Students of ICSE Class 10 should refer to Practical Chemistry ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Questions below which have come in past board exams. You should always go through questions that have come in previous years. This will help you to understand the pattern of questions in ICSE Class 10 Chemistry and prepare accordingly. This will help you to get better marks in ICSE Class 10 Board Exams
ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Important Questions Practical Chemistry
Practical Chemistry is an important chapter in ICSE Class 10 Chemistry. Our faculty has prepared the following ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Questions and answers based on the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Please refer to the solved questions below and also see links provided for other chapters.
Practical Chemistry ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Questions
Practical Chemistry ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Questions
I. Name the following
1. Name one gas that turns moist red litmus blue.
Ans. Ammonia.
2. Name any one gas which turns lime water milky.
Ans. Carbon dioxide or sulphur dioxide.
3. A greenish yellow coloured gas which bleaches moist blue litmus
Ans. Chlorine
4. Two carbonates which do not produce carbon dioxide on heating.
Ans. Potassium carbonate and sodium carbonate.
5. A gas with a rotten egg odour.
Ans. Hydrogen sulphide.
6. A colourless gas which turns blue cobalt chloride paper pink.
Ans. Water vapour.
7. A gas which turns alkaline pyrogallol solution dark brown
Ans. Oxygen.
8. A black solid which acts as a strong oxidising agent.
Ans. Manganese dioxide.
II. Select the correct word from the words in bracket :
1. The solution which on heating with CaCO3 evolves CO2 gas. [Conc. H2SO4/ dil.H2SO4/Conc.HCl]
2. The solution which can be used to distinguish an ammonium salt from a sodium salt. [CuCl2 soln./NaOH/Conc.H2SO4/AgNO3 soln.]
3. The pH of blood is around 7.4, of saliva is 6.5 and of acid rain is around 4.5. The solution which is slightly alkaline of the three. [saliva/acid rain/blood]
4. Decomposition of [NaCl/NaHCO3/NaNO3] by dil. H2SO4, forms an unstable acid.
5. A metal which reacts with an alkali to liberate hydrogen. [iron/copper/ aluminium]
Ans. 1. dil. H2SO4
2. NaOH
3. blood
4. NaHCO3
5. aluminium
III. Complete the table given below :

Ans.

IV. Select the correct ‘anion’ of a salt from the anions given, which matches with description 1 to 5.
A : CO3 –, B : NO31–, C : SO42– , D : Cll–, E : S2–
1. The salt soln. reacts with AgNO3 soln. to give a white ppt. insoluble in dil. HNO3.
2. The salt soln. reacts with Ba(NO3)2 soln. to give a white ppt. insoluble in dil. HNO3.
3. The salt soln. reacts with Ba(NO3)2 soln. to give a white ppt. soluble in dil. HNO3 but insoluble in dil. H2SO4
4. The salt reacts with dil H2SO4 on heating evolving a gas which turns KMnO4 soln. pink to colourless.
5. The salt reacts with conc. H2SO4 on heating evolving a coloured gas which turns potassium iodide paper brown.
Ans. 1. D : Cll–
2.C : SO42–
3. A : CO32–
4. E : S2–
5. B : NO31–
V. Identify the following:
1. Two gases A and B are bleaching agents. A is greenish yellow and bleaches due to its oxidising property, while B is a colourless gas bleaches due to reduction. Identify A and B.
Ans. A is chlorine and B is Sulphur dioxide.
2. Identify the anion present in the following:
(a) Compound A when warmed with concentrated sulphuric acid gives a gas which fumes in moist air and which gives dense white fumes with ammonia.
(b) When barium chloride solution is added to a solution fo compound B, a white precipitate insoluble in dilute hydrochloric acid is formed.
(c) The action of heat on the insoluble compound C produces a gas which turns lime water turbid.
(d) Compound D when warmed with dilute sulphuric acid gives a gas which turns acidified dichromate solution green.
Ans. a) Cl1– b) SO42– c) CO32– d) S2–
3. Name the cation present :
(a) Sodium hydroxide solution is added to solution A. A white precipitate is formed which in insoluble in excess sodium hydroxide solution. Name the metal ion present in solution A.
(b) When ammonium hydroxide is added to solution B, a pale blue precipitate is formed. This pale blue precipitate dissolves in excess ammonium hydroxide giving an inky blue solution. Name the cation present in solution B.
Ans. (a) Ca2+ (b) Cu2+
4. Identify the substances P, Q, R, S and T in each case based on the information given below :
(a) The deliquescent salt P, turns yellow on dissolving in water, and gives a reddish brown precipitate with sodium hydroxide solution.
(b) The white crystalline solid Q is soluble in water. It liberates a pungent smelling gas when heated with sodium hydroxide solution.
(c) The pale green solid R turns reddish brown on heating. Its aqueous solution gives a white precipitate with barium chloride solution. The precipitate is insoluble in mineral acids.
(d) The reddish brown liquid S is dissolved in water. When ethyne gas is passed through it, turns colourless.
(e) The nitrate T does not leave any residue on heating.
Ans. (a) FeCl3
(b) NH4Cl
(c) FeSO4
(d) Bromine
(e) NH4NO3
5. A given white crystalline salt was tested as follows :
(a) It is dissolved in water and the resulting solution of the salt turned blue litmus red.
(b) Addition of barium chloride solution into this solution gave a white precipitate.
(c) A flame test on the salt gave a persistent golden-yellow colourisation. What conclusions can be drawn for each observation?
Ans. (a) The salt is NH4Cl
(b) The solution contains SO42- ions
(c) The salt contains Na+ cation
VI. State your observations :
1. What would you observe in each of the following cases ?
(a) Ammonium hydroxide is first added in a small quantity and then is excess to a solution of copper sulphate.
Ans. A pale blue precipitate is formed which is soluble in excess of ammonium hydroxide to give inky blue solution.
(b) Sugar crystals are added to a hard glass test tube containing concentrated sulphuric acid.
Ans. A black spongy mass is formed.
(c) Copper is heated with concentrated nitric acid in a hard glass test tube.
Ans. A reddish brown gas is evolved and a blue coloured solution left behind.
(d) Water is added to the product formed, when aluminium is burnt in a jar of nitrogen gas.
Ans. A colourless gas is evolved which turns moist red litmus blue.
(e) When carbon monoxide is passed over heated copper oxide.
Ans. A colourless gas is evolved which turns lime water milky and pinkish brown metal is seen.
(f) Moist blue litmus is introduced into a gas jar of sulphur dioxide.
Ans. The blue litmus turns red and then bleaches.
(g) Dry red rose petals are placed in the jar of sulphur dioxide.
Ans. The rose petals are bleached.
(h) Ammonia gas is burnt in a atmosphere of oxygen in the absence of a catalyst.
Ans. It burns with greenish yellow flame.
(i) Glass rod dipped in ammonium hydroxide is brought near the mouth of the concentrated hydrochloric acid bottle.
Ans. Dense white fumes are released.
(j) Sodium sulphite is heated in the presence of sulphuric acid.
Ans. A colourless gas is evolved. which turns acidified KMnO4 pink to clearcolourless or acidified K2Cr2O7 orange to clear green.
(k) Copper chloride is introduced to a non – luminous flame
Ans. A bluish green colour is imparted to the flame.
(l) Manganese dioxide is heated in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid.
Ans. A greenish yellow coloured gas is evolved.
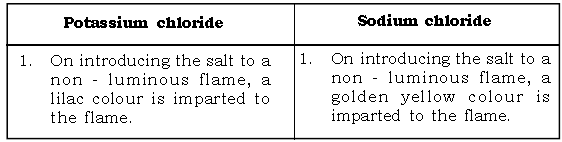
m) Potassium chloride is introduced to a non – luminous flame.
Ans. A lilac colour is imparted to the flame.
VII. Use the information given in (a) to (h) to identify the substance P to W selecting your answers from the given list.
List : Calcium Oxygen Copper (II) Oxide
Carbon Calcium hydroxide Copper (II) nitrate
Lead (II) oxide Hydrogen chloride Chlorine
Lead (II) nitrate Calcium oxide Ammonium chloride
(a) P is a white solid. When heated produces white fumes (sublime).
(b) P and R on warming produce an alkaline gas.
(c) On adding water to T, heat is evolved and R is formed.
(d) Q burns brightly in air to form T.
(e) When S is heated, it gives off brown fumes and leaves a black residue of U.
(f) A solution of S is formed by warming U with dilute nitric acid.
(g) V is a gaseous non metallic element that reacts with hydrogen to form W.
(h) A solution of W will neutralise the solution of R.
Ans. (a) P is Ammonium chloride
(b) R is Calcium hydroxide
(c) T is Calcium oxide
(d) Q is Calcium
(e) U is Copper oxide
(f) S is copper nitrate
(g) V is chlorine
(h) W is hydrogen chloride
VIII. Select from the list given (A to E) one substance in each case which matches the description given in parts (i) to (v). (Note : Each substance is used only once in the answer.)
(a) Nitroso Iron (II) sulphate
(b) Iron (III) chloride
(c) Chromium sulphate
(d) Lead (II) chloride
(e) Sodium chloride.
(i) A compound which is deliquescent.
(ii) A compound which is insoluble in cold water, but soluble in hot water.
(iii) The compound responsible for the brown ring during the brown ring test of nitrate ion.
(iv) A compound whose aqueous solution is neutral in nature.
(v) The compound which is responsible for the green coloration when sulphur dioxide is passed through acidified potassium dichromate solution.
Ans. (i) (b) Iron (III) chloride
(ii) (d) Lead (II) chloride
(iii) (a) Nitroso Iron (II) sulphate
(iv) (e) Sodium chloride
(v) (c) Chromium sulphate
IX. X, Y and Z are three crystalline solids which are soluble in water and have a common anion.
To help you to identify X, Y and Z, you are provided with the following experimental observation. Copy and write the corresponding inferences in (a) to (d).
(a) A reddish-brown gas is obtained when X, Y and Z are separately warmed with concentrated sulphuric acid and copper turning added to mixture.
INFERENCE 1 : The common anion is the ……….. ion.
(b) When X is heated, it melts and gives off only one gas which relights a glowing splint.
INFERENCE 2 : The cation in X is either ………. Or ……….. .
(c) The action of heat on Y produces a reddish brown gas and a yellow residue which fuses with the glass of the test tube.
INFERENCE 3 : The metal ion present in Y is the ……………….ion.
(d) When Z is heated it leaves no residue. Warming Z with sodium hydroxide solution liberate a gas which turns moist red litmus paper blue
INFERENCE 4 : Z contains the ………… cation.
Ans. (a) NO32- (b) K+ or Na+ (c) Pb2+ (d) NH41+
X. Give balanced equations for the conversions A and B.

XI. Distinguish between the following using a chemical test :
1. Sodium carbonate and sodium sulphite.
Ans.

2. Sodium sulphite and sodium sulphide.
Ans.

3. Hydrogen chloride and Sodium hydroxide.
Ans.

4. Potassium chloride and sodium chloride.
Ans.
5. Copper oxide and manganese dioxide.
Ans.

6. Carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide
Ans.

7. Sodium sulphite and sodium sulphate.
Ans.

8. Sulphur dioxide & Hydrogen sulphide.
Ans.

9. Zn2+ and Pb2+.
Ans.

10. Fe2+ and Fe3+.
Ans.

11. dil H2SO4 and dil HCl.
Ans.

12. dil H2SO4 and dil HNO3.
Ans.

13. Ca2+ and dil Cu2+.
Ans.

14. dil H2SO4 and dil HNO3.
Ans.




