Students should refer to Structure of Chromosomes Cell Cycle and Cell Division ICSE Class 10 Biology Board Exam Questions provided below with solutions. These will help the students to understand the type of questions which have been asked in previous year examinations and the type of solutions which the student should give to get good marks. You should also refer to ICSE Class 10 Biology Sample papers for more practice
ICSE Class 10 Biology Structure of Chromosomes Cell Cycle and Cell Division Important Questions
Students should learn the important questions and answers given below for Chapter Structure of Chromosomes Cell Cycle and Cell Division in Biology for ICSE Class 10. These board questions are expected to come in the upcoming exams. Students of ICSE Class 10th should go through the Important questions and answers ICSE Class 10 Biology which will help them to get more marks in exams.
Structure of Chromosomes Cell Cycle and Cell Division ICSE Class 10 Biology Board Exam Questions
Structure of Chromosomes Cell Cycle and Cell Division ICSE Class 10 Biology
Choose the correct alternative for each :-
Question: __________________ occupies the longest period in a cell cycle.
a. Interphase,
b. prophase
c. metaphase
Ans.
Interphase
Question: A duplicated chromosome has _______________ chromatids.
a. One
b. two
c. three
Ans.
two
Question: Abnormal and uncontrolled mitosis in an organ will result in ______________________ .
a. new organ
b. zygote
c. cancer
Ans.
cancer
Question: DNA content doubles during _________________ .
a. Interphase
b. Prophase
c. Metaphase
Ans.
Interphase
Question: The nuclear membrane disappears completely during ______________________ .
a. Early prophase
b. later prophase
c. Metaphase
Ans.
later prophase
Question: Chromatin fibre consists of _________________.
a. DNA only
b. DNA and Proteins
c. DNA and membranes
Ans.
DNA only
Question: Centromere is concerned with _________________ .
a. duplication of DNA
b. formation of spindle fibres
c. splitting of chromosomes
Ans.
splitting of chromosomes
Question: _____________ is not a stage of mitosis.
a. Prophase
b. Interphase
c. Metaphase
Ans.
Interphase
Question: The chromosomes are most distinct during ____________________ .
a. prophase
b. metaphase
c. anaphase
Ans.
metaphase
Question: Meiosis __________________ the parental chromosome number.
a. doubles
b. reduces
c. maintains
Ans.
reduces
Name the phase of Mitosis characterized by the following :
Question: The nucleoli and nuclear membrane disappear ____________ .
Ans.
prophase
Question: Sister chromatids move towards opposite poles ____________ .
Ans.
anaphase
Question: The nucleolus reappears ____________ .
Ans.
telophase
Question: The chromosomes become disorganized to form chromatin granules. ____________
Ans.
telophase
Question: The centrioles divide and move towards the poles ____________ .
Ans.
prophase
Question: The sister chromatids split longitudinally into two halves and undergo mutual repulsion.
___________
Ans.
anaphase
Question: The chromosomes arrange themselves upon the equator____________ .
Ans.
metaphase
Question: Chromatin threads condense to form thick threads called chromosome ____________.
Ans.
prophase
Give one word for each of the following :
Question: Small constriction on the chromosome where spindle fibres are attached ____________
Ans.
Centromere
Question: A complex consisting of DNA strand and a core of histones _____________.
Ans.
Nucleosome
Question: Exchange of genetic material between non sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes ___________.
Ans.
crossing over
Question: Division of the nucleus ____________.
Ans.
karyokinesis
Question: A type of chromosome where the centromere is located at the centre of the chromosome ____________ .
Ans.
Metacentric
Question: Period of rest in between two successive cell divisions ___________.
Ans.
interphase
Question: A type of cell division by which gametes are formed ____________.
Ans.
meiosis
Question: Type of cell division that leads to the formation of two identical daughter cells. _________.
Ans.
mitosis
Question: A special cell division by which sperms are produced ___________.
Ans.
meiosis
Question: Division of the cytoplasm _____________.
Ans.
cytokinesis
Question: Lateral pairing of homologus chromosomes____________.
Ans.
synapsis
Question: A repeating unit of which the DNA strand is made up of_____________ .
Ans.
Nucleotide
Question: Method by which new cells are formed from pre-existing cells ___________.
Ans.
cell division
Question: Network of long, thin, dark staining fibres seen in the interphase nucleus ____________.
Ans.
chromatin fibres
What kind of cell division takes place in each of the following?
Question: To repair a fractured bone _________
Ans.
mitosis
Question: To produce pollen grains ________
Ans.
Meiosis
Question: To produce sperms in a male __________
Ans.
Meiosis
Question: At the tip of the root __________
Ans.
mitosis
Question: To produce egg in the ovary ________
Ans.
Meiosis
Question: To increase length of a cartilage __________
Ans.
Mitosis
Question: To add girth to the stem _________
Ans.
Mitosis
Question: To replace worn out RBCs ___________
Ans.
Mitosis
Fill in the blanks.
Question: The nitrogen bases are joined to each other by __________ bonds
Ans.
hydrogen
Question: Each DNA strand is made up of repeating __________
Ans.
Nucleotides
Question: DNA molecule replicates in the __________ of cell cycle
Ans.
interphase
Question: In a DNA strand adenine is complementary to ________ and cytosine is complementary to ______
Ans.
thymine, guanine
Study the relationship between the first pair and complete and rewrite the second pair.
Question: mitosis : equational division :: meiosis : ________
Ans.
meiosis : reduction division
Question: Adenine : thymine :: cytosine :_________
Ans.
cytosine : guanine
Question: nuclear membrane disappears : Prophase :: nuclear membrane reappears: _________
Ans.
nuclear membrane reappears : Telophase
Question: plants : centrifugal : : animals :_________
Ans.
animals : centripetal
Question: skin cell : mitosis :: sperms :__________
Ans.
sperms : meiosis
Question: mitosis : 2 cells :: meiosis: ___________
Ans.
meiosis : 4 cells
Question: man : 46 chromosomes :: cat :_________
Ans.
cat: 38 chromosomes
Question: cytoplasmic division :: cytokinesis : nuclear division: ________
Ans.
nuclear division : karyokinesis
Each of the following statements are incorrect. Correct and rewrite the statements.
Question: The four nitrogenous bases are thymine, cytosine, penicillin and guanine.
Ans. The four nitrogenous bases are thymine, cytosine, adenine and guanine.
Question: If there are 23 pairs of chromosomes in a cell, there are 23 chromatin fibres inside the nucleus during interphase.
Ans. If there are 23 pairs of chromosomes in a cell there are 23 pairs / 46 chromatin fibres inside the nucleus during the interphase
Question: A nucleotide is made up of a nitrogenous base, a sulphate group and pentose sugar.
Ans. A nucleotide is made up of nitrogenous base, a phosphate group and a pentose sugar.
Question: Genes are specific sequences of bases on a chromosome.
Ans. Genes are specific sequences of nucleotides on a chromosome.
Question: Nucleosomes are group of histamine molecules surrounded by DNA strand.
Ans. Nucleosomes are group of histone molecules surrounded by DNA strands.
Question: What are the differences in cytokinesis of an animal cell and plant cell?
Ans.
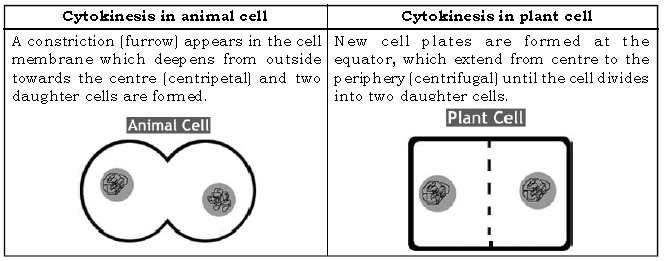
Question: What does a cell cycle consist of ?
Ans. The cell cycle involves two main stages :
a. Interphase : It is a period between two cell divisions.
b. Division / M phase – In this phase the cell divides.
The following diagram depicts the cell cycle.

Question: What are the differences in cytokinesis of an animal cell and plant cell?
Ans.

Question: What are the stages in a mitotic division ?
Ans.

a. Prophase (Pro : First)
b. Metaphase (Meta : after)
c. Anaphase (Ana : back)
d. Telophase (Telo : end)
Question: What is the Watson and Crick’s model of DNA ?
Ans.
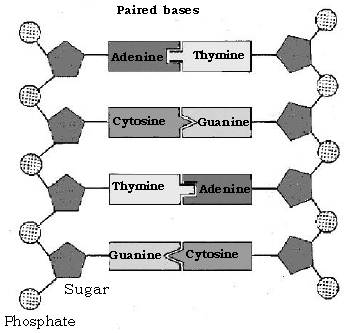
DNA is a double helix.
i. The two strands are spirally twisted around each other.
ii. The two strands are complementary to each other.
iii. Each strand is a polynucleotide strand i.e., it is made up of many nucleotides.
iv. Each nucleotide is made up of 3 components –
a. A pentose sugar.
b. A phosphate group represented by phosphoric acid.
c. A nitrogen base : which may be
i. Adenine ii. Thymine iii. Cytosine iv. Guanine
Adenine of one strand pairs with thymine of the other strand and there is a double hydrogen bond between them.
Cytosine of one strand pairs with guanine of the other strand and there is a triple hydrogen bond between them
Question: Given below is a diagram representing a stage during mitotic cell division in an animal cell.

Question: Mention two points of difference between mitosis and meiosis with regard to
a. The no. of daughter cells formed.
b. The chromosome no. in the daughter cells
Ans.

Question: Name the cell organelle that forms the ‘aster’
Ans. Centrioles
Question: Identify the above stage. Give a reason to support your answer.
Ans. Late prophase.Reason
(i) Sister chromatids attached to each other at a small region called centromere
(ii) Spindle fibres appear between daughter centrioles.
Question: Name the stage that follows this stage. How can this stage be identified.
Ans. Metaphase. This can identified by the arrangement of chromosomes in the equatorial plane.
Each chromosome gets attached to a spindle fibre by its centromere.
Question: Name the parts labelled 1 to 6.
Ans. 1. Centrioles 2. Sister chromatids
3. Spindle fibres 4. Aster
5. Chromosomes 6. Nuclear membrane
Question: Explain the structure of chromatin?

Ans. Chromatin is made up of DNA and proteins called histones.
a. Chromatin fibre appears like a string of beads. The beads are called nucleosomes.
b. Each nucleosome has a core of eight histone molecules around which a spiral of DNA is wound.
Question: What is Go phase?
Ans. In certain cells, the cell growth is arrested at a specific point during the G1 phase.
Thus the cell withdraws from cell cycle and the cell is said to be in Go phase. Eg., Nerve cells.
MEIOSIS
This cell division shows following features :
i. It takes place in the reproductive organs to form gametes (sex cells)
ii. One parent cell divides to form four daughter cells.
iii. Each daughter cell gets half the number of chromosomes to that in the parent cell.
Question: Draw neat labelled diagrams to show the different stages of mitosis in an animal cell with 4 chromosomes.
Ans.

Question: What is the significance of meiosis ?
Ans. a. Reproductive cells are formed by meiosis to form haploid gametes which then fuse to form a diploid zygote. Thus it helps in maintaining the number of chromosomes in a species.
b. During crossing over, genetic material is exchanged leading to variation.
c. Variation provides basis for evolution.
Question: Describe the events taking place in the various stages of karyokinesis of a cell undergoing mitosis. (Structure of Chromosomes Cell Cycle and Cell Division ICSE Class 10 Biology)

Ans. a. Prophase
Chromatin fibres, condense, become short and thick to form chromosomes. Each chromosome has 2 chromatids joined at the centromere. Centrioles divide, move past and occupy opposite poles. Each centriole is surrounded by radiating rays called ‘asters’ Spindle fibres appear between centrioles and chromosomes Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear.
b. Metaphase
The chromosomes arrange themselves on the equatorial plane Each chromosome gets attached to a spindle fibre by its centromere.
c. Anaphase
The sister chromatids of each chromosome separate. Chromatids move to opposite poles due to contraction of spindle fibres.
d. Telophase
Each chromatid /daughter chromosome uncondenses and forms a network of chromatin fibres. Nuclear membrane and nucleolus reappears.
Question: Given below is a diagram of a part of DNA. Study the diagram and answer the questions.

Question: How many nucleotides have been shown?
Ans. Four nucleotides.
Question: Label the parts 1 to 7.
Ans. 1. Phosphate 2. Pentose sugar (Deoxyribose)
3. Nitrogen base (Adenine)/(Thymine) 4. Double hydrogen bond.
5. Nitrogen base (Thymine)/(Adenine) 6. Nitrogen base (Cytosine)/(Guanine)
7. Nitrogen base (Guanine)/(Cytosine) 8. Triple hydrogen bond.
Question: How many strands are shown here ?
Ans. Two strands.
Question: What is a nucleotide ?
Ans. A nucleotide has 3 components:
a. A pentose sugar (S)
b. A phosphate group (P)
c. A nitrogen base which may be A,T, C or G

Question: Meiosis is called a reduction division. Explain.
Ans. Meiosis is a reduction division because during Anaphase–I of meiosis–I, the homologous chromosomes of a bivalent move towards the opposite poles. This results in the number of chromosomes getting reduced to half in each daughter cell. Thus each daughter cell formed is haploid.
Question: Who worked out the structure of DNA ?

Ans. Its structure was discovered by Watson and Crick for which they were awarded the Nobel Prize.
Question: Explain replication of DNA ?
Ans. i. DNA molecule duplicates during interphase of cell cycle.
ii. DNA helix opens at one end.
iii. Two strands become free bit by bit.
iv. New strands begin to form for the whole length of DNA.

Question: Why does cell division occur or why do new cells need to be produced?
Ans. New cells need to be produced for :
a. Growth : Addition of new cells leads to growth in size.
b. Replacement : The worn and torn out cells are replaced by new cells formed.
c. Repair : Repair of cells / tissue damaged in injury. Eg., Repair of a fractured bone or a cut in the skin.
d. Reproduction : In higher organisms, the cells in the reproductive organs undergo special division (meiosis) to form sex cells.
Question: The diagram below shows a certain phenomenon . Study it and answer the question.

Question: What is the significance of this phenomenon?
Ans. Crossing over causes exchange of chromatid material between chromosomes from the parent. This leads to a new combination of genes in the sex cells.
Question: i. Name the phenomenon being shown.
Ans. Crossing over.
Question: In which kind of cell division , does this phenomenon occur?
Ans. Meiosis.
Question: What kind of a pair of chromosomes does part 1 form ?
Ans. Homologous chromosomes.
Question: Define it
Ans. It is the exchange of genetic material between the non -sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes.
Question: Label the parts 2 and 3
Ans. Part 2 : Chiasma.
Part 3 : Mixing of maternal and paternal chromosomes.
Question: How many chromosomes will be visible in a dividing human cell?
Ans. 46 chromosomes.
Chromosomes occur in even numbers. There are two of each kind.. Thus there are 23 pairs of chromosomes visible.
Question: What is interphase ? Briefly explain the various stages of interphase.
Ans. It is a period between two successive cell divisions. It consists of 3 stages as follows.
i. G1 phase or First growth phase
The duration of this phase is 1/2 of the interphase.
During this phase :
– cell grows in size as cytoplasm increases.
– RNA and proteins are synthesized.
– Certain cell organelles like mitochondria divide.
In certain cells the cell growth stops at a specific time in G phase and they withdraw from the cell cycle and the cell is said to be in Go phase (quiescent phase)
ii. S phase or synthesis phase
The duration of this phase is ¼ of the interphase.
The DNA synthesis and replication takes place.
iii. G2 phase or second growth phase
The duration this phase is ¼ of the interphase.
Cell grows in size and produces proteins
Question: Mention three significant changes that occur in a cell during interphase.
Ans. a. DNA is synthesized.
b. Chromatin material duplicates.
c. Cell increases in size and prepares proteins.
Question: Define meiosis.
Ans. Meiosis is a type of cell division that gives rise to four reproductive cells (daughter cells) each with half the number of chromosomes to that of parent cell. Two consecutive cell divisions take place here.
Question: Define mitosis. Where does it take place ?
Ans. Mitosis is a type of cell division in which two identical daughter cells are produced by division of a parental cell. Mitosis occur in all body cells called ‘somatic cells’.
Question: Describe a typical chromosome as it would appear in the prophase of mitosis.
Ans. Each chromosome is visible as a condensed, short thick thread like structure. Each chromosome is made up of two identical threads, each called a chromatid. Sister chromatids of a chromosome are attached at a particular point called centromere
Question: What follows karyokinesis in cell division?
Ans. Cytokinesis, at the end of telophase, the cell undergoes cytoplasmic division called cytokinesis.
Question: Name the two types of cell divisions.
Ans. In sexually reproducing organisms there are two types of cell division.
a. Mitosis
b. Meiosis
Question: When and where does mitosis take place ?
Ans. Mitosis takes place in all the body cells i.e., somatic cells It takes place for:
a. Growth – new cells are added that leads to growth in size.
b. Replacement – old worn and torn cells are replaced.
c. Repair – injured cells / tissue are repaired by addition of new cells.
Question: When and where does meiosis occur in man ?
Ans. In sexually reproducing organisms like man, it occurs in reproductive organs to form the gametes i.e., the reproductive cells. In male it occurs in the testis to form sperms In female it occurs in the ovary to form egg / ovum.
Question: What is the significance of mitosis ?
Ans. a. Mitosis maintains the same number of chromosomes in daughter cells as in parent cell.
b. It promotes growth of an organism.
c. It helps to replace the worn out or dead cells in the body.
Question: What is the function of DNA ?
Ans. DNA has the following functions:
i. Transmission of hereditary characters.
ii. Control of metabolic activities of the cell.
Question: Where is DNA found ?
Ans. Deoxyribonucleic Acid is found in the nucleus as well in certain organelles like mitochondrion and chloroplast.
Question: Name the nitrogen bases of the DNA.
Ans. There are 4 nitrogen bases namely:
a. Adenine (A) b. Thymine (T) c. Cytosine (c) d. Guanine (G)
Adenine and guanine are called purines.
Cytosine and Thymine are called pyrimidines.
We hope you liked Structure of Chromosomes Cell Cycle and Cell Division ICSE Class 10 Biology notes provided above.






