Students of ICSE Class 10 should refer to Soil Resources ICSE Class 10 Geography previous year questions and solutions. below which have come in past board exams. You should always go through questions that have come in previous years. This will help you to understand the pattern of questions in ICSE Class 10 Geography and prepare accordingly. This will help you to get better marks in ICSE Class 10 Board Exams
Short Answer Type Questions
Question: (i) How is black soil formed?
(ii) Name one cash crop for which black soil is most suited. [ICSE Specimen
Answer: (i) Black soil is formed by the weathering of igneous rock.
(ii) Cotton.
Question: (i) Name the transported soil most widely found in India.
(ii) How is this soil formed?
Answer: (i) Alluvial soil.
(ii) Alluvial soil is formed by the deposition of sediments and silts brought down and deposited by the rivers.
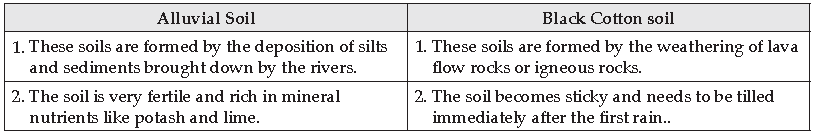
Question: Mention two differences between Alluvial Soil and Black Cotton Soil or Black soil.
Answer:
Question: Mention the two similarities between red soil and laterite soil.
Ans. Both are red in colour because of the presence of iron oxide / both are infertile soils / both are friable /
both are not moisture retentive /both are poor in organic matter.
Question: State the characteristic of each of the soils named below that makes them most suitable for crop cultivation:
(i) Black Soil
(ii) Red Soil
Ans. (i) Black soil- moisture-retentive/self-ploughing/ rich in lime, iron, cacium, alumina, potash/
deep and fine grained / clayey …
(ii) Red soil- rich in iron/porous/friable/does not get water-logged/responds to manures or
fertilizers /rich in potash …
Question: Mention two differences between Alluvial Soil and Red Soil.
Answer:

Question: Name the process by which Laterite soil is formed. Mention one disadvantage of this soil.
Ans. Formed in-situ as a result of leaching under typical monsoonal conditions with high temperature and
heavy rainfall with alternating wet and dry spells.
Question: State two differences between Bhangar and Khadar.
OR
State two differences between Khaddar and Bhangar soils.
Answer:

Question: Mention two differences in the alluvial soil of the northern plains and the alluvial soil on the coastal plains of India.
Answer:

Question: Name two states in India where Regur soil is found. In what way Regur soil help agriculture?
Answer: (i) Maharashtra
(ii) Gujarat
Regur soil help agriculture due to the following qualities-
(i) Regur soil has the quality of self-ploughing.
(ii) Due to the occurrence of deep cracks during period it helps in oxygenation.
(iii) It is moisture retentive.
Question:. Mention two characteristics of Laterite soil.
Answer: (i) Laterite soil is highly acidic in nature.
(ii) It is a leached soil and thus, infertile.
(iii) Rich in iron and poor in silica, lime, nitrogen and humus.
(iv) It is porous and coarse in texture.
Question: Name the soil which:
(i) covers the summits of the Eastern Ghats.
(ii) makes up the delta of the River Ganga.
(iii) is the most suitable for the cultivation of cotton.
(iv) is sticky when wet and cracks when dry.
Answer: (i) Laterite soils.
(ii) Alluvial soils.
(iii) Black soil, Regur soil or Black cotton soil.
(iv) Black soil.
Question: Name the soil which is formed due to high temperature and heavy rainfall with alternating
wet and dry periods. Name two states where this type of soil is found.
Ans. Laterite soil.
(i) Kerala
(ii) Odisha
Question: Write any two characteristics of Red Soil.
Answer: (i) It is porous, friable and coarse.
(ii) It does not retain moisture.
(iii) Rich in iron and potash.
(iv) Deficient in lime, nitrogen, phosphorous and humus.
(v) Responds to manures or fertilizers.
(vi) It is red in colour due to presence of iron oxides.
Question: Explain the formation of Laterite soil. Why is Laterite soil not suitable for cultivation?
Answer: Laterite soils are formed in-situ as a result of leaching under typical monsoonal conditions with high
temperature and heavy rainfall with alternating wet and dry spells.
This soil is not suitable for cultivation because it is highly acidic in nature and is not moisture retentive.
Question: Give reasons as to why –
(i) Red soil is red in colour?
(ii) Large tracts in Maharashtra are covered with Black soil?
Answer: (i) Red soil is red in colour due to high iron oxide content.
(ii) Large tracts in Maharashtra are covered with Black soil because it is formed from weathered lava rocks which have solidified during volcanic activity.
Question: Name an area of Black soil in India. Mention two crops grown in this soil.
Answer: Maharashtra. Two crops grown in this soil are Cotton and Sugarcane.
Question: Mention two ways by which soil can get nitrogen.
Answer: With the help of growing leguminous crops after harvesting of cereal crops and from the fertilizers,
soil can get nitrogen.
Question: Why is Laterite soil unsuitable for cultivation of crops? Name an area in India where this soil is found.
Answer: This soil is not suitable for cultivation because it is highly acidic in nature and is not moisture retentive.
This soil is found in the Summits of Eastern Ghats and Western Ghats, West Bengal, Odisha.
Question: Define ‘Leaching’. In which region, south of the Tropic of Cancer, can one firm soil formed by ‘Leaching’.
Answer: It is a process by which soluble substances from the soil are removed through percolation.
A region, south of the Tropic of Cancer, formed by ‘Leaching’ is the Highland areas of peninsular Plateau.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question: (i) Name the soil found on the summits of Eastern Ghats.
(ii) How is this soil formed?
(iii) Why is this soil not suitable for cultivation?
Answer: (i) Laterite soil.
(ii) Laterite soils are formed in-situ as a result of leaching under typical monsoonal conditions
with high temperature and heavy rainfall with alternating wet and dry spells.
(iii) This soil is not suitable for cultivation because it is highly acidic in nature.
Question: Name the soil which:
(i) is good for cultivation of sugarcane.
(ii) is acidic in nature.
(iii) occurs ex-situ.
Answer: (i) Alluvial soil
(ii) Laterite soil
(iii) Alluvial soil
Question: Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i) Alluvial soil differs in texture.
(ii) Black soil does get leached.
(iii) Khadar is more fertile than Bhangar.
Answer: (i) Alluvial soil is coarse in the upper valley of the rivers because the eroded matter is carried away by the fast flowing river but in the lower course, the river reduces its speed and the soil particles become finer due to attrition or
because the load itself gets eroded.
(ii) Black soil does not get leached because it is clayey and sticky and moisture retentive and therefore the rain cannot wash out the silicates.
(iii) Khadar is the newer alluvium which keeps getting replenished by the river bringing down more eroded material.
Question: Define the following:
(i) Pedogenesis.
(ii) Humus
(iii) Bhangar
Answer: (i) Pedogenesis- the process of soil formation.
(ii) Humus- the decayed organic matter that helps make soil fertile.
(iii) Bhangar- the older ,less fertile alluvial soil
Question: Name the soil which-
(i) is good for the cultivation of cashew nuts.
(ii) covers almost all of West Bengal.
(iii) is a result of leaching.
Answer: (i) Laterite soil
(ii) Alluvial soil
(iii) Laterite soil
Question: Differentiate between Transported soil and In Situ soil, quoting a suitable example for each.
Answer:

Question: With reference to Red soils in India, answer the following questions:
(i) Name two states where it is found.
(ii) State two advantages of this type of soil.
(iii) Mention two important crops grown in this soil.
Answer: (i) Karnataka and Tamil Nadu
(ii) 1. Wheat and rice are well grown on this soil.
2. Responds to manures or fertilizers.
3. Rich in iron and potash. [Any two points]
(iii) Wheat and Rice.
Question: Mention any three characteristics of black soil which makes the soil fertile.
Answer: (i) It is fine textured and clayey in nature.
(ii) Its moisture retentive and becomes sticky when wet.
(iii) Rich in lime, magnesium and iron.
Question: Give geographical reasons for the following:
(i) Laterite soil is not suitable for cultivation.
(ii) Red soils are red in colour.
(iii) Khadar soils are preferred to Bhangar soils.
Answer: Laterite soil is not suitable for cultivation because it is highly acidic in nature and is not moisture retentive.
(ii) Red soils are red in colour due to high content of iron oxide present in it.
(iii) Khadar soils are preferred to Bhangar soils because Khadar soils are fertile due to fine silts
and clay as they are replenished every year by floods.
Question: State the differences between Alluvial soils found in the lower courses and the upper courses of the rivers.
Answer:

Question: Give reasons for:
(i) Black soil is largely found in the Deccan Trap region.
(ii) Khadar is more fertile than Bhangar.
(iii) Soil erosion by wind is common in arid regions.
Answer: (i) Black soil is largely found in the Deccan Trap region because it is formed by the denudation of volcanic rocks, found in that region.
(ii) Khadar is composed of newer alluvium deposits and is fertile as it is formed of fine silt and clay.
(iii) Soil erosion by wind is common in arid regions because these regions are devoid of vegetation and moisture due to scanty rainfall and as such the soil is blown away by strong winds.
Question: Explain the following terms-
(i) Transported soil
(ii) In situ
(iii) Humus
Answer: (i) Transported soil- These soils are formed by the deposition of silts and sediments brought down by the rivers, e.g. Ganga, Yamuna, Brahmaputra, etc.
(ii) In situ- It is formed in their original position by the breaking up of parent rocks, e.g. Black Soil, Red soil, Laterite Soil, Desert Soil etc.
(iii) Humus- It is the organic matter present in the soil formed by the decomposition of plants and animals that helps to make soil fertile.
Question: Mention two characteristics of Black soil. Why is this soil agriculturally important?
Answer: Two characteristics of Black soil-
(i) It is fine textured and clayey in nature.
(ii) It has a self-ploughing quality.
(iii) Its moisture retentive and becomes sticky when wet and forms crack when dry.
(iv) Rich in lime, magnesium, potash, aluminium and iron.
(v) Poor in phosphorous, nitrogen and organic matter. This soil is agriculturally important because it is
moisture retentive and is rich in minerals like lime, magnesium, potash, iron and aluminium.
Question: How is Alluvial soil formed? Why is this soil agriculturally important?
Answer: These soils are formed by the deposition of silts and sediments brought down by the rivers. This soil is agriculturally important because it is rich in potash, lime and humus of the Ganga deltaic region.
Question: How is Red soil formed? State two reasons for the low productivity of Red soil.
Answer: Red soil is formed by the weathering of old hard crystalline and metamorphic rocks. The reasons
for its low productivity is due to deficiency of lime, nitrogen, phosphorous and humus in the soil.
Question: How is Regur soil formed? Mention four important properties of Regur soil.
Answer: Regur soil is formed by the weathering of lava flow rocks or igneous rocks. Four important properties
of Regur soil are-
(i) It is fine textured and clayey in nature.
(ii) It’s colour vary from deep black to chestnut brown.
(iii) Its moisture retentive and becomes sticky when wet and forms crack when dry.
(iv) Rich in lime, magnesium, aluminium and iron.
Soil Erosion- Causes, Prevention and Conservation
Short Answer Type Questions
Question: Name an area in India in which each of the following processes takes place:
(i) Sheet erosion
(ii) Gully erosion
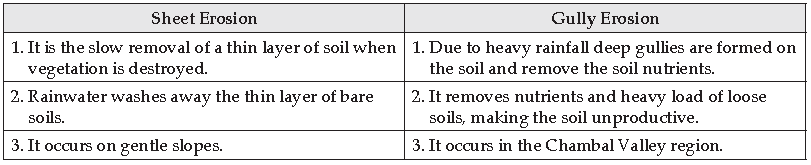
Answer: (i) Sheet erosion- The foothills of Shiwalik range.
(ii) Gully erosion- Chambal Valley region.
Question: What is soil erosion? Mention two steps that could be taken to prevent soil erosion.
Answer: Removal or destruction of top soil is called soil erosion.
Terrace farming / contour ploughing / crop rotation etc.
Question: State the geographic term for each of the following processes:
(i) The process by which soluble minerals dissolve in rain water and percolate to the
bottom, leaving the top soil infertile.
(ii) The process by which rain water, flowing in definite path removes the top soil, thus causing deep cuts to the surface of the land.
Answer: (i) Leaching
(ii) Gully Erosion
Question: State any two methods of controlling soil erosion.
Answer: Any two of the following: Terrace farming / contour ploughing Strip cropping Preventing over grazing Planting shelter belts and trees Constructing dams and plugging gullies Introducing better methods of cultivation, use of fertilizers, rotation of crops
Question: State two methods of controlling of soil caused by running water.
Answer: (i) Contour Ploughing- Contours act like bunds. Ploughing along contours on a slope prevents soil being washed away by rainwater or by surface run-off.
(ii) Constructing Dams- Rivers cause soil erosion, therefore, dams are built in the upper course to control the erosion.
Question: What is soil conservation? How does Re-afforestation help in soil conservation?
Answer: Soil Conservation is the effort made by man to prevent soil loss from erosion or reduced fertility caused by over usage. Re-afforestation is planting of trees in lieu of the number of trees being cut. It helps as the roots of the trees planted again hold the soil tightly and prevents it from eroding.
Question:. (i) Give one difference between Sheet Erosion and Wind Erosion.
(ii) Man is largely responsible for soil erosion. Give reason.
Answer: (i)

(ii) Man is largely responsible for soil erosion because he is involved in deforestation, overgrazing of domestic animals, shifting agriculture and faulty farming practices.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question: (i) What is meant by soil erosion?
(ii) How is it caused?
(iii) Give two methods adopted by the government to conserve soil.
Answer: (i) The removal or destruction of the top soil is called soil erosion.
(ii) Soil erosion is caused due to increasing population pressure on land, overgrazing by domestic animals, floods, deforestation and bad farming techniques.
(iii) (a) Scheme of Integrated Watershed Management.
(b) Scheme for Reclamation and development of ravine areas.
(c) Scheme for Control of Shifting Cultivation.
(d) National Project on Development and use of Bio-Fertilizers and National Project on Quality Control implemented.
(e) Rainwater Harvesting.
Question: Define the following:
(i) Sheet erosion
(ii) Soil Conservation
(iii) In situ soil
Answer: (i) Sheet erosion is the slow removal of a thin layer of soil by rainwater washing it away.
(ii) Soil conservation refers to the efforts made to prevent soil from getting eroded.
(iii) In situ means to develop in one area without any movement. It refers to residual soil.
Question: Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i) Alluvial soil is extremely fertile.
(ii) Need for soil conservation.
(iii) Re-afforestation should be practiced extensively.
Answer: (i) As it contains minerals like iron, potash, lime../ is loamy/has sufficient depth/is renewed
annually/ It is a transported soil which brings along lots of minerals …
(ii) As soil supports all plant life/to increase our agricultural output/ Various methods/ Efforts
made by man to check soil erosion and retain the fertility of the soil… [Any one point]
(iii) As it helps prevent soil erosion/holds the soil together/helps maintain the ecological balance/ checks global warming/reduces severity of drought…
Question: Give a geographical reason for:
(i) different regions in India having different kinds of soil.
(ii) black soil being suitable for the growth of cotton.
(iii) the conservation of soil as a natural resource.
Answer: (i) Different regions in India have different kinds of soil because of the different rocks which get weathered to form soil and the different agents of erosion minerals present / difference in temperature and rainfall.
(ii) Black soil is suitable for the growth of cotton because it is moisture retentive, has self ploughing qualities and is rich in lime, iron, potash, calcium, claying in nature.
(iii) Soil is a natural resource which must be conserved or else the land becomes barren and cannot be cultivated, food crops will have to be imported and the agro-based industries will suffer. Some kinds of soil are also required for construction purposes. It takes very long for an inch of top soil to be formed.
Question: Name two important agents of erosion. For each, state one method of controlling the erosion caused.
Answer: Two important agents of erosion are- Running Water and Wind.
(i) Running water- It can be controlled by methods like contour ploughing, terracing, plugging gullies and planting trees.
(ii) Wind- It can be controlled by the methods like strip cropping to check the impact of the winds, by planting trees along the edges of the fields, waste lands and on steep slopes.
Question: What is conservation of soil? Name any two farming techniques which help in soil conservation.
Answer: Soil Conservation is the preventing of soil loss from erosion or reduced fertility caused by over usage.
Two farming techniques which help in soil conservation are-
(i) Contour Ploughing
(ii) Terrace Farming.
Question: Explain the need for soil conservation in India. State two methods of soil conservation.
Answer: India is an agricultural country and its economy depends on it. So soil conservation is needed to
check floods, soil erosion, etc.
Two methods of soil conservation are-
(i) Contour ploughing
(ii) Planting trees or Afforestation
Question: Differentiate between Sheet erosion and Gully erosion.
Answer:
Question. State the effects of soil erosion. OR Why is soil conservation is nessesary ?
Answer: (i) Loss of fertile top soil together with its mineral nutrients, from the upper surface leads to gradual loss of soil fertility and agricultural productivity.
(ii) Lowering of the underground water table and decreasing soil moisture.
(iii) Drying of vegetation and extension of arid lands; Increase in the frequency of droughts and floods.
(iv) Silting of river and canal beds; Recurrence of landslides; Adverse effect on economic prosperity and cultural development.
Question. Name the sources which affect the formation of soil.
Answer: Changing temperature, running water and wind affect formation of soil.
Question. How were the soils of Gangetic Plains formed?
Answer: The alluvial soil of Ganga plain is formed due to the deposition of alluvium which is brought from the Himalayan region.
Question. What is loam ?
Answer: Alluvial soil which is a mixture of sand, clay and silt is called loam.
Question. Explain the two varieties of alluvial soil.
Answer: Khadar and Bhangar.
Question. Mention any two states where alluvial soils are found.
Answer: Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar etc.
Question. List four measures taken by farmers to conserve soil.
Answer: Planting trees, strip cropping, shelter belts, terrace farming.
Question. Soils of the Western Ghats are affected by wind erosion.
Answer: Due to high rate of deforestation on the Western Ghats they are affected by soil erosion.
Question. Black soil is suitable for the growth of cotton.
Answer: Black soil is very fertile, fine textured and moisture retentive, clayey in nature and thus suitable for growth of cotton.
Question. Reforestation should be practiced extensively.
Answer: Reafforestation should be practised extensively in order to compensate for the large scale deforestation occuring because of industrialization and other factors, which certainly results in soil erosion and land degradation.
Question. State the area where alluvial soil is found ?
Answer: (i) Alluvial soils are found on the plains of the Indus, the Ganga and the Brahmaputra rivers.
(ii) The Deltaic alluvium is found in the deltas of the Ganga-Brahmaputra, Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna and Kaveri river.
(iii) It is also found in the coastal strips of Peninsular India. It is also found in the plains of Gujarat.
Question. The need for conservation of soil as a natural resource.
Answer: As the soil supports all forests, grasslands and crops from which all living creatures on earth derive their food and clothing directly and indirectly
and also ensures agricultural prosperity, Hence there is a need for conservation of soil.
Question. Black soil is called as black cotton soil.
Answer: Black Soil is fertile, fine textured, clayey and moisture retentive and this is suitable for cotton cultivation. Hence it is called as black cotton soil.
Question. Name the crops which can be grown on alluvial soil ?
Answer: (i) The soils are fertile and suitable for cultivation of rice, wheat, sugarcane, cotton, tobacco, gram and oilseeds.
(ii) In the lower Ganga-Brahmaputra Valley they are useful for jute cultivation.
Question. Black soil is largely found in the Deccan Trap region.
Answer: Deccan trap is formed by weathering of volcanic rocks. So Black soil is largely found in the Deccan Trap region.
Question. Soil erosion by wind is common in arid regions.
Answer: In arid areas there is very little vegetation because of which it is exposed to high velocity winds causing soil erosion.
Question. How is laterite soil formed ?
Answer: (i) Laterite soils are formed from lateritic rocks.
(ii) It is formed in heavy rainfall regions where silica and lime are leached.
(iii) After this the rocks are subjected to weathering which forms laterite soils.
Question. State the disadvantages of laterite soil.
Answer: (i) Laterite soil is a porous soil; silica is removed from it by chemical action. It is poor in lime and magnesium and deficient in nitrogen.
(ii) It does not retain moisture and hence is not fertile.
(iii) It is acidic in nature as alkalis are leached.
Question. Man is largely responsible for soil erosion.
Answer: Man is largely responsible for soil erosion because more forests are being destroyed to house and feed the increasing population. Cutting of trees exposes the soil to water and wind which leads to soil erosion on a large scale.
Question. What are the characteristics of fertile soil ?
Answer: Fertile soil has the following characteristics:
(i) It contains adequate amount of moisture to supply essential nutrients to the p1ants
(ii) It has sufficient depth to enable the plants to grow their roots as per their requirement
(iii) It is rich in nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, that are necessary for basic plant nourishment
(iv) It contains organic matter that improves the structure of soil.
Question. Name the 3 river systems because of which alluvial soil is found in North India.
Answer: The Indus, the Ganga and the Brahmaputra.
Question. What is the disadvantage of clay content in the black soil ?
Answer: Black soils contain high clay content. These soils expand when wet and become difficult to plough.
Question. Name any four type of soils in India. Which one of them is the most important for agriculture?
Answer: (i) Alluvial, black, red, laterite are four types of soils in India.
(ii) Alluvial is the most important soil for agriculture.
Question. How is red soil formed ?
Answer: Un de r pro l ong e d we athe ring by rai nfal l , anci e nt c ry st al l i ne and metamorphic rocks of the Peninsular plateau break up to form red soils.
Question. Name one soil of volcanic origin commonly found in India. Name one crop widely grown on this soil.
Answer: (i) Black soil is the soil of volcanic origin commonly found in India.
(ii) Cotton crop is widely grown on this soil.
Question. Red soil is red in colour.
Answer: Red soil is red in colour as they contain large amount of iron oxides.
Question. What is Soil Erosion ?
Answer: The removal of the top soil cover by water, wind and human activities is called soil erosion.
Question. Name the natural agents of soil erosion.
Answer: The agents of soil erosion are running water, wind, glaciers.
Question. Khadar soils are preferred to Bangar soils.
Answer: Khadar soils are preferred to Bangar soils because they are more fertile as they are replenished every year by floods.
Question. What is soil erosion ?
Answer: The removal of top soil cover by water, wind, glaciers or by human activities is known as soil erosion.
Question. Name the states in which black soils are found.
Answer: Gujarat, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh.
Question. Name two important agents of erosion. For each, state one method of controlling the erosion caused.
Answer: Wind – strip cropping and shelter belts Running water – terrace farming
Question. Name any three states in India where Red soil is found.
Answer: Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh.
Question. Name the process by which Laterite soil is formed. Mention one disadvantage of the soil.
Answer: Laterite soil is formed by the process of leaching.
(i) It is poor in lime, silica and potash.
(ii) It is acidic in nature as alkalis are leached.
Question. Which is second largest soil group in India ?
Answer: Red soil form the second largest soil group in India.
Question. How is black soil formed? Why is it largely found in the plateau region of India ?
Answer: (i) Black soil is formed due to the denudation of volcanic rocks.
(ii) It is largely found in the plateau region of India because the plateau region of India (Deccan trap) is formed because of volcanic eruption and volcanic rocks are found here.
Question. Where is regur soils found in India ?
Answer: The regur soils are concentrated over the Deccan lava track which include parts of Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh and some parts of Tamil Nadu.
Question. Alluvial soils are also called Riverine soils.
Answer: Alluvial soil is also known as riverine soil because it is mainly found in the river basins.
Question. Deltaic alluvium is more fertile than the coastal alluvium.
Answer: Deltaic alluvium is more fertile than the coastal alluvium due to high precentage of organic content in it.
Question. Name the crops grown in red soil.
Answer: Rice, ragi, tobacco, sugarcane, potatoes etc.
Question. Name the areas which are mainly affected by soil erosion in India.
Answer: The worst affected areas include:
(i) The badlands of the Chambal and Yamuna rivers;
(ii) The piedmont zone of the Western Himalayas;
(iii) The Chotanagpur plateau region;
(iv) The Tapi-Sabarmati valley region in Gujarat;
(v) The regur soil area of Maharashtra; and
(vi) The dry areas of Rajasthan, Gujarat and Haryana.
Question. Describe the soil conservation methods.
Answer: (i) Terrace Farming : On hilly slopes, terraces act as bunds and prevent the soil from being washed away by running water. Terrace farming is practised with successful results in Japan, South-East Asia and the USA.
(ii) Shelter Belts : Farmers plant trees in several rows to check wind erosion. They are known as wind breaks.
(iii) Contour Ploughing : Ploughing along contours on a slope prevents soil being washed away by rainwater or by surface run off.
(iv) Strip Cropping : Crops are grown in alternate strips of land to check the impact of the winds.
(v) Construction of Dams : Rivers cause soil erosion. Dams are built in the upper course of rivers to control erosion of soil.
(vi) Plugging Gullies : The gullies made in the soil are plugged with deposition of silt during heavy rains.
(vii) Planting Trees : The trees, like in the case of shelter belts, are planted along the edges of the fields, the waste land and on steep slopes to prevent soil erosion as well as to enhance the capacity of the soil to retain water.
Question. Where is laterite soil found ?
Answer: Laterite soils mainly occur in the highland areas of the Peninsular Plateau, especially on the summits of the Sahyadris, Eastern Ghats, Rajmahal Hills and many other hills in the eastern parts of the peninsula.
Question. What is leaching ? OR What is desilication ?
Answer: Leaching is the process in which the nutrients get percolated down below the soil due heavy rainfall; thus leaving the top soil infertile. This is also called desilication



