Q) Multiple Choice Type:-
1) The most convenient reusable wastes are
a) Old newspapers
b) Broken glass
c) Flyash
d) Medical instruments
Solution:: (a) Old newspapers
2) The most rapidly increasing and much harmful waste today is
a) plastics
b) pesticides
c) municipal sewage
d) electronic waste
Solution:: (a) plastics
Q) Name the Following:-
Question 1) The solid precipitated material produced during secondary treatment of the effluent carried out in the effluent treatment plants.
Solution::
The solid precipitated material produced during secondary treatment of the effluent carried out in the effluent treatment plants:- Sludge
Question 2) The two types of devices commonly used for removing the particulate air pollutants.
Solution::
Scrubber, Plate type electrostatic precipitator
Q) Mention whether the following statement is true (T) or False (F).
1) Some of the electronic wastes may contain valuable metals such as copper.
a) True
b) False
Solution: True
2) Flyash is the gaseous waste of cement industry.
a) True
b) False
Solution: True
3) Electricity is one of the primary needs of human society.
a) True
b) False
Solution: False. Electricity is one of the secondary needs of human society.
Q) Match the items in Column I with as many times as possible in Column II.
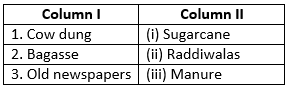
Solution:

Q) Short Answer Type:-
Question 1. Differentiate between:-
i) Degradable and non-degradable type of waste.
ii) Sewage and Effluents.
Solution:
(i) Degradable waste:- Degradable waste is defined as waste that can be broken down by microorganisms. E.g. Vegetable peel, paper, cloth etc.
Non-degradable waste:- Non-degradable waste is garbage that cannot be broken down by microorganisms. E.g. Plastic
(ii) Sewage:- Wastewater created by a community of people when bathing, washing, etc. is known as sewage.
Effluents:- The liquid waste that escapes from a factory, farm, etc. and flows into bodies of water like rivers, ponds, lakes, etc. is known as effluent.
Question 2. Give reason for the following:
a) Broken glass utensils are a kind of non-degradable waste.
b) Landfills are coming up fast near large cities.
Solution:
(a) Because they cannot be broken down and degraded by live microorganisms, shattered glass utensils are a type of non-degradable trash. To ensure that they don’t hurt anything, they need to be disposed of in deep holes. But occasionally, after being melted, considerable amounts of shattered glass might be utilized in the glass industry.
(b) Due to rapid population increase and a lack of effective and secure disposal methods, landfills are quickly emerging close to major cities. New colonies are being established, and building units are operating at a high level of activity. These generate a lot of waste wood, stones, and pebbles, as well as broken bricks. These are mostly utilized as landfills. In the suburbs, one may see mountains of landfills.
Question 3. Why is municipal sewage is first separated into degradable and non-degradable wastes?
Solution:
Municipal sewage is initially divided into degradable and non-degradable wastes because non-degradable waste has to be buried or deposited in safe locations to prevent any hazardous impacts while degradable waste may be broken down into non-toxic waste in septic tanks.
Q) Long Answer Type:-
Question 1. Define electronic waste and list at least six items which come under this category.
Solution:
The garbage produced by abandoned electrical appliances is known as electronic waste. Electronic trash includes the following items:
1. Fluorescent tubes
2. Medical instruments
3. Toys
4. Lead acid batteries
5. Mobile phones
6. Radios
Question 2. List some of the common wastes produced in mining operation and mention how these can be reused.
Solution:
Coal, dust, iron, copper, zinc, and other materials are common mining wastes.
Utilizing trash generated during mining operations: A significant amount of waste material is created throughout the mining process. Mine tailing is the name for this waste material. It is what is leftover. Tiles and masonry cement may be made by combining the mine tailing with other materials.
Question 3. Describe the procedure how compost is usually produced.
Solution:
Composting is the process through which organic waste rots and becomes manure. Compost is the end result of the composting process.
Compost preparation technique:
(i) A 1.5-m-deep, 5 m-long trench is excavated. Its width and depth are both 1.5 meters.
(ii) A layer of well-mixed trash and rubbish is put out 30 cm thick on top of it. A runny slurry of cow poo and some mud covers the whole stratum.
(iii) After spreading the initial layer with a second layer of mixed trash, the pile is raised by roughly half a meter.
(iv) The setup is left in place for roughly three months while being periodically misted with water.
(v) After that, a trench is excavated, its contents removed, rearranged in conical heaps, and then covered with earth.
(vi) Compost is ready for use in agriculture areas, flower beds, etc. after 50–60 days.
Question 4. Describe the usefulness of incineration of wastes, and also mention the precautions required in it.
Solution:
The following Utilization of waste incineration:
i) It decreases the weight of the trash.
ii) It lessens the amount of garbage generated.
iii) It transforms harmful wastes into less harmful or even harmless wastes.
The following precautions must be taken while incinerating:
i) It must be done at extremely high temperatures.
ii) Pollution control equipment ought to be installed.
iii) It ought to be put in place distant from populated regions.




