Students should refer to Sense Organs ICSE Class 10 Biology Board Exam Questions provided below with solutions. These will help the students to understand the type of questions which have been asked in previous year examinations and the type of solutions which the student should give to get good marks. You should also refer to ICSE Class 10 Biology Sample papers for more practice
ICSE Class 10 Biology Sense Organs Important Questions
Students should learn the important questions and answers given below for Chapter Sense Organs in Biology for ICSE Class 10. These board questions are expected to come in the upcoming exams. Students of ICSE Class 10th should go through the Important questions and answers ICSE Class 10 Biology which will help them to get more marks in exams.
Sense Organs ICSE Class 10 Biology Board Exam Questions
Sense Organs ICSE Class 10 Biology
Question. Odd one out :
1. Iodopsin, Rodopsin, Pepsin, Retina, Yellow spot
Ans.
Pepsin
2 Semicircular canals, Malleus, Cochlea, Utriculus, Sacculus.
Ans.
Malleus
3. Malleus, Incus, stapes, middle ear, Cochlea
Ans.
Cochlea
4. Myopia, hypermetropia, xerophthalmia, astigmatism
Ans.
Xeropthalmia
Question. Name the following :
1. Place of best vision in the retina of the eye
Ans.
yellow spot.
2. Is the exact centre of the posterior portion of the retina
Ans.
yellow spot.
3. The ear ossicle attached to the tympanum
Ans.
malleus (hammer).
4. The fibres which collectively hold the lens in position
Ans.
ciliary muscle fibres.
5. Helps to change the focal length of the eye lens ciliary muscles
Ans.
ciliary muscles.
6. The layer of the wall of the eye ball that corresponds to the black lining of box of a camera
Ans.
retina.
7. Fluid in the eye that fills the space between the lens and the cornea
Ans.
aqueous humour
8. The auditory canal directs sound waves towards
Ans.
tympanum.
9. The power of the eye to focus images of distant and near objects on the retina to assure clear vision is called
Ans.
power of accommodation.
10. The part which equalizes the air pressure in the middle and external ear
Ans.
tympanic membrane (tympanum or ear drum).
11. The outer transparent part of the eye which is continued on the inner side of the eye lid
Ans.
conjunctiva.
12. The kind of lens required to correct near sightedness
Ans.
concave lens.
13. The tube which connects the cavity of the middle ear with the throat
Ans.
eustachian tube.
14. Transmits impulse to the brain from the ear
Ans.
auditory nerve.
15. Part of your hand which is most sensitive to touch
Ans.
finger tips.
16. The photoreceptors found in the retina of the eyes
Ans.
rods and cones.
17. The eye defect caused due to shortening of the eye ball from front to back
Ans.
hypermetropia.
18. Its secretion is called tears
Ans.
lacrimal gland/ tear gland.
19 Fluid contained in the labyrinth of inner ear
Ans.
perilymph.
20. Kind of retinal cells sensitive to dim light
Ans
rods.
21. The smallest bone in the human body
Ans.
stapes (stirrup)./ (Bones of ear ossicles)
22. This organ present in the cochlea help in hearing
Ans.
organ of Corti.
23. In the tongue is located the sense of
Ans.
taste.
24. Sensory cells in the eye concerned with the colour vision
Ans.
cones.
25. The circular window enclosed by iris
Ans.
pupil.
26. Which structure converts sound waves into the mechanical vibrations
Ans.
ear drum.
27. The ear ossicles are located in
Ans.
middle ear
28. The part of the eye responsible for its shape
Ans.
sclera (sclerotic layer).
29. Responds to the change in position of the body
Ans.
semi-circular canals.
30. The biological term for semi circular canal and the cochlea
Ans.
membranous labyrinth
31. Part of the ear concerned with dynamic balance
Ans.
semi – circular canals.
32. Photoreceptor cells that are sensitive to dim light
Ans.
rods.
33. Capacity of the eye to focus at different distances
Ans.
accomodation.
34. The photosensitive pigment present in the rods of the retina
Ans.
rhodopsin.
35. This secretion protects the eye from
Ans.
infection of microbes lysozyme/ Tear.
36. The olfactory nerves are concerned with the sense of
Ans.
smell.
37. Equalizes the atomospheric pressure and the pressure in the ear
Ans.
eustachian tube.
38. Place of no vision in the retina of the eye
Ans.
blind spot.
39. Converts vibrations into nerve impulses
Ans.
cochlea.
40. Is free of rods cells
Ans.
blind spot.
Question. Fill in the blanks :
(a) The sequence of ear ossicles of vertebrates starting from the tympanum is ________.
Ans.
malleus, incus, stapes
(b) Place of no vision in the retina of the eye is ____________.
Ans.
blind spot
(c) The three small bones in the middle ear are called _____________.
Ans.
ear ossicles
(d) The middle ear is separated from the external ear by the _____________.
Ans.
tymanic membrane
(e) The structure that equalises the air pressure on either side of the eardrum is ___________
Ans.
Eustachian tube
(f) Retina of vertebrate eye consists of ____________.
Ans.
rods and cones
(g) The thin transparent membrane covering the eye is ____________.
Ans.
conjunctiva
(h) The three layers of the eye constitute ___________, ____________ and ___________.
Ans.
sclera, choroid, retina
(u) Tympanic duct is filled with ___________.
Ans.
perilymph
(j) Passage connecting middle ear with nasopharynx is called ___________.
Ans.
Eustachian tube
(k) The cones are sensitive to _____________ light.
Ans.
bright
(l) The ear ossicle attached to the oval window is ____________.
Ans.
Stapes
(m) Capacity of the eye to focus at different distances is ______________.
Ans.
power of accommodation
(n) Cochlea is filled with ____________.
Ans.
endolymph
Question. Match the following
Column – I Column – II
(a) Myopia (i) Old sightedness
(b) Rods (ii) Long sightedness
(c) Cones (iii) Yellow spot
(d) Presbyopia (iv) Short sightedness
(e) Hypermetropia (v) Perceive light
(vi) Distinguish colours
Ans. (a) – (iv) Short sightedness
(b) – (v) Perceive light
(c) – (vi) Distinguish colours
(d) – (i) Old sightedness
(e) – (ii) Long sightedness
Question. Complete the following table by filling in the correct location of the following structure in the human body and mention one main function.

Ans.

Question. The diagram given represents a defect of vision of the human eye.
(a) Name the defect.
(b) What is the effect of this defect in man?
(c) Mention two causes for this defect.
(d) How can this defect be rectified
(e) What is the nature of the image that falls on the retina of a normal eye?

Ans. (a) Hypermetropia or Far sightedness
(b) The man fails to see near objects clearly.
(c) The causes are :
(i) Abnormally short eye ball. (ii) Abnormally low convexity of eye lens.
(d) Use of bioconvex lenses rectifies this defect.

(e) An inverted and real image falls on retina of a normal eye.
Question. Complete the following sentence using the correct word from the alternatives given :
(a) The part of the eye responsible for change in the size of the pupil in the ____ (Ciliary muscles, Aorta, Stapes, Dorsal Aorta)
(b) The ear ossicle in contact with the oval window of the inner ear is the _____ (Alveoli, Malleus, Bronchioles, Iris)
Ans. (a) The part of the eye responsible for change in the size of the pupil is the ciliary muscles
(b) The ear ossicle in contact with the oval window of the inner ear is the malleus.
Question. The diagram on the side represents the cross-section of the human eye :

(a) Name the parts labelled 1 to 13.
(b) What is the function of the part marked ‘10’
(c) What would happen if part ‘5’ is damaged or cut?
Ans. (a) 1. Sclera 2. Choroid 3. Retina 4. Yellow spot 5. Optic nerve 6. Blind spot 7. Lens 8. Aqueous humour 9. Pupil 10. Iris 11. Vitreous humour 12. Cornea 13. Conjunctiva 14. Ciliary body 15. suspensory Ligament
(b) Function of Iris : The radial and circular muscles of the iris contract and reflex and thereby the size of the pupil is adjusted
(c) Visual stimuli will not be there from the retina to the brain.
Question. The diagram on the side represents a certain defect of vision of the human eye.
(a) Name the defect.
(b) Describe briefly the conditions in the eye responsible for the defect.
(c) Re-draw the figure by adding a suitable lens correcting the defect. Label the parts through which the light-rays pass.

(d) What special advantages do human beings derive in having both eyes facing forward?
Ans. (a) Short-sightedness
(b) Either the eye-ball is lengthened from the front to back or the lens is too curved.
(c)

(d) Binocular vision is the characteristic of man. This type of vision plays an important ole in adjusting the distance and depth of the object. This is made possible by the arrangement of both the eyes facing forward.
Question. (i) What is meant by power of accommodation of the eye? Name the muscles of the eye responsible for the same.
(ii) Draw a labelled diagram of the inner ear. Name the part of the inner ear that is responsible for static balance in human beings.
Ans. (i) Power of accommodation of eye : By changing the curvature of the eye lens, the images of objects of different distance is focused sharply. Ciliary muscles are responsible for this accomodation of eye.
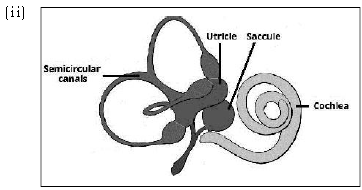
Parts responsible for static balance is utriculus and sacculus which are part of vestibular apparatus.
Question. (a) Describe briefly about the following :
Position of image in myopia and hypermetropia, and the kind of lenses used for correcting these defects.
Ans. (a) Short-sightedness or Myopia: The myopic eye ball is abnormally long from front to back or its lens has more curvature than normal. Hence, light rays coming from a long distance focus at a point in front of the retina and then spread out ; as a result the image is blurred. Nearer objects can be brought into focus on the retina with less bulging of the lens than in a normal eye. In myopia, eye can see near objects clearly. People with myopia need concave lenses to diverge the rays somewhat before hitting the eye so that the image is focussed on the retina. The power of glasses used to remedy short sightedness by using a concave lens, is stated as negative (–ve)
(b) Long sightedness or Hypermetropia : The hypermetropic eye ball is either shorter from front to back than the normal eye or has a lens with less than the normal curvature. Any of these deviations from the normal implies that there is difficulty in seeing near objects as rays do not converge enough. In hypermetropia, eye can see distant objects clearly. Therefore, light rays coming from near objects need to be converged by using a convex lens. The power of glasses used is stated as positive (+ve).
Question. Complete the following :
Location, Function
Yellow spot
Ans. Location : Present in the retina also called fovea centralis or macula lutea.
Function : It is the area of acute image formation as it has maximum rods and cones.
Question. The given diagram refers to the ear of a mammal:
(a) Lable the parts 1 to 10 which the guidelines point.
(b) Which structure:
(i) Converts sound waves into mechanical vibrations?
(ii) Responds to different types of sound vibrations?
(iii) Responds to change in position?
(iv) Transmits impulses to the brain?
(v) Equalizes atmospheric pressure and pressure in the ear?

Ans. (a) (1) Cochlea (2) Auditory nerve (3) Semi-circular canals (4) Ossicles (5) Auditory canal (6) Pinna (7) Ear drum (8) Round window (9) Eustachian canal (10) Oval window.
(b) (i) Ear drum (ii) Cochlea (hair cells) (iii) Semi-circular canals (iv) Auditory nerve (v) Eustachian canal
Question. State the accessory structure of eye.
Ans. The eye is organ of vision consisting of the eyeball and accessory structures.
Accessory structures : Among the accessory structures are the eyebrows, eyelids, eye lashes and the lacrimal glands.
(a) Eyebrows : Eyebrows forms a hairy transverse arch at the junction of the upper eyelid and forehead. The coarse, lateral hair protect the eyes from perspiration and the direct rays of the sun.
(b) Eyelids : Eyelids are also protective structures. They shade the eye during sleep, protect the eyes from excessive light and foreign particles and spread lubricating secretion over the eyeballs. The upper eyelid is more movable than the lower eyelid.
(c) Eyelashes : Eyelashes line the eyelids. They consist of a row of short, thick hair. Sebaceous glands at the base of the hair follicles of the eyelashes pour a lubricating fluid into the follicles. Infection to these glands is called stye.
(d) The lacrimal glands : The lacrimal glands are structures that manufactures and drain tears. Each gland is about the size and shape of an almond and is located at the upper, outer end of the eyeball, beneath eyelid. The lacrimal secretion (called tears) is a watery solution containing salts, and a bactericidal enzyme called lysozyme. It cleans and lubricates the eyeball. After being secreted by the lacrimal glands, it is spread over the surface of the eyeball by the blinking of the eyelids.
Question. Name the photoreceptors found in the retina of the eye.
Ans. Photoreceptors
Rods – contain pigment rhodopsin Cones – contain pigment iodopsin
Question. Name the following :
(a) Two types of light sensitive cells present in the retina
(b) The aperture in the eye through which light enters into the eye ball.
Ans. (a) Rods and cones (b) Pupil
Question. Explain how the shape and position of the eye is maintained in normal condition.
Ans: In normal condition (ciliary’s muscles relaxed), the lens remains stretched by the suspensory ligament and it is less convex , suited for viewing distant objects. When we look at nearby objects, the ciliary muscles (which are circular) contracts and tend to pull the ciliary body slightly forwards. This releases the tension on the suspensory ligament making it loose and the lens on account of its elasticity, turns thicker and more rounded or convex.
Question. Name the following – The part of the eye responsible for its shape.
Ans. Vitreous humour
Question. Given below is the diagram of the human ear. Study the same and answer the questions that follow :
(i) Give the biological term for the part labelled ‘A’ and state its function.
(ii) Name the part labelled ‘B’ and state its function.
(iii) Name the part labelled ‘C’ and state its function.
(iv) Give the function of ear wax.

Ans. (i) Part labelled ‘A’ is called as ear ossicles. It is made up of three bones malleus, incus and stapes. The ear ossicles transmit the sound waves from external ear to the internal ear.
(ii) Part labelled ‘B’ is called as eustachian tube. It acts as a link to equalize pressure of air on both the sides of tympanic membrane and allow it to vibrate freely.
(iii) Part labelled ‘C’ is auditory nerve which carries hearing impulses to the brain.
(iv) Ear wax lubricates the external ear and tympanum for proper functioning. It traps the dust and other small molecules present in ear.
Question. Given alongside is the diagram of the human ear. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow :
(i) What role does the ear drum play in hearing?
(ii) What is the common term given to the parts labelled A, B and C?
(iii) Would there be any difference if these parts mentioned in question (ii) above were replaced by big one? Why?
(iv) Give the biological term for the parts labelled E and D.
(v) Name the fluid which fills the parts mentioned in question (iv) above.
(vi) State the functions of the ear.

Ans. (i) Ear drum receives sound vibrations from pinna through auditory canal and transfers them to ear ossicles for the purpose of transmission and amplification of vibrations.
(ii) The common term given to the parts labelled A, B and E are ear ossicles.
(iii) One big ossicle would not be able to produce effective amplification because, it would require a greater force of vibration than supplied by the ear drum normally. Moreover, these smaller ossicles with proper distance between them produces multiple amplification and effective transmission.
(iv) Part E and D are biologically termed as semi-circular canals and cochlea respectively.
(v) Endolymph
(vi) Ear performs two functions : (i) hearing and (ii) balancing of body.
Question. Match the items in column A with those which are most appropriate in Column B. You must rewrite the matching pairs

Ans.

Question. The diagram shown below give the power of accommodation in the human eye. Complete the diagrams by striking off the incorrect alternatives in the labels.
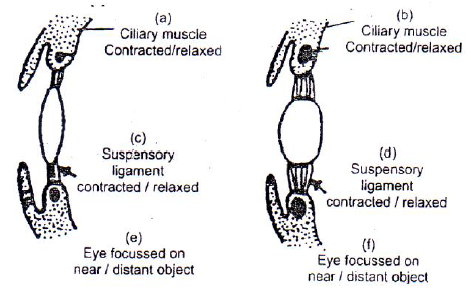
Ans. (a) Contracted / relaxed (b) Contracted / relaxed
(c) Contracted / relaxed (d) Contracted / relaxed
(e) near / distant (f) near / distant
Question. Explain binocular vision (stereoscopic).
Ans. In humans the eyes are set in the front part of the face. Each eye sees an object under observation oriented slightly differently from the other and forms its own separate image of the object on the retina. The brain correlates the two images and interprets the two images as a single impression. If the sensory impressions from the eyes are not properly correlated we see ‘double’. This problem could rise if the eyes are not
Question. Draw a neat labelled diagram of human ear (Internal structure).
Ans.

Question. Mention if the following statement is true or false and rewrite the wrong statement. Cones are the receptor cells in the retina of the eye sensitive to dim light.
Ans. False. Rods are the receptor cells in the retina of the eye sensitive to dim light.
Question. Where are the following located in the ear?
a) Oval window b) Cochlea c) semi-circular canals
Ans. a) The oval window is a membrance covered opening leading from middle ear to the inner ear.
b) The cochlea is the Ist part of the inner ear. It is connected to the round window on one side and to the auditory nerves on the other side.
c) The semicircular canal is located in the inner ear. These have three canals arranged at the right angles to each other – one horizontal and other two are vertical. The nerve fibres from the semi-circular canals join the auditory nerve, on the inner side.
Question. The diagram shown below gives how lenses are used to correct eye defects. Complete the diagrams by cutting the incorrect alternatives in the lables.
Short Sight
Normal light from a
(a) Distance / close object is
(b) focussed in front of / behind the retina
Converging / diverging lens

Long Sight
Normal light from a
(c) Distance / close object is
(d) focussed in front of / behind the retina
Converging / diverging lens

Ans. (a) distant / close
(b) infront of / behind
(c) distant / close
(d) infront / behind
Question. Given below is the diagram of a part of the human ear. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow :

(i) Give the biological term for Malleus, Incus and Stapes.
(ii) Name the parts labelled A, B and C in the diagram
(iii) State the functions of the parts labelled ‘A’ and ‘B’
(iv) Name the audio reception region present in the part labelled ‘A’
Ans. (i) Ear ossicles
(ii) A – Cochlea, B – Semicircular canal, C – Vestibule
(iii) A – hearing. It transmits impulses from the inner ear to the auditory nerve.
B – Maintains static and dynamic equilibrium.
(iv) Organ of Corti.
Question. Study the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow.

a) Label the parts 1 to 8
Ans. 1 = Pinna 2 = Auditory canal 3 = Tympanum 4 = Eustachian tube
5 = Cochlea 6 = Saccule/Vestibule 7 = Semi – circular canals 8 = Malleus
b) Why does a man lose his balance after turning round quickly several times?
Ans. If you spin round and round, the fluid in the semi-circular canals continues to spin for
a short time, even after you stop and man feels dizzy and may lose his balance
Question. The diagram alongside represents a defect of vision of the human eye:
(i) Name the defect.
(ii) What is the effect of this defect on man?
(iii) Mention two causes for this defect.
(iv) How can this defect by rectified?
(v) Draw a neat labelled diagram to show how this defect can be rectified.

(vi) What is the nature of the image that falls in the retina of a normal eye?
Ans. (i) Hypermetropia or far sightedness.
(ii) The man fails to see the near objects clearly.
(iii) The causes are – (1) Abnormally shortened eye ball (2) Abnormally low convexity of eye lens.
(iv) Use of biconvex lenses rectifies this defect.
(v)

(vi) An inverted and real image falls on the retina of normal eye.
Question. Draw and label only the vertical section (V.S.) of human eye.
Ans. Anatomically, the eye ball is divided into three layers – The fibrous sclerotic layer, vascular choroid layer and the nervous retina layer, each of them have their own functions to perform.

Question. Write briefly as indicated in the brackets, on the following :
(a) Myopia (symptom and cause)
(b) Tympanum (Location and Function)
Ans. (a) Myopia – Symptom : In this condition near vision is clear while distant vision is blurred.
Cause : In myopia, image of distant objects is formed in front of the retina. This happens when the eyeball is too elongated. This can also happen when the eye lens is too convex.
(b) Tympanum – Location : Tympanum, a thin membranous tissue is located between the external and middle ear.
Function : Sound waves from outside causes the tympanum to vibrate which are ultimately transmitted across the middle ear and produces sound.
Question. Which structure in the ear is responsible for :
(a) Equalizing air pressure on both sides of the tympanum?
(b) Receiving vibrations from auditory canal and transmitting them to the ear ossicles?
(c) Carrying impulses from inner ear to the brain?
(d) Amplifying the vibrations received from eardrum?
Ans. (a) Eustachian tube
(b) Eardrum/Tympanic membrane
(c) Auditory nerve
(d) Ear ossicles
Question. The diagram below shows a mammalian eye as seen from front.
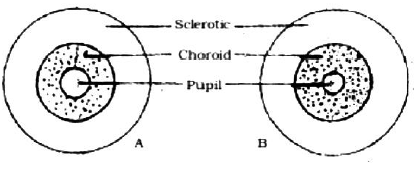
(a) What has caused from A to B?
(b) What is the function of sclerotic layer?
(c) Name the muscles that bring about this change?
Ans. (a) In A there is dilation of pupil and B there is contraction of pupil.
(b) The white portion on front of eye is sclerotic layer, itself visible through conjuctiva. It bulges and becomes transparent in the front region where it covers the coloured part of the eye, this part is called the cornea.
(c) Ciliary muscles.
Question. Given below is the diagram of the human ear. Study them and then answer the following questions.
(a) What role does the ear drum play in hearing?
(b) What common term is given to the parts labelled A, B and E?
(c) Would there be any difference if these three parts mentioned in (b) above were replaced by a bigger one? Why?
(d) Give the biological term for the parts labelled C and D
(e) Name the fluid which fills the parts mentioned in (d) above.
(f) State the functions of the ear.

Ans. (a) Ear drum receives sound waves from pinna through auditory canal, convert them into mechanical vibrations and transfers them to ear ossicles for the purpose of transmission and amplification of vibrations
(b) The common term given to the parts labelled A, B and E is ear ossicles.
(c) The big ossicle would not be able to produce effective amplification because, it would require a greater force of vibration than supplied by the ear drum normally. Moreover, three smaller ossicles with proper distance between them produces multiple amplification and effective transmission.
(d) Parts C and D are biologically termed as semicircular canals and cochlea respectively.
(e) Endolymph
(f) Ear performs two functions : hearing and equilibrium
Question. What is an eye? Give its accessory structures?
Ans. The eye is the organ of vision consisting of the eyeball and accessory structures. Among the accessory structures are the eyebrows, eyelids, eye lashes and the lacrimal glands.

Question. Mention one major function of the following :
(a) Ear ossicles (b) Iris (c) Tympanum
Ans. (a) Ear Ossicles : The function of the ear ossicles is to transmit the vibrations caused by the tympanic membrane to the inner ear.
(b) Iris of the eye : The radial and circular muscles of the iris contract or relax and thereby the size of the pupil is adjusted.
(c) Tympanum : Vibrations of very low frequency can be preceived by the eardrum and passed further.
Question. Categorise the following parts under
a) External b) Middle and c) Internal ear Ear drum, hammer, pinna, cochlea, anvil, stirrup, eustachian tube, tympanum, oval window, semi-circular canals, auditory canal, vestibule.
Ans. a) External ear : Pinna , ear drum (tympanum), auditory canal
b) Middle ear : hammer (malleus), anvil (incus), stirrup (stapes), eustachian tube, oval window.
c) Inner ear or Internal ear or membranous labyrinth : Vestibule, Cochlea, semi-circular canals.
Question. What is the function of auditory nerve?
Ans. The auditory nerve send sound impulses to the temporal area of the brain. This temporal area of the brain are stimulated and the interpretation of the impulses by the brain results in hearing.
Question. Name the 5 sensory organs in our body giving their sensitivity ?
Ans. The major sense organs in our body are the eyes, ears, tongue, nose and skin which are sensitive to light, sound, taste, smell and touch respectively. The actual sensation is perceived by the nerve cells located in these organs – such cells are known as receptors.
Question. Give appropriate terms for the following :
(a) Adjustment of the eye in order to obtain a clear vision of objects at different distances.
Ans. (a) Accomodation
Question. How do the ear ossicles contribute in the mechanism of hearing?
Ans. The ear ossicles viz., malleus, incus and stapes, help in the mechanism of hearing by transmitting (transferring) the sound waves which strike the ear drum causing vibrations. The vibrating ear drum, sets the three ossicles also into vibration. The vibration of the last ossicle (stapes) is magnified due to lever-like action of the first two ossicles (malleus and incus). The vibrating stapes transmits the vibration to the membrane of the oval window.
Question. State one difference of the following on the basis of what is indicated within bracket.
(a) Myopia and hypermetropia (position of image with reference to retina)
Ans. (a)

Question. State the function of the following :
(a) Eustachian tube (b) Membranous labyrinth
(c) Auditory canal (d) Cochlea
Ans. (a) Eustachian tube : The movement of air into air or out of the tympanic chamber takes place through the eustachian tube. It serves to adjust the pressure inside the middle ear to changes in atmospheric air pressure for normal hearing.
(b) Membranous labyrinth : It has two main parts – cochlea and semicircular canals. Cochlea contains nerve fissures joining auditory nerve and semicircular canals contain sensory cells. Thus functions of internal ear are hearing and body balance.
(c) Auditory canal :Transfers sound waves to the ear drum.
(d) Cochlea : It is concerned with hearing as it has sensory cells which which convert sound vibration into nerve impulses and send these impulses to auditory nerve.







