Students should refer to The Circulatory System ICSE Class 10 Biology Board Exam Questions provided below with solutions. These will help the students to understand the type of questions which have been asked in previous year examinations and the type of solutions which the student should give to get good marks. You should also refer to ICSE Class 10 Biology Sample papers for more practice
ICSE Class 10 Biology The Circulatory System Important Questions
Students should learn the important questions and answers given below for Chapter The Circulatory System in Biology for ICSE Class 10. These board questions are expected to come in the upcoming exams. Students of ICSE Class 10th should go through the Important questions and answers ICSE Class 10 Biology which will help them to get more marks in exams.
The Circulatory System ICSE Class 10 Biology Board Exam Questions
The Circulatory System ICSE Class 10 Biology
Question. What is circulatory System?
Ans. Blood is the circulating fluid, the blood flow is powered by a muscular pump called the heart, which together with the vast network of blood vessels constitutes the circular system or cardio – vascular system
Question. Draw a labelled sketch of internal structure of the human heart.
Ans.

Question. Describe the Heart Beat in Humans ?
Ans. Heart Beat
It is also known as cardiac cycle. It is completed in 0.8sec. It is completed in the following 3 Phases:
Phase – I : Also known as auricular systole, it is completed in 0.1sec. In this phase the auricle contract and push the blood into respective ventricles.
Phase- II : Also known as vertricular systole. It is completed in 0.3sec. The ventricles contract and push the blood into pulmonary artey and aorta. The right ventricle pushes the blood in pulmonary artey whereas the left ventricle pushes the blood in aorta.
Phase – III : Also known as general pause. It is completed in 0.4sec. In this phase the auricle and ventricle relax to allow the blood to be collected in the auricles.
Question. What are blood corpuscles.
Ans. They consist of the cellular part of the blood, about 42 – 45% of blood is made up of blood corpuscles, they are Erythrocytes (RBC’s), Leucocytes (WBC’s) and Thrombocytes (platelets).
Question. How many blood groups are seen in a human beings? Explain it in brief.
Ans. There are four blood groups in human beings.
a) Blood group A : Individuals with agglutinogen A
b) Blood group B : Individual with agglutinogen B
c) Blood group AB : Both agglutinogen are present
d) Blood group O : Neither of agglutinogen are present
Question. Enlist the functions of blood platelets.
Ans. (a) Clotting of blood
(b) Phagocytosis
(c) Prevent undue loss of blood
(d) Healing of wounds
Question. Where are red blood cells produced and destroyed?
Ans. The red blood cells are produced in the marrow of long bones, while in embryonic stage they are formed in the liver and spleen- The worn out RBCs are destroyed in the spleen, liver and bone marrow.
Question. What are blood vessels ? Explain the type of blood vessels.
Ans. Blood vessels form a network of tubes that carry blood away from the heart,transport it to the tissues of the body and then return it to the heart. There are three main types :
1. Arteries : Arteries carry blood from the heart to the tissues. The aorta is the largest artery in human body, they further divide to form still smaller tubes called arterioles.
Arteries generally carry oxygenated blood except pulmonary artery. The wall of the arteries are thick and muscular being composed of elastic and collagen fibers. The arteries are generally deep seated and the blood flows through the arteries under pressure.
2. Veins : Veins carry blood towards the heart. The blood flowing through them is generally deoxygenated except pulmonary vein. The walls of the veins are much thinner than the arteries. Many veins, especially those in the limbs, which bring blood against the force of gravity contain valves that prevent backflow.
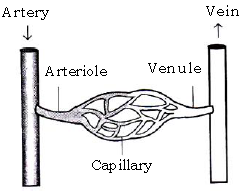
3. Capillaries: They are thin-walled microscopic blood vessels made upto single layer of epithelial tissue. Capillaries branch to form an extensive network throughout the tissue. Its branching nature helps to increase the surface area and the thin walls allow rapid exchange of materials between blood and tissue cells.
Question. Enlist the functions of leucocytes Functions of leucocytes
Ans a) Phagocytosis : Neutrophils and monocytes engulf and destroys the foreign bodies entering the blood.
b) Diapedesis: They move in amoeboid fashion and engulf microbes by squeezing out of blood capillaries.
c) Production of antibodies and antitoxins : Lymphocytes are involved in the production of antibodies while basophils and eosinophils produce anti-toxins.
d) Immunity: Immunity is the ability of an organism to resist infections.
Question. Give Chambers of the Heart?
Ans. Chambers of the Heart
The interior of the heart is divided into four chambers which receive the circulating blood.
1. The Atria (auricles): The two superior chambers are called the right and left atria. The atria are seperated by a partition called the inter-atrial septum. Located in the upper wall of the right atrium is the sino-atrial node (SAN) or the pacemaker. The pacemaker is a specialized tissue which regulates the contraction and relaxation of the heart muscles.
2. The Ventricles : The two inferior chambers of the heart are the right and left ventricles. They are seperated from each other by an interventricular septum. The atria and ventricles are separated by connective tissue that also form the valves.
Question. Label the diagram of Human Heart.
Ans.

Question. What is diapedesis?
Ans. Most of the WBCs are amoeboid and can produced pseudopodia with which they can squeeze through the walls of the capillaries into the tissues . This is called diapedesis.
Question. What is Pulmonary Circulation?
Ans. Pulmonary Circulation: The pulmonary circulation is maintained by the right side of the heart. It begins in the right ventricle which expels the blood into the pulmonary trunk. The blood flows into the vascular system of the lungs, becomes oxygenated and returns to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins.
Question. Enlist the step in clotting of blood?
Ans. Blood clotting prevents blood loss when blood vessels are damaged. This clotting is achieved in 3 steps.
(i) The platelets release a chemical compound thromboplastin at the site of injury.

These fibrin fibres form a mesh in which dead cells of the blood are entrapped and a thrombus (clot) is formed, which prevents the further loss of blood and helps in healing of wounds.

Question. State the function of the blood?
OR
Function of the circulatory system.
Ans. Blood is a liquid connective tissue and thus performs functions such as
1. Transportation of respiratory gases, hormones, nutrients.
2. Regulation of body temperature (thermoregulation).
3. Prevention against blood loss (through the clotting process).
4. Protection against invasion of foreign microbes through antibody and anti – toxin production (immunity)
Question. What are platelets (Thrombocytes)?
Ans. Blood platelets are oval or special cells numbering between 2,50,000 and 4,00,000 / mm3, lifespan is 2 – 3 days. They are produced in Red bone marrow from giant cells like Megakaryocytes. Human and mammalian platelets do not have nuclei.
Question. Sketch and label the diagram of cross section of Blood Vessels.
Ans.

Question. What is blood plasma?
Ans. The blood plasma is the fluid part, about 55 – 58% of blood is made up of plasma which contains, 90% water, 7 – 8% Blood proteins, 1% salt and other substances like hormones, respiratory gases, nutrients and excretory products.
Question. What are blood groups?
Ans. A groups of people having blood with similar agglutinogen (antigen) on its RBC’s are aid to belong to the same blood group
Question. What is Cardiac Cycle?
Ans. (a) Blood flows through the heart with a definite pattern of systoles and diastoles. The whole sequence of events in the heart beat constitute a cardiac cycle.
(b) It lasts for about 0.8 secs.
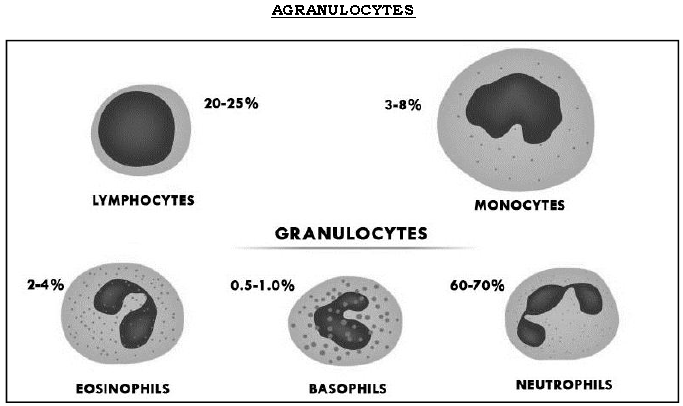
Question. Explain the types of Leucocytes (WBCs).
Ans. There are two types of WBCs :
A] Agranulocytes : These have clear cytoplasm. They develop from lymph nodes and red bone marrow. They are of two types lymphocytes and monocytes.
(i) Lymphocytes : Round nucleus, phagocytosis, antigen – antibody reaction (immunity)
(ii) Monocytes : Kidney shaped nucleus, phagocytosis.
B] Granulocytes : These develop from red bone marrow, have granules in the cytoplasm and possess lobed nuclei.
Three kinds of granulocytes are present, they are Eosinophils, Basophils and Neutrophils.
(i) Eosinophils : The nucleus is bilobed and the lobes are connected by strands. The cytoplasmic granules get stain with red acidic dyes like Eosin.
(ii) Basophils : The nucleus is large, irregular in shape. They stain with basic dyes like methylene blue.
(iii) Neutrophils : They are multilobed i.e., have 2 to 6 lobes. The granules stain with neutral dyes
Question. What is blood composed of?
Ans. The blood is composed of two main components
a) Plasma and
b) Blood corpuscles
Question. What is blood blister?
Ans. Some times an injury or a sharp pinch can cause the blood to clot inside blood vessels. This is called blood blister and is visible on the skin surface as a bluish mark.
Question. What are erythrocytes?
Ans. They are red blood cells, devoid of nucleus. They contain respiratory pigments haemoglobin which imparts red colour to blood.
Question. Give functions of erythrocytes.
Ans. The functions of erythrocytes are as follows
1. To transport oxygen to the cells and tissue of the body, with the help of haemoglobin, in the form of oxyhaemoglobin

3. They impart red colour to the blood.
Question. State a point of difference between Systole and Diastole.
Ans. Systole : It is phase of contraction of a chamber of the heart.
Diastole : It is the phase of relaxation of a chamber of the heart.
Question. Mention the abnormalities of Blood cells.
Ans. a) If the number of RBC’s increase to a high level condition is called Polycythemia.
b) If the number of WBC’s increase above the number of RBCs the condition is called Leukemia.
c) If RBC number decreases the condition is called Erythropenia
d) If the number of WBC’s fall the condition is called Leucopenia.
Question. What are Rhesus factor?
Ans. It is a substance present in the red blood cells of most people. Such people are said to be Rhesus positive (Rh positive)
People who do not have this substance in their blood, are said to be Rhesus negative (Rh negative)
Question. What is Heart Sound?
Ans. The first sound ‘LUBB’ is produced when the atrio-ventricular valves gets closed sharply at the start of ventricular systole. The second sound “DUP” is produced when at the begining of ventricular diastole, the semilunar valves at the roots of aorta and pulmonary artery get closed
Question. What is Blood?
Ans. Blood is a fluid connective tissue that performs a number of critical functions.
Question. What are anticoagulants?
Ans. Anticoagulants like heparin are present in blood which prevents blood clot.
Question. Give diagrammatic representation of the process of Double Circulation.
Ans.

Question. What is hepatic portal vein?
Ans. The hepatic portal vein is formed by the union of the capillaries in the liver. The vein carries the blood which contains nutrients absorbed from the alimentary canal to the liver. The liver checks these substances before they pass into general circulation by detoxification and deamination
Question. State the two phases of cardiac cycle.
Ans. The cardiac cycle comprises of two phases, the systole and the diastole.
(a) The systole: This is the phase during which the heart contracts. During systole, the auricle sends blood into the ventricles. Time taken for arterial systole is 0.1 — 0.16 sec. and ventricular systole is 0.3 secs.
(b) The diastole: This is the phase of rest or relaxation of the heart muscles. Arterial diastole lasts for 0.7 – 0.76 sec and ventricular diastole lasts for 0.5 — 0.56 sec. The entire cardiac cycle lasts for about 0.85 seconds.
Question. Name the components of circulatory system?
Ans. Blood, Lymph, Blood vessels, and heart.
Question. What is Double Circulation?
Ans. Heart is said to have double circulation because the blood passes through the heart twice.
1. It first leaves throught the right ventricle, goes to the lungs, and then returns to the heart (left artium)
2. Leaves through the left ventricle, circulates through the body, and again returns to the heart (right atrium)
Question. What are Leucocytes?
Ans. Leucocytes are WBCs are nucleated cells, ranging from 8 to 20 (microns). The main types are agranulocytes and granulocytes. They are the defence cells of the body.
Question. What is Systemic Circulation?
Ans. This circulation is maintained by the left ventricle which sends the blood into the aorta. Two of the several sub-division of the systemic circulation are coronary (cardiac) circulation and hepatic portal circulation.
Question. What is a pulse?
Ans. Pulse is a wave of distension and recoil. It is felt in some of the superficial artery such as the radial artery of the wrist.
Question. What is Lymph ? Give its functions.
Ans. Lymph
1. Lymph is a colourless fluid derived from the blood.
2. It is similar in composition to plasma and contains lymphocytes, blood proteins, waste matters but no erythrocytes.
Function of Lymph
1. Lymph provides a free exchange of substances between the blood and protoplasm of the cells.
2. It collects waste materials from the cells and brings them to the blood.
3. It transports nutrients to the tissues.
4. Lymphocytes of lymph play an important role in fighting against infection.
5. Lymph maintains the body temperature distributing the body heat.
6. It absorbs fats from the villi of small intestine and supplies it to the venous blood.
Question. How many times per day does the human heart beat ?
Ans. 72 beats per minute.
72 × 60 mins x 24 hours = 1,03,680 (more than one lakh times per day)
Question. What is Heart Rate ?
Ans. It is the total number of beats per minute. In a normal healthy human it is found to be 72 times per minute.
Question. Describe the internal structure of the Heart / Its conducting system.
Ans. Conducting System
Human heart is an autonomous organ controlled by autonomic nervous system and flow of blood into it. It is a highly rhythmic organ controlled by a precise conducting system.

Question. Describe the valves present in the heart.
Ans. Valves of the Heart
Valves are muscular flaps which prevent the blood which has once passed through it, to flow back through it. The opening and closing of valve is due to pressure difference across the valves. Two types of heart valves are distinguished – the atria-ventricular valves and the semi-lunar valves.
1. The atrio-ventricular valves: These valves separate the atria from the ventricles. They consist of fibrous tissues that grow out of the walls of the heart. The pointed ends of the flaps (or cusps) project into the ventricles. Tendon-like fibrous cords called chordae tendinae connect the pointed ends to small conical projections called papillary
muscles, located on the inner surface of the ventricles.
a. Tricuspid valve (Right atrio-ventricular valve): The right side of the heart possess the tricuspid valve (with three cusps) which prevents the backflow of the blood into the right auricle during contraction of the left ventricle.
b. Bicuspid valve (Mitral): Located on the left side of the heart, the bicuspid valve consisting to two flaps prevents the backflow of the blood into the left atrium during contraction of the ventricle.
2. Semilunar valves : These have three half-moon-shaped folds (pockets). Located in the arteries leaving the heart, they prevent the blood from flowing back into the heart.
a. Pulmonary semilunar valve: This valve lies in the opening where the pulmonary trunk leaves the right ventricle. It prevents the backflow of the blood into the right ventricle during its relaxation.
b. Aortic semilunar valve: Located at the opening between the left ventricle and aorta, this valve prevents the flow of blood from the aorta into the left ventricle during its relaxation








