates food in plants is ___________ .
Ans.
phloem
l. _____________ is called the energy of particular wavelength.
Ans.
Photon
m. Photolysis of water and phosphorylation take place in __________ .
Ans.
thylakoid of grana
n. _____________ is the most common storage product of plants.
Ans.
Starch
Question. Name the following :
1. Organisms which prepare their own food from basic raw materials. ________
Ans.
Autotroph
2. The light independent phase of photosynthesis. ________
Ans.
Dark phase
3. An enzyme that helps to convert starch to soluble glucose for translocation.________
Ans.
Diastase
4. The plastids which store starch in plants. __________
Ans.
Leucoplast
5. The natural energy source for photosynthesis. _________
Ans.
Sunlight
6. Low light intensity when rate of photosynthesis equals respiration. ________
Ans.
Compensation Point
7. Part of chloroplast where biosynthetic phase occurs. _________
Ans.
Stroma
8. Process by which green plants prepare their own food. _________
Ans.
Photosynthesis
9. Linking of glucose molecules to form a molecule of starch. __________
Ans.
Polymerization
10. The source of oxygen during photosynthesis is a plant. ___________
Ans.
Water
11. The first stable intermediate product of photosynthesis. _________
Ans.
PGA (Phosphoglyceric Acid)
12. Light induced reactions which leads to splitting of water. _________
Ans.
Photolysis
13. A plant with variegated leaves. _________
Ans.
Coleus / Croton
14. The plastids which impart green colours. __________
Ans.
Chloroplast
15. A plant which absorbs CO2 for photosynthesis from medium. _________
Ans.
Hydrilla/Vallisneria
16. The chemical used to test starch. ___________
Ans.
odine solution
17. Scientist who discovered the events of dark phase. _________
Ans.
Calvin
18. Compound which stores energy in the cells. ___________
Ans.
ATP
19. The source of CO2 in terrestrial plants. __________
Ans.
Atmosphere
20. Structure in the woody stem through which CO2 enters. _________
Ans.
Lenticels
Question. State whether the following statements are True of False. Change the false statements by changing the underlined word only.
1. During sunlight guard cells turn flaccid to open the stomata. ________
Ans.
False – Turgid
2. Carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere by combustion. __________
Ans.
True
3. Too much light destroys chlorophyll. _________
Ans.
True
4. Photosynthesis occurs only in cells containing chloroplast. ________
Ans.
True
5. Proton is the smallest unit of light energy. __________
Ans.
False – Photon
6. The dark reaction of photosynthesis is dependent on light. _________
Ans.
False – independent of
7. Dark reaction occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast. __________
Ans.
True
8. Photosynthesis results in loss of dry weight of the plants. ___________
Ans.
False – Gain
9. Carbon dioxide is the source of O2 released during photosynthesis. __________
Ans.
False – Water
10. Photosynthesis is the only biological process that releases O2 to the atmosphere._____
Ans.
True
11. All green plants are categorised as consumers. ____________
Ans.
False – Producers
12. The tissue that transports food from leaves to other parts is xylem. __________
Ans.
False – Phloem
13. Photosynthesis is maximum in green light. _________
Ans.
False – Red
14. Methylated spirit is used to perform starch test. __________
Ans.
Flase – lodine solution
15. Chlorophyll absorbs light at both ends of visible spectrum. __________
Ans.
True







