Students should refer to The Reproductive System ICSE Class 10 Biology Board Exam Questions provided below with solutions. These will help the students to understand the type of questions which have been asked in previous year examinations and the type of solutions which the student should give to get good marks. You should also refer to ICSE Class 10 Biology Sample papers for more practice
ICSE Class 10 Biology The Reproductive System Important Questions
Students should learn the important questions and answers given below for Chapter The Reproductive System in Biology for ICSE Class 10. These board questions are expected to come in the upcoming exams. Students of ICSE Class 10th should go through the Important questions and answers ICSE Class 10 Biology which will help them to get more marks in exams.
The Reproductive System ICSE Class 10 Biology Board Exam Questions
The Reproductive System ICSE Class 10 Biology
Question. Why must a living organism reproduce?
Ans. Living organism must reproduce for the continuity of its generation.
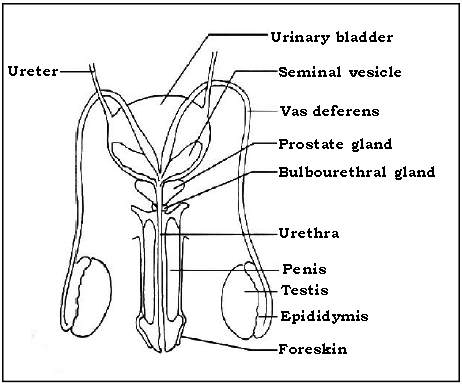
Question. Name the primary and accessory organs of human male reproductive system?
Ans. It consists of :
a. A pair of testes in the scrotal sac. The testes produce sperms at a temperature of 2º to 30 C lower than the body temperature.
b. Sperm ducts (Vas deferens) – Carry the sperms from the testis. The sperm ducts are a pair.
c. Accessory glands :- (Seminal vesicles – a pair, single prostate gland and pair of Cowper’s glands). These three accessory glands contribute to the formation of seminal fluid.
d. A penis – For transferring the sperms into the female.
e. Urethra – Urethra is contained inside the penis, carrying the sperms and the urine, but at different times.
Question. What is secondary sexual character?
Ans. Male and female sexes often show outward differentiating features called secondary sexual characters, or sexual dimorphism.
Question. How does the temperature regulation occurs in the testes?
Ans. Sperms are produced in the testes, at a temperature 2o to 30c lower than that of the body, this temperature is regulated through the movements of the scrotum wall. When it is too hot, the skin of the scrotum loosens, testes hang down, away from the body. When it is cold, the skin contracts and draws the testes closer to the body for warmth.
Question. What is the significance of the testes being located in scrotal sacs?
Ans. The high temperature of the body does not permit the maturation of sperms. Being in the scrotal sac, the testes escape too much body heat and the sperms remain 2o – 3oC below the body temperature.
Question. State the functions of seminiferous tubules?
Ans. a. The seminiferous tubules are inside the testis and their main function is to produce sperms by the process called spermatogenesis.
b. The interstitial cells which are between the semiferous tubules (also called Leydig cells) produce the male hormone testosterone
Question. What are the secondary sexual characters in human male?
Ans. Outwardly differentiating features for male and female are called secondary sexual characters. In human male, the secondary sexual characters are :
i) Hair on the chest, arms and legs.
ii) Presence of facial hair
iii) Deeper voice.
iv) Hips are smaller
v) Muscular body.
Question. Match the column A with those which are most appropriate in column B. You must rewrite the matching pair.
Column A Column B
1. Scrotum i. Energy giver.
2. Meiosis ii. Prostate gland.
3. Mitochondria iii. Common passage
4. Acrosome iv. Lower temperature
5. Urethra v. Urinary bladder
vi. Sperm head.
vii. Epididymis
viii. Haploid
Ans. Column A – Column B
1. Scrotum – i. Lower temperature.
2. Meiosis – ii. Haploid
3. Mitochondria – iii. Energy giver
4. Acrosome – iv. Sperm head
5. Urethra – v. Common passage.
Question. What is inguinal canal?
Ans The inguinal canal originally, is the one which allows the descent of testes, along with their ducts, blood vessels and nerves, into the scrotal sac.
Question. Name the two basic types of reproduction and bring out two main difference in
Ans. There are two basic types of reproduction – Asexual Reproduction and Sexual Reproduction.
The differences between asexual and sexual reproduction are

Question. Give the exact location and one function of each of the following :-
i. Prostate gland ii. Cowper’s gland. iii Urethra.
iv. Epididymis. v. Seminal vasicles vi. Vas deferens.
Ans. i) Prostate gland – Encircles urethra, at the base of urinary bladder, is a single gland
Function – The secretion is alkaline – and thus protects sperms by neutralizing the acidic environment of the uterus.
ii) Cowper’s gland:- A pair of oval glands, located beneath the prostate gland, one on either side of the urethra, Their ducts open into the urethra.
Function – a) Secretes mucus, which lubricates the end of penis during sexual intercourse.
iii) Urethra – It is a long duct which runs from the urinary bladder, through the penis and opens at its tip.
Function – It serve to carry urine as well as sperms at different times, during urination and copulation respectively.
iv) Epididymis – Is a comma-shaped, highly coiled organ- and has a connection with testis.
Function – Sperms leaves the testis and enter the epididymis.
a) It is a site for sperm maturation.
b) Sperms are stored in epididymis
v) Seminal vesicles – are a pair of glands, lying posterior and at the base of urinary bladder.
Function – They secrete an alkaline and sugary fluid and pass it on to ejaculatory duct which is a source of energy for motility of sperms.
vi) Vas deferens – Sperm duct or vas deferens, starts from the end of epididymis, ascends along the posterior border of the testis, penetrate the inguinal canal, enters the pelvic cavity where it loops over the urinary bladder and then descends to join the urethra, at the back of urinary bladder.
Function – Carry sperms, straight from epididymis to urethra
Question. What is semen?
Ans The secretion of seminal vesicles and the sperms produces a milky fluid, known as semen.
Question. What are the primary sex organs of human male and female called?
Ans. Sex organs of man is known as Testes.
Sex organs of woman is known as Ovaries.
Question. Name the passages in sequence through which the sperms are carried from the seminiferous tubules to the urethral opening in human male.
Ans. The passage of sperms in human male is as follows :-
Seminiferous Tubules → network of tubules → efferent ducts → epididymis → Vas deferens → urethra → urethral opening.
Question. Study the diagram and answer the following : –
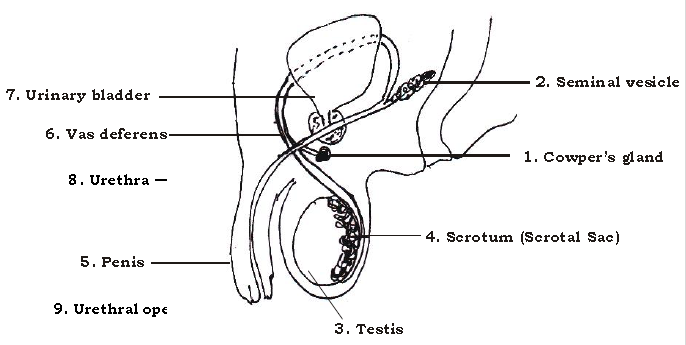
a. Why are the sperms produced in large numbers?
Ans. i. The life span of sperm is 3 to 5 days and it is only by chance the sperm can fertilize the ovum.
ii. The ovum is produced once in 28 days cycle and that too only one ovum.
iii. The ovum also remains mature for 2 days and within that time one, sperm must fertilise it, and that is why the sperms are produced in large numbers.
b. Identify the above diagram giving its view.
Ans. The above diagram is the male reproductive system of humans, as seen from side view.
Question. What is the role of male penis?
Ans. During sexual intercouse, [coitus / copulation] the erect penis is introduced into the vagina, where the seminal fluid its deposited. The propulsion of semen from the urethra to the exterior its called ejaculation. It also helps in elimination of urine, hence also refered as urinogenital.
Question. What is reproduction?
Ans. Reproduction is the process by which the continuity of a species is maintained.
Question. How does the uterus prepare for the reception of a zygote?
Ans. The uterus lining gets thickened in readiness to receive the zygote.
Question. Draw a well labelled diagram of a sperm or spermatozoa?
Ans.
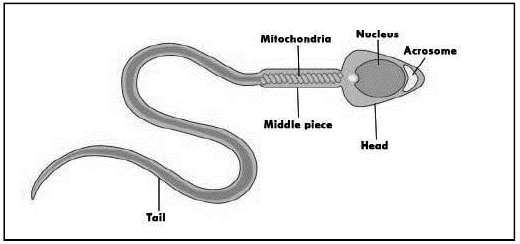
Question. What is the external female genitalia called?
Ans. The external female genitalia is called vulva, which contains indepedent openings of the urethra and vagina.
Question. What is the life span of an egg or ovum?
Ans. The life span of a mature ovum is about 2 days
Question. What is Graafian follicle? Mention the path of ova ?
Ans. As the egg grows larger, the cellular sac around, called follicle also enlarges and gets filled with a fluid and now it is known as Graffian follicle. The ova released from Graafian follicle is picked up by fimbriae passes through oviducal funnel into oviduct, remains there for fertilisation, if not moves into the uterus.
Question. Give one point of difference between prostate gland and cowper’s gland and in their nature of secretion.
Ans.

Question. How many ova are formed in a month?
Ans. Normally a single ovum is formed in 28 days in the ovary by the process called oogenesis.
Question. Name the human female reproductive system organs giving one function each.
Ans. The female reproductive system consist of the following :
a. A pair of ovaries, in the abdominal region, the main function being production of Ova or egg and production of important hormones like oestrogen and progesterone
b. A pair of oviducts (or Fallopian tubes), having funnel shaped Oviducal funnels.
The function of oviduct is to receive the egg released from the ovary.
c. Single, pear – shaped Uterus, for the growth and development of the embryo. Uterus opens into narrow cervix.
d. Vagina – Vagina starts from the lower end of the uterus, up to the outside. The great muscular elasticity of vagina’s walls – allows the passage of the baby during child birth and also receives the penis during mating called copulation and thus receives sperms.
e. Vulva – Also known as the external female genitalia contains separate openings of the urethra and vagina, guarded by 2 pairs of muscular lips like folds – inner being smaller called labia minora and outer, bigger pair, known as labia majora.
Question. What is clitoris?
Ans. On the upper part of vulva, just above the urethral opening, is a small erectile clitoris which is highly sensitive to touch.
Function : Increases sensitivity
Question. What happens to the uterus if fertilization takes place?
Ans. The fertilized egg starts developing and when it reaches the uterus it already forms a ball of numerous cells. The embryo forms the pit in the wall of the uterus and gets fixed in it (Implantation).
Question. Name the female reproductive system organs 1 to 6 in the given diagram below
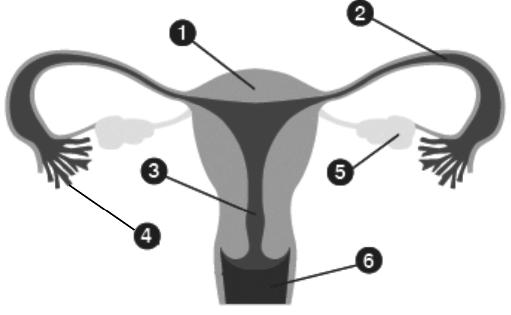
Ans. 1. Uterus 2. Oviduct or Fallopian tube 3. Cervix 4. Oviduct funnel 5. Ovary 6. Vagina with fimbrae
Question. Name the two hormones secreted by the follicles with their functions.
Ans. Follicles secrete oestrogen prior to ovulation, which is responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sexual characteristics. The second hormone progesterone prepares the uterus for receiving the embryo.
Question. The following diagram represent the side view of the female reproductive system. Label all the parts in the diagram 1 to 8
Ans.

Question. What happens to the uterus, it fertilization has failed to take place?
Ans. The uterus lining (endometrium) which has got thickened earlier in readiness to ertilization and thereby implantation of the embryo, breaks down, causing discharge of blood and mucus, resulting in menstruation.
Question. What happens to the follicle, after releasing the egg?
Ans. The remnant of the follicle, after releasing the ovum, persists for some time to convert into yellow mass now known as corpus luteum.
Question. With the help of T.S. of ovary (human), explain in short, maturation and ovulation of the ovum.
Ans.
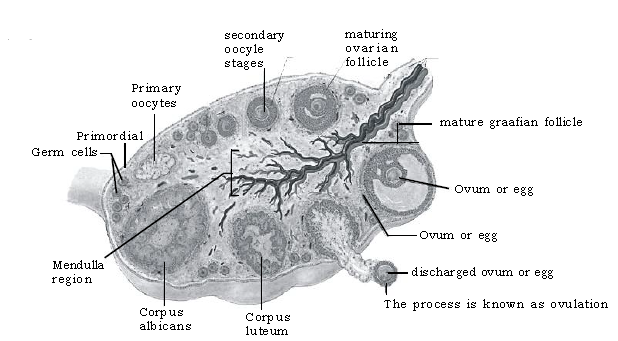
a. The reproductive cycle (menstral cycle) in female continues from about the age 12 – 13 yrs. to 45 – 50 yrs. and this period is marked by a characteristic event, repeated almost every month (28 day with minor variations) in the form of menstrual flow.
b. In the ovary the egg grows larger and become mature Graafian or ovarian follicle.
c. When the Graafian follicle is mature enough or ripe, it comes to the edge of ovary,burst and release the ovum into the oviducal funnel and this process is called ovulation.
Question. What is copulation (or Coitus) ?
Ans. Mating of male and female, to release the sperms in the vagina of female is called coitus or copulation.
Question. How is placenta formed?
Ans. The placenta is formed of two sets of minute finger-like processes called the villi. One set of villi are given out by the uterine wall and the other set by Allantois (an extension from the embryo). The two sets of villi get interlocked, but they never open into each other.
Question. What is the real composition and function of semen?
Ans. The white, sticky fluid containing millions of sperms is a discharge from the male reproductive system. This secretion contains seminal vesicle fluid, prostate gland and cowper’s gland fluid. This helps the sperms to get their nutrition and motility to swim and reach the fallopian tube of female.
Question. Give Reasons.
a. The umbilical cord is the lifeline of the foetus.
Ans. The capillaries in the placenta are connected to an artery and vein which runs into the umbilical cord from the embryo’s abdomen. The maternal blood carries nutrients, oxygen, hormones and water to the placenta, from where they are passed on by diffusion to the blood vessels of the umbilical cord, which is connected to the embryo. That is why umbilical cord is called the life line of the foetus.
b. The mother’s blood does not circulate through the embryo.
Ans. If there was a direct continuity of blood between the mother and the foetus, without a placenta, the relatively high pressure of the mother’s blood, would seriously damage the soft and very delicate tissues of the foetus.
Question. Describe the process of fertilization in human.
Ans.During sexual union or copulation (mating or coitus), the sperms are discharged into the vagina of the female. These sperms, swim up to the uterus and further up to the fallopian tube. It the sperm meets an ovum, it fuses with it, to form diploid zygote and this process is called Fertilisation.
Question. Which is the most favourable time for conception in human female?
Ans. In human female, soon after ovulation (after 14 days) of the onset of menstruation, are the most favourable time for conception.
Question. What happens to the just fertilised egg (zygote)?
Ans. The zygote divides and redivides and forms a ball of cells called blastocyst, which forms a pit in the wall of the uterus (now called endometrium) and gets fixed to it.
Question. How does the new born announces its arrival?
Ans. The new – born announces its arrival by letting out sharp cry.
Question. A single ejaculation by human male contains how many sperms?
Ans. A single ejaculation by human male contains about four hundered million sperms.
Question. What is the result of implantation?
Ans. The result of implantation (conception), produces the state of pregnancy.
Question. What does the Ist cry of the baby signify?
Ans. The first cry of the baby signifies the nature’s clearing process of the baby’s respiratory passage (the baby’s Ist breath – on its own)
Question. What are the functions of placenta?
Ans. i. The foetal blood gives off excreetory material like – CO2 and urea, into the mother’s blood by diffusion.
ii. By diffusion, the mother’s blood supplies O2 and food substances to the foetal blood.
iii. Placenta also acts as an endocrine gland, producing hormones called oestrogen and progesterone.
Question. What is Amnion?
Ans. Amnion is a sac which develops around the embryo, even before the formation of allantois. It is filled with amniotic fluid.
Question. Match the items in column I, with those in column II and write down the matching.

Question. Describe the role of pituitary in the birth process.
Ans. The pituitary releases the hormone oxytocin which causes contraction of the uterus during childbirth.
Shortly after birth, it releases the hormone prolactin which stimulates the breasts to produce milk.
Prolactin also inhibits or blocks the action of other pituitary hormones on the ovaries so that while a mother is nursing (feeding) her baby she is less likely to become pregnant again.
Question. For how long does fixation take place?
Ans. The fixation of the ball of cells (blastocyst) to the endometrium happens in about a week’s time .
Question. Diagram below is 8 weeks old foetus of human.
Ans.

Question. What is the function of amniotic fluid?
Ans. i. The amniotic fluid acts as a cushion for the embryo and protects it from jerks.
ii. Prevents the embryo from mechanical shocks.
iii. The fluid also prevents sticking of the foetus to the amnion.
Question. What is Artificial insemination ?
Ans. The semen, collected from the male is introduced into the women by means of a syringe at the time of ovulation. There are sperm banks where sperms are stored in liquid nitrogen for several years without losing fertility.
Question. Give the stages in the development of human embryo.
Ans. Man (testis) × Women (ovary )
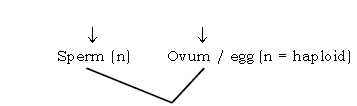
Fertilization zygote (2n) = diploid but single cell stage
Cleavage (division of cell into 2, 4, 8, 16 etc)
↓ ↓
MORULA – Ball of cells.
↓
TROPHOBLAST – single layer of cells.
↓
BLASTOCYST – Inner mass of cells
↓
IMPLANTATION – After 7 to 8 days of fertilization
↓
DEVELOPMENT OF EMBRYO
(3 weeks) – Tiny organism – about the size of pea
↓
ADVANCED EMBRYO – Heart and blood vessels are formed
(5 weeks)
↓
FOETUS – Limbs appear and resembles human being
(8 weeks)
↓
INFANT – born at the end of 40 weeks / 280 days.
Q.27. Explain the concept of formation of twins ?
Ans. Identical twins : are formed when one fertilized egg splits into two. Each part develops into separate individuals but shares a common placenta. Identical twins bear a striking resemblance to each other and are always of the same sex.
Fraternal twins : (or non-identical twins) occur when two separate eggs are fertilized at the same time, but by different sperms. Each egg develops independently on individual placenta. Fraternal twins may be of the same sex or of opposite sex and they resemble or differ from each other as much as any other brother or sister who are not twins.

Siamese twins : Siamese twins are identical twins, born joined to each other at some point of their bodies.

Question. How long the sperms remain alive in female genital passage?
Ans. The sperm may remain alive for few days, but their fertilizing power is limited to one or two days only.
Question. How does oestrogen and progesterone help?
Ans. These two hormones help in making the uterus more vascular (full of blood) and help in implantation to a great extent – these also help in maintaining pregnancy.
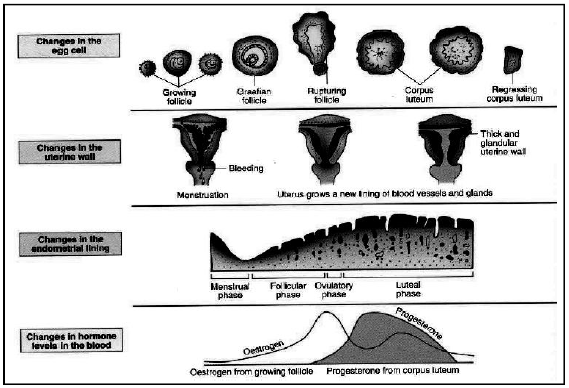
Question. Stages of Menstrual phase.
Ans. Menstrual phase : It lasts for 3-5 days during which the uterine lining is shed off with blood flow.
Follicular phase : It starts from the 5th day and lasts up to the 13th day, i.e., the onset of menstrual cycle. During this phase, the ovary begins to form a new egg that grows inside a follicle and matures to form the Graafian follicle. The Graafian follicle produces a hormone called oestrogen. This hormone stimulates the uterus to prepare itself to receive the ovum. The uterine wall becomes thickened and develops a dense network of blood vessels.
Ovulatory phase : On the 14th day of menstrual cycle the Graafian follicle ruptures and releases the ovum. The release of ripe ovum by the rupture of Graafian follicle is called ovulation. The released egg is picked up by the fimbriae of ostium. It descends through the oviduct (fallopian tube) by the contraction of its muscular wall.
Luteal phase : Following the discharge of the ovum, the cells of ruptured follicle form corpus luteum. If the liberated ovum is fertilised, the corpus luteum remains intact and continuously secretes the hormone progesterone and the embryo is implanted in the wall of uterus. During pregnancy. further menstrual cycles stop. If the ovum is not fertilised, the corpus luteum stops producing progesterone hormone due to which the lining of uterus breaks down. The periodic discharge of blood, mucus and epithelial cells from the lining of the uterus is called menstruation. Menstruation occurs every 28 days and lasts 4 to 5 days. Luteal phase lasts for 15-28 days
Question. What is Amniocentesis ?
Ans. It is process in which the amniotic fluid is taken from the mother’s womb to detect any chromosomal or genetic defect in the feotus. [This process is misused as the sex of the foetus is known, as female foetus are killed on a large scale].

Question. What facilitates the entry of sperm into the egg?
Ans. The acrosome at the top of the head of the sperm, secretes an enzymes called lysin, which facilitates the entry of sperm, by dissolving the wall of the ovum.
Question. Draw a neat labelled diagram of Male reproductive system (front view).
Ans.
Question. Describe the process of child birth or delivery.
Ans. The female body prepares for childbirth and delivery in several ways :
1. The heart is enlarged slightly and blood volume increases by nearly 25% in order to care for the requirements of the baby.
2. The mouth of the womb, instead of being hard and fibrous, becomes soft and pliable. This is because the cervix, which normally has a diameter no larger than a drinking straw has to dilate by five or six inches to permit passage of the baby.
3. Muscle fibres of the birth canal elongate and become more elastic. This is because the shorter fibres normally present would never be able to withstand the stress of delivery.
4. A new system of blood vessels develop.
5. The tissues of the birth canal, secrete a starchy substance glycogen which changes into glucose and finally into lactic acid. This highly acidic environment is a natural protection against bacteria.
6. Under the influence of hormones, the ligaments holding the pelvic bones soften to allow the widening of the pelvic joints.
7. Under pressure of increased sex hormones, breasts enlarge, develop an intricate network of milk ducts and an even more elaborate system of blood vessels to nourish these ducts
Question. How does the retention of blood within penis help human male?
Ans. This causes the penis to enlarge, harden and become erectile.
Question. Explain the concept of Test-Tube baby.
Ans. Test-Tube babies : Test tube babies are produced by collecting egg cells from a female and sperm from a male, and allowing them to fertilise outside the body in a test-tube or small dish. The egg has to be in exactly the right state for fertillisation. If the egg is removed too soon, it would not be mature and if removed too late the pregnancy might be abnormal. Usually there is a surge of luteinising hormone that triggers the final stages of egg maturation, and exactly 36 hours after the hormone peak, the egg is ready to be harvested. Once the egg is successfully harvested, it is mixed with the sperm and kept at body temperature in exactly the right mixture of salts, glucose, and a chemical called pyruvate for fertilisation to be successful. Fertilisation usually occurs within 12 to 48 hours. After fertilisation the cell begins to divide. This process must continue for several cycles before the embryo is sufficiently well developed to attach to the wall of the uterus. The embryo is transferred from the test-tube into the uterus through the cervix. It may float in the uterus for about three days before it implants itself in the endometrium. The rest of the pregnancy proceeds just like a natural pregnancy.
Question.. Draw a neat labelled diagram of female reproductive system (front view)
Ans.
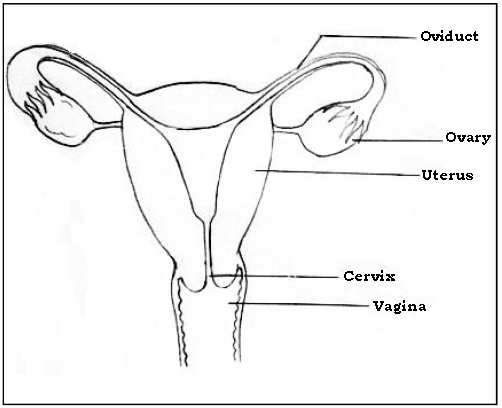
Question. Choose the correct alternative from those given in the brackets.
1. Storehouse for sperms (Vasdeferns / epididymis / seminal vesicles)
Ans.
epididymis
2. Human gestation period is about (250 days / 280 days / 260 days).
Ans.
280 days
3. These parts of the human sperm enter the ovum during fertilization. (tail and middle piece / head and tail / head and middle piece.)
Ans.
head and middle piece
4. In the female, equivalent of the penis is the (Vestibule / Hymen / Clitoris)
Ans.
Clitoris
5. The ruptured Graafian follicle persists and converts into an endocrine tissue called (Corpus luteum / Corpus albicans)
Ans.
Corpus luteum
6. One egg is normally released from one ovary in the human females after (28 days /40 days / 38 days)
Ans.
28 days
7. The middle piece of sperm in human male reproductive system has abundant (Mitochondria / acrosome)
Ans.
Mitochondria
8. The expulsion of the foetus from the body of mother in a human female is called (gestation / parturition)
Ans.
parturition
9. The ovaries produce ova by the process called (Spermatogenesis / Oogenesis)
Ans.
Oogenesis
10. Fertilization of the human egg normally occurs in the (Uterus / Fallopian tube / Vagina)
Ans.
Fallopian tube
Question. State whether the following statements are True (T) or False (F). If it is False, write the correct answer.
a. Fertilisation occurs in vagina
Ans.
False – Fertilization occurs in fallopian tube or Oviduct.
i. Uriniferous tubule is a part of testis.
Ans.
False – Seminiferous tubule is a part of testis.
f. Fimbriae fringing the oviducal funnel, push the released ovum into uterus
Ans.
True
c. Nutrition and O2 diffuse from the mother’s blood into the foetus’s blood through amnion.
Ans.
False – It is through the placenta.
e. Zygote is the product of fusion of male and female gametes.
Ans.
True.
b. Uterus is also known as birth canal –
Ans.
False – Vagina is also known as birth canal.
h. Amniotic fluid acts as a shock absorber.
Ans.
True
d. Gestation period in humans is about 380 days.
Ans.
False – Gestation period in humans is about 280 days.
g. Menarch is the stoppage of menstruation.
Ans.
False – Menarch is the beginning of menstruation.
Question. Choose the odd one out :
1. Relaxin ; Cervix dilates ; Amniotic sac ruptures ; Child birth ; Follicle.
Ans
.Follicle
2. Seminiferous tubule ; Ovum ; Epididymis ; Sperm duct ; Urethra.
Ans
.Ovum
3. Sperm ; Implantation ; Fertilisation ; Ovum ; After birth.
Ans.
After birth
4. Sperm ; Implantation ; Fertilisation ; Ovum ; Prolactin.
Ans
.Prolactin
5. Oestrogen ; Progesterone ; Testosterone ; Prolactin.
Ans.
Testosterone
6. Graafian follicle ; Ostium ; Uterus ; Fallopian tube
Ans.
Graafian follicle
7. Puberty ; Menopause ; Menstruation ; Menarche ; Reproductive age.
Ans.
Menopouse
8. Ovary ; Fallopian tube ;Ureter ; Uterus.
Ans.
Ureter
Question. Give one term for each of the following
1. The permanent stoppage of menstrual cycle.
Ans.
Menopause
2. The release of the mature egg by the rupture of the Graafian follicle.
Ans.
Ovulation
3. The onset of reproductive phase in a young female.
Ans.
Menarche
4. The process of fusion of ovum and sperm.
Ans.
Fertilization
5. The expulsion of the foetus from the body of human female.
Ans.
Parturition
6. Fixing of developing zygote (blastocyst) on the uterine wall.
Ans.
Implantation
7. Rupture of follicle and release of ovum from the ovary .
Ans.
Ovulation
8. The process by which ova are produced in the ovary.
Ans.
Oogenesis
9. The period of intra – uterine foetal development.
Ans.
Gestation
11. Monthly discharge of blood and disintegrated tissues in human female.
Ans.
Menstruation
12. The attachment of the fertilised egg to the roof of the uterus.
Ans.
Implantation
13. The process by which sperms undergo maturation.
Ans.
Spermatogenesis
Question. Choose the most appropriate answer in each of the following
1. Number of ova produced in the life time of a women is approximately –
a. 50
b. 500
c. 5000
d. millions
Ans.
500
2. Route followed by a sperm.
a. Vas deferens → Epididymis →Urethra
b. Urethra → Epididymis →Vas deferens
c. Epididymis → Urethra → Vas deferens
d. Epididymis → Vas deferens → Urethra
Ans.
Epididymis → Vas deferens → Urethra
3. Fertilization occurs in –
a. Ovary
b. Oviduct
c. Uterus
d. Vagina
Ans.
Oviduct
4. Reproduction is
a. Increase in population
b. Increase in number of parents
c. Production of new individuals
d. Production of identical individuals
Ans.
Production of new individuals
5. If the twins are a girl and a boy, then it is sure that
a. It is produced by 2 eggs fertilized by two sperms
b. It is produced by one eggs fertilized by two sperms
c. It is produced by two eggs fertilized by one sperm
d. It is produced by one egg, fertilized by one speerm which splits later.
Ans.
It is produced by 2 eggs fertilized by two sperms
6. After a sperm has penetrated the ovum in the process of fertilization, entry of further sperms is prevented by :
a. developed of the vitelline membrane
b. development of pigment layer
c. condensation of yolk
d. formation of a fertilization membrane
Ans.
formation of a fertilization membrane
7. Development of Graafian follicle and ovulation are under the control of
a. Oestrogen
b. Progesterone
c. Relaxin
d. FSH and LH
Ans.
FSH and LH
8. Time taken by zygote to get implanted
a. few months
b. One month
c. Three weeks
d. about seven days
Ans.
About seven days
9. The middle piece of sperm provides :
a. Chromosomes
b. Energy
c. Food
d. Genes
Ans.
Energy
10. The number of sperms present in one single ejaculation is
a. 1 – 2 million
b. 10 – 20 million
c. 300 – 400 million
d. 30 – 40 million
Ans.
300 – 400 million
11. When pregnancy does not occur, the life of corpus luteum is about –
a. 4 days
b. 10 days
c. 14 days
d. 28 days
Ans.
28 days
12. During sexual reproduction, chromosome number is restored to the normal dilpoid in the process of –
a. Fertilization
b. Spermatogenesis
c. Oogenesis
d. all of these
Ans.
Fertilization
13. Major part of the semen is secreted by
a. Cowper’s gland
b. Pineal gland
c.Prostate gland
d. Seminal vesicles
Ans.
Seminal vesicles
14. Sexually reproducing organism contributes to his offspring
a. All their chromosomes
b. 1/4th of chromosomes
c. half of their chromosome
d. None of thier chromosome
Ans.
Half of their chromosome
15. During child birth, the main function of relaxin is :
a. To increase the force and frequency of uterine contractions.
b. To increase the opening of vagina
c. To relax and loosen the uterine cavity
d. To increase the diameter of cervix
Ans.
To relax and loosen the uterine cavity
Question. Given below are groups of terms. In each group the Ist indicates the type of relationship that exists between the terms. Rewrite and complete the second pair on a similar basis.
1. Baby out : childbirth :: Placenta out :
Ans.
Baby out : ‘childbirth” :: Placenta out : after birth
2. Testes : Sperms :: Ovaries :
Ans.
Testes : Sperms :: Ovaries : Ova
3. Production of sperms : Spermatogenesis :: Production of ova :
Ans.
Production of sperms : Spermatogenesis :: Production of ova : Oogenesis
4. Ovary : Oestrogen :: Testis :
Ans.
Ovary : Oestrogen :: Testis : Testostrone
5. Uterus : Implantation :: Fallopian Tube :
Ans.
Uterus : Implantation :: Fallopian Tube : Fertilization
Question. Rewrite the terms in correct order so as to be in a logical sequence –
1. Graafian follicle, Ostium, Ovum, Uterus, Fallopian tube
Ans.
Graafian follicle → Ovum → Ostium → Fallopian tube →Uterus
2. Sperm duct, penis, testes, sperms, semen
Ans.
Testes → Sperms → Sperm duct → Semen → Penis
3. Implantation, Ovulation, Child birth, Gestation, Fertilization
Ans.
Ovulation → Fertilization → Implantation → Gestation → Child birth
4. Vas deferens, Seminiferous tubule, Epididymis, Urethra.
Ans.
Seminiferous Tubule → Epididymis → Vas deferens → Urethra
5. Coitus, Ovum, Sperm, Sperm duct, Urethra, Vagina.
Ans.
Sperm → Sperm duct → Urethra → Vagina → Ovum → Coitus.
Question. Name the following.
1. The process by which the ovaries form ova.
Ans.
Oogenesis
2. The structure where the embryo develops.
Ans.
Uterus
3. The accessory gland in human males whose secretion activates the sperms.
Ans.
Seminal vesicles
4. The canal through which the testes decend into the scrotum just before birth in human male child.
Ans.
Inguinal canal
5. The fully developed sac containing a mature egg in it.
Ans.
Graafian follicle
6. The hormone which plays an important role in child birth.
Ans.
Oxytocin
7. The tubular knot fitting like a cap on the upper side of the testis.
Ans.
Epididymis
8. The membrane which protects the foetus and encloses a fluid.
Ans.
Amnion
9. The physiological process by which CO2 and urea, are excreted by the foetus.
Ans
.Diffusion
10. Finger – like projections of the oviducal funnel.
Ans.
Fimbriae
11. The body part in which the testes are present in a human male.
Ans.
Scrotal sac
12. The tube that leads from ovary to the uterus.
Ans.
Fallopian tube / Oviduct
13. The fluid surrounding the developing embryo.
Ans.
Amniotic fluid
14. The duct in the male reproductive system where sperms are stored.
Ans.
Epididymis
15. The cells that secrets male hormone.
Ans.
Interstitial cells
16. The hormone produced by the ovary.
Ans.
Oestrogen, Progesterone and Relaxin
17. The part where the sperms are produced in the testes.
Ans.
Seminiferous Tubules
18. The stage of maturity when an individual develops secondary sexual characteristics and is capable of sexual reproduction.
Ans.
Puberty
19. The lower part of the birth canal.
Ans.
Vagina
20. The hormone secreted by the Graafian follicle.
Ans.
Oestrogen







