Question 1) Multiple Choice Question:-
1) Glycolysis is a process ___________.
a) in which glycogen is broken down into glucose
b) which occurs in mitochondria
c) in which glucose is broken down into pyruvate
d) that occurs next to the Krebs cycle
Solution: (c) in which glucose is broken down into pyruvate
2) One same common function is performed by?
a) Stomata and veins
b) Stomata and lenticels
c) Lenticels and sepals
d) Lenticels and hydathodes
Solution: (b) Stomata and lenticels
3) Anaerobic respiration normally occurs in
a) Grass
b) Cactus
c) Coconut
d) Baker’s yeast
Solution: (d) Baker’s yeast
Question 2) Very Short Answer Type:-
1) Do the plants respire all day and night or only during the night?
Solution:
Respiration is an essential life process for all living organisms. Therefore, plants also respire all day and all night.
Q3) Name the Following:-
a) Energy currency of cell.
b) Oxidative breakdown of carbohydrates to release energy.
c) An organism which respires throughout life anaerobically
d) A common phase in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
e) Aerobic respiration requires_________ .
f) A chemical which removes CO2 from the air.
Solution:
(a) ATP
(b) Respiration
(c) Fungus
(d) Glycolysis
(e) Oxygen
(f) Soda lime
Question 3) Mention if the following statement is true or false. If false, rewrite them correctly
1) Aerobic respiration of one mole of glucose yields 138 ATP.
2) Anaerobic respiration in plants yields lactic acid.
3) Carbon dioxide readily dissolves in limewater.
4) All leaves of a green plant normally respire anaerobically at night.
Solution:

Question 4) Short Answer Type:-
Question 1) What happens to the energy liberated during respiration?
Solution:
The ATP that is produced during breathing is kept in reserve by the cells. It loses some of it as heat to the surroundings.
Question 2) Why is it usually difficult to demonstrate respiration in green plants?
Solution:
During the day, green plants perform photosynthesis and respiration. The development of CO2 is a marker for the presence of breathing in living things. There is no CO2 evolution since the CO2 produced during plant respiration is used up during photosynthesis. Due to the lack of CO2 evolution during the day, it is difficult to demonstrate respiration in green plants.
Question 3) Explain why respiration is said to be a reversal of photosynthesis?
Solution:
For the following reasons, respiration is considered to be the opposite of photosynthesis:
(1) Organic food is broken down into its inorganic components, such as CO2 and H2O, during respiration, whereas during photosynthesis, organic food is created from its inorganic components, such as CO2 and H2O.
(2) CO2 is released during respiration, whereas it is absorbed during photosynthesis.
(3) O2 is used during respiration, whereas O2 is released or evolved during photosynthesis.
(4) Energy is released during respiration, whereas it is absorbed during photosynthesis.
Question 4) How is tilling of the soil useful for the crops growing in it?
Solution:
The soil becomes airy and permeable after tilling. The plants’ subterranean regions receive enough oxygen for respiration. Tilling promotes quicker crop growth in this way.
Question 5) Write the full forms of ATP and ADP.
Solution:
ATP: Adenosine triphosphate
ADP: Adenosine diphosphate
Question 6) Can cell respiration occur in any organism at a temperature of about 65°C? Give reason.
Solution:
Because the enzymes involved in respiration become inactive at high temperatures, cell respiration cannot take place in any creature below roughly 65 °C.
Question 5) Fill in the blank:
1) _________ are the openings found on older stems.
2) Glycolysis occurs in the _______of the cells.
3) _____________ is a respiratory substrate
4) Rate of ____________ is more than the rate of ___________ in the daytime in the case of green plants.
5) _____________ is a chemical which absorbs oxygen of the air.
6) ______________ is used to create vacuum to show anaerobic respiration.
Solution:
1) Lenticels are the openings found on older stems.
2) Glycolysis occurs in the Cytoplasm of the cells.
3) Glucose is a respiratory substrate
4) Rate of Photosynthesis is more than the rate of respiration in the daytime in the case of green plants.
5) Pyrogallate of potash is a chemical which absorbs oxygen of the air.
6) KOH (caustic potash) is used to create vacuum to show anaerobic respiration.
Question 6) Long answer type:-
Question 1) What is respiration? How are respiration and burning similar and how are they different?
Solution:
Respiration is the process through which organic food, particularly carbohydrates, are oxidized within living cells to release energy.
Similarities between burning and breathing
(i) Both call for oxygen.
(ii) Both generate energy.
(iii)Both lead to the production of CO2 and water (iii).
Differences between respiration and burning:

Question 2) How are aerobic and anaerobic respiration different in plants?
Solution:
Difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration in plants:

Question 3) Describe one experiment you would perform to demonstrate the following phenomena:
(a) The germinating seeds produce heat.
(b) The germinating seeds to give out carbon dioxide.
(c) The germinating seeds can respire even in a total absence of air.
Solution:
(a) The germinating seeds produce heat:-
(a) Heat is generated while seeds germinate.
(1) Grab two thermos bottles, “A” and “B.”
(2) Soak around 200 bean or pea seeds for more than 24 hours in water.
(3) Split the seeds evenly into two groups. To avoid bacterial degradation, boil one batch of seeds, then wash them in diluted formalin. Put the living seeds that are developing in flask A and the dead seeds in flask B.
(4) Place a thermometer and cotton wool plugs in the mouths of each flask. Take note of the thermometer’s initial reading.
(5) After a few hours, the flask A thermometer will register higher, indicating that the seeds are producing heat as they germinate. The temperature of flask B won’t increase at all.

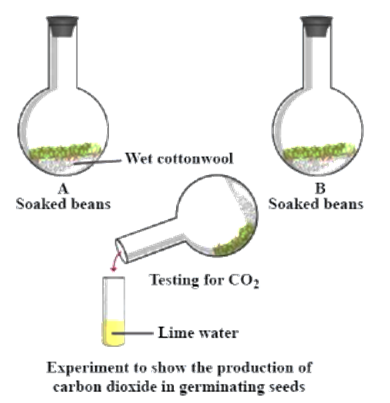
(b) Carbon dioxide emissions from the germination of seeds.
(1) Grab flasks “A” and “B”.
(2) Fill the bottom of each flasks with some moist cotton wool.
(3) Put some pea seeds in flask A that have been soaked, and put an equal quantity of dead or boiling seeds in flask B. To stop bacteria from growing on dead seeds, add some carbolic acid to flask B.
(4) Seal the flasks with a cork and leave them alone for a few days.
(5) The seeds in flask A will have germinated after a few days, but the seeds in flask B will not have done so.
(6) After removing the cork from each flask, the gases inside are next examined by tipping the flask over a test tube filled with limewater and shaking it.
(7) While the gas in flask B has no impact on the limewater, the predicted CO2 present in flask A would render the limewater milky, demonstrating that germination of seeds releases CO2.
(c) The germinating seeds can respire even in a total absence of air.
(1) Place a few pea seeds that have been soaked and peeled into the opening of a test tube that has been filled with mercury and placed upside down in a beaker of mercury. The mercury will completely encircle the seeds as they float to the top.
(2) After a few days, the mercury level drops and a small amount of gas may be seen in the test tube.
(3) Fill the test tube with KOH. As the gas in the test tube is absorbed, the mercury level will increase once more, indicating that the gas was CO2. So, we can demonstrate that seeds can breathe even when there is no air present at all.

Question 2) How do the following structures help in respiration in plants?
Lenticels _____________
Stomata _____________
Root hairs ____________
Solution:
1) Lenticels help the stem to participate in respiration.
2) Stomata help the leaves to participate in respiration.
3) Root hairs help the roots to participate in respiration.
Question 9) Structure Application Skills:-
1) The following two chemical reactions are supposed to indicate a certain process occurring in the green plants under two different conditions:
(a) C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + _______ + 38ATP
(b) C6H12O6 → ________ + 2CO2 + 2ATP
(i) Fill in the blank in each reaction.
(ii) Name the process represented by the two reactions.
(iii) What are the conditions under which the two reactions (a) and (b) are occurring respectively?
Solution:
(i) (a) C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6CO2 + 6H2O + 38ATP
(b) C6H12O6 → C2H5OH + 2CO2 + 2ATP
(ii) (a) Aerobic respiration;
(b) Anaerobic respiration
(iii) Reaction:- (a) can be completed only in the presence of oxygen, while reaction
(b) can be completed in the absence of oxygen.
Question 2) The following diagram refers to an apparatus which is used to demonstrate a physiological process:
1.) What is the purpose of keeping potassium hydroxide solution in test tubes X and Y?
2.) Why has the coloured water risen in tubing 1?
3.) What is the purpose of keeping boiled peas soaked in a disinfectant in test tube Y?
4.) Name the biological process which causes the above rise.
5.) Define the biological process shown in the experiment.

Solution:
1.) Potassium hydroxide solution is kept in test tube X and Y to check the presence of CO2, as KOH can absorb CO2 if it is produced.
2.) The O2 in test tube X is used up during breathing, which happens during the test tube’s operation. The KOH in the test tube absorbs the CO2 released during respiration. As a result of the oxygen being used, space is created, and tube 1’s colored water rises as a result.
3.) Because the boiled seeds are dead and unable to breathe, test tube Y is filled with boiled peas that have been immersed in a disinfectant. As a result, test tube Y does not include the mechanism of breathing.
4.) The aforementioned increase is a result of respiration.
5.) Respiration is the catabolic process through which simple carbohydrates are converted into energy for use in vital bodily functions.
Question 3) Given below is a set of six experimental set-ups (A-F), kept in this state for about 24 hours.
a) In how many flasks, the different plant parts have been kept under observation?
b) What is the purpose of keeping a test-tube containing limewater in each flask?
c) In which tube/tubes the limewater will turn milky?
d) What conclusion can you draw from this experiment?

Solution:
a) For observation, five flasks (A through E) contain various plant sections.
b) CO2 in the flasks is absorbed by limewater. Limewater turns milky if CO2 is created.
c) The tubes carrying limewater will turn milky and all five flasks (A-E) holding plant parts will exhibit respiration. There are no plant components in flask F. As a result, there is no respiration and no change.
d) This experiment has shown that CO2 is created during respiration.
Question 18) In order to study and prove a particular physiological process in plants, the following experiment was set up. Study the same and then answer the question that follows:

a) Name the physiological process being studied.
b) What is the function of soda lime in the bottle ‘A’ and why is limewater placed in bottle ‘B’?
c) What change would you expect to observe in bottle ‘D’?
d) Represent the physiological process named in question 4.1 in the form of a chemical equation.
e) In order to obtain accurate results, the bottle ‘C’ should be covered with black cloth. Why?
f) If bottle ‘C’ was fitted with a 3-holed rubber stopper and a thermometer was introduced in such a way that its bulb reaches close to the germinating seeds, what would you observe? Why?
Solution:
a) The experiment was designed to investigate how living plant material that engages in respiration emits CO2.
b) To check the (existence of) passage of CO2 present in bottle “B,” soda-lime is preserved in bottle “A.” This is due to the fact that soda lime tends to absorb atmospheric CO2. With the air moving through bottle C, the limewater in bottle “B” demonstrates that no CO2 is entering bottle C.
c) The bottle “D” containing limewater will demonstrate that CO2 is created as a result of respiration occurring in the bottle “C” containing germination-stage seeds. The limewater turns milky as it goes through bottle “D” as a result of the CO2 created in bottle C.
d) C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + 38ATP (Energy)
e) When the bottle “C” is covered with a black cloth, photosynthesis will not be possible. Therefore, just the breathing process can be seen.
f) The temperature difference is checked or noticed by inserting a thermometer into bottle “C”. Temperature will rise if respiration happens, and if there is no temperature increase, then no respiration takes place. As a result, a thermometer and a three-holed rubber stopper were added.



