Get ICSE User defined Methods Solutions for class 10. It will help you to make good preparation before attending the ICSE Board exam. We have provided you with User defined Methods Solutions class 10 to score good marks in your exam.
In ICSE CLass 10,User defined Methods Solutions is compulsory to score good marks in computer application. Students Who are planning to score higher marks in class 10 should practice ICSE User defined Methods Solutions class 10.
ICSE User defined Methods Solutions for class 10 Computer Application
A. Tick (✓) the correct option.
1. Once a function is defined, it can be invoked repeatedly. What is this feature called?
a. Interface
b. Reusability
c. Restructuring
d. All of these
Answer
B
2. If a function does not return any value, its return type should be:
a. int
b. no-return
c. void
d. empty
Answer
C
3. A function that computes a value and returned is called:
a. Computational function
b. Manipulative function
c. Procedural function
d. None of these
Answer
A
4. A type of parameter that are used to identify what data is to be passed to a function is called:
a. Formal parameter
b. Actual parameter
c. Both a and b
d. None of these
Answer
A
5. The parameter list in a function definition is called:
a. Function prototype
b. Function signature
c. Both a and b
d. None of these
Answer
B
6. The first line of the function definition is called:
a. Function prototype
b. Function signature
c. Both a and b
d. None of these
Answer
A
7. The number of values that a function can return is:
a. 1 b. 2
c. 3 d. 4
Answer
A
8. A local variable in a function has its scope:
a. Limited within the function
b. Can be accessed anywhere within the same class
c. No limitation at all
d. None of these
Answer
A
9. Which among the following is a valid name for a function?
a. function
b. 2function
c. fun in action
d. fun#
Answer
A
10. Which among the following is not a valid access specifier?
a. public
b. private
c. partially
d. protected
Answer
C
B. Fill in the blanks.
1. In Java functions are known as ________.
Answer
methods
2. Methods are contained in ________.
Answer
class
3. The function name and the parameter list together is known as ________.
Answer
function signature
4. The access specifier, return type and the function signature together is known as ________.
Answer
prototype
5. The arguments of the function given in function prototype are called ________.
Answer
formal arguments
6. The arguments of the function given in statement that calls the function are called ________.
Answer
actual arguments
7. If a function does not return any value, the returning type in the function prototype will be ________.
Answer
void
8. When a function is called by ________, the values of actual parameters are copied into separate memory locations as allocated by the formal parameters.
Answer
value
9. Impure functions uses call by ________.
Answer
reference
10. One of the practical implementation of polymorphism is ________.
Answer
overloading
SECTION A
A. Answer the following questions.
1. What is a method?
Ans. A Java method is a collection of statements that are grouped together to perform an operation.
2. Write two advantages of using functions in a program.
Ans. Reduces complexity and Reusability.
3. Explain the function of the ‘return’ statement.
Ans. The ‘return’ statement is used to return a value from a method, before exiting from the function.
4. If a function contains several return statements, how many of them will be executed?
Ans. The first one.
5. Name the keyword that causes the control to transfer back to the method call.
Ans. return
6. What is the role of the keyword ‘void’ in declaring functions?
Ans. The void keyword ensures that a method do not return any value.
7. Classify functions depending upon the value it returns.
Ans. Computational function, Procedural functions and Manipulative functions
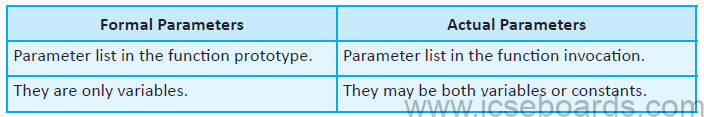
8. Differentiate between Formal Parameter and Actual Parameter.
Ans. Difference:
9. State the difference between function prototype and function signature.
Ans. Function prototype is the first line of the function definition that consist of return type function name and the parameter list. Function signature on the other hand only specifies the parameter list.
10. How are functions called? How does it return a value?
Ans. Functions are called using the name of the function, they may be called using either:
• Call by Value • Call by reference
The return statement is used to return a value from a function.
11. State the difference between Call by Value and Call by Reference.
Ans.


12. How are the following passed?
(i) Primitive types (ii) Reference types
Ans. (i) Call by value
(ii) Call by reference
13. Differentiate between pure and impure function.
Ans.

14. Explain function overloading with an example.
Ans.
Example of function overloading:
class Overload
{
static void num_calc(int num,char ch)
{
if(ch==’s’)
System.out.println(“Square:”+(num*num));
else
System.out.println(“Square:”+(num*num*num));
}
static void num_calc(int a,int b,char ch)
{
if(ch==’p’)
System.out.println(“Product:”+(a*b));
else
System.out.println(“Sum:”+(a+b));
}
static void num_calc(String s1,String s2)
{
if(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2))
System.out.println(“Equal”);
else
System.out.println(“Not Equal”);
}
}
15. Which OOP principle implements function overloading?
Ans. Polymorphism
16. When there are multiple definitions with the same function name, what makes them different from each other?
Ans. Function signature
17. What are the different access specifiers available in Java?
Ans. default, public, private and protected
18. What is the use of main() method?
Ans. The main() method, in general, is from where a program execution begins in Core Java.
19. How are static methods of one class called by methods in other classes?
Ans. The function invocation should be preceded with the name of the class followed by the dot operator.
B. Write function prototypes for the following:
1. Private access method sum which accepts three int type variables as parameters and return a float type.
Ans. private float sum(int a,int b,int c)
2. Default access method “length” which accepts a String type variable as parameter and returns an int type.
Ans. int length(String s)
3. Public access method “increment” which accepts an object of Myclass type as parameter and does not return any value.
Ans. public void increment(Myclass ob)
4. Protected access method largest which accepts a float type, int type and double type data as parameters and have a byte type as return type.
Ans. protected byte largest(float a, int b, double c)
5. Public access static method calculate which accepts a byte and int type data type as parameters and return float type.
Ans. public static float calculate(byte b, int d)
6. Write the function prototype for the function “sum” that takes an integer variable (x) as its argument and returns a value of float data type.
Ans. float sum(int x)
7. Write the prototype of a function which takes in 2 integers and 1 String arguments and returns a value which is either ‘true’ or false’.
Ans. boolean function(int a,int b,String c)
C. Answer as directed:
1. In the program given below:
class MyClass
{
static int x = 7;
int y = 2;
public static void main(String args[ ])
{
MyClass obj = new MyClass();
System.out.println(x);
obj.sampleMethod(5);
int a= 6;
System.out.println(a);
}
void sampleMethod(int n)
{
System.out.println(n);
System.out.println(y);
}
}
State the name and value of the:
(i) method argument or argument variable.
(ii) class variable.
(iii) local variable.
(iv) instance variable.
Ans.
(i) main() =String args[] value=none
sampleMethod=int n value=5
(ii) x value=7
(iii) a value=6
(iv) y value=2
SECTION B
Write programs for the following:
1. Create a method which accepts two int type variable a and b as parameter and evaluate the following expression:
4.52a + b2 / a-b and return it.
Ans.
class Sol1
{
static double method(int a,int b)
{
double c;
c=(4.2*a+b*b)/(a-b);
return c;
}
}
2. Create a function which accepts an integer as parameter and return true if it is a prime number otherwise return false. In the main() method input an integer and using the above method check whether it is a prime number or not.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol2
{
static boolean isPrime(int n)
{
int i,c=0;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(n%i==0)
c++;
}
if(c==2)
return true;
else
return false;
}
static void main()
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int n;
System.out.println(“Enter a number:”);
n=sc.nextInt();
if(isPrime(n)==true)
System.out.println(“Prime Number”);
else
System.out.println(“Not a Prime Number”);
}
}
3. Create a function which accepts an integer as parameter and return true if it is a perfect number otherwise return false. In the main() method input two integers and check whether both the numbers are perfect numbers or not.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol3
{
static boolean isPerfect(int n)
{
int i,s=0;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
if(n%i==0)
s+=i;
}
if(s==n)
return true;
else
return false;
}
static void main()
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int a,b;
System.out.println(“Enter 2 numbers:”);
a=sc.nextInt();
b=sc.nextInt();
if(isPerfect(a)==true && isPerfect(b)==true)
System.out.println(“Both are prefect numbers”);
else
System.out.println(“Both are not perfect numbers”);
}
}
4. Create a function which accepts an integer as parameter and return the sum of the square of its digits. In the main() method display all three digit Armstrong numbers.
Ans.
class Sol4
{
static int sum(int n)
{
int i,s=0,d;
for(i=n;i>0;i=i/10)
{
d=i%10;
s+=d*d*d;
}
return s;
}
static void main()
{
int i;
for(i=100;i<=999;i++)
{
if(sum(i)==i)
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
5. Create a function which accepts an integer as parameter and return true if it is a palindrome number or not. In the main() method input 10 integers and print the largest palindrome number if any.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol5
{
static boolean isPal(int n)
{
int i,r=0,d;
for(i=n;i>0;i=i/10)
{
d=i%10;
r=r*10+d;
}
if(r==n)
return true;
else
return false;
}
static void main()
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int i,max=0,n;
System.out.println(“Enter 10 numbers:”);
for(i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
n=sc.nextInt();
if(isPal(n)==true)
{
if(max==0)
max=n;
if(n>max)
max=n;
}
}
if(max>0)
System.out.println(“Largest Palindrome Number:”+max);
else
System.out.println(“No palindrome number present”);
}
}
6. Create a function which accepts an integer as parameter and return the sum of its digits. Create another function to input 10 integers and find the sum of the digits of each number.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol6
{
static int sum(int n)
{
int i,s=0,d;
for(i=n;i>0;i=i/10)
{
d=i%10;
s=s+d;
}
return s;
}
static void main()
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int i,s,n;
System.out.println(“Enter 10 numbers:”);
for(i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
n=sc.nextInt();
s=sum(n);
System.out.println(“Sum of the digits of”+n+“is”+s);
}
}
}
7. Create a function which accepts an integer as parameter and return the largest digit. Create another function to input 10 integers and find the sum of the largest digit of each number.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol7
{
static int largest(int n)
{
int i,max=0,d;
for(i=n;i>0;i=i/10)
{
d=i%10;
if(d>max)
max=d;
}
return max;
}
static void main()
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int i,s=0,n,max;
System.out.println(“Enter 10 numbers:”);
for(i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
n=sc.nextInt();
max=largest(n);
s+=max;
}
System.out.println(“Sum =”+s);
}
}
8. Create a method which accepts temperature in Celsius and return its Fahrenheit equivalent. Create another method which accepts temperature in Fahrenheit and return its Celsius equivalent. Also create a method to invoke the above methods.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol8
{
static double CelToFar(double C)
{
double F=9*C/5+32;
return F;
}
static double FarToCel(double F)
{
double C=(F-32)*5/9;
return C;
}
static void main()
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
double C,F;
System.out.println(“Enter temperature in Celcius:”);
C=sc.nextDouble();
F=CelToFar(C);
System.out.println(“Temperature in Farenheit:”+F);
System.out.println(“Enter temperature in Farenheit:”);
F=sc.nextDouble();
C=FarToCel(F);
System.out.println(“Temperature in Celcius:”+C);
}
}
9. Create a class with the following methods:
a. int sum(int n), which finds the sum of the digits in n and returns it.
b. void call() to input an integer using scanner and find the sum of its digits using the above method.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol9
{
static int sum(int n)
{
int i,d,s=0;
for(i=n;i>0;i=i/10)
{
d=i%10;
s+=d;
}
return s;
}
static void call()
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int n,s;
System.out.println(“Enter a number:”);
n=sc.nextInt();
s=sum(n);
System.out.println(“Sum:”+s);
}
}
10. Create a class with the following methods:
a. int sum(int n), which finds the sum of the digits in n and returns it.
b. void call() to input 10 integers using scanner and find the sum of its digits of each integer value entered by the user using the above method.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol10
{
static int sum(int n)
{
int i,d,s=0;
for(i=n;i>0;i=i/10)
{
d=i%10;
s+=d;
}
return s;
}
static void call()
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int n,s,i;
System.out.println(“Enter 10 numbers:”);
for(i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
n=sc.nextInt();
s=sum(n);
System.out.println(“Sum of the digits in:”+n+ “is”+s);
}
}
}
11. Create a class with the following methods:
a. boolean prime(int n), which returns true if n is prime otherwise returns false.
b. void call() to input 10 integers using scanner and find the sum of those integers which are prime numbers using the above method.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol11
{
static boolean prime(int n)
{
int i,c=0;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(n%i==0)
c++;
}
if(c==2)
return true;
else
return false;
}
static void call()
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int n,i,s=0;
System.out.println(“Enter 10 numbers:”);
for(i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
n=sc.nextInt();
if(prime(n)==true)
s+=n;
}
System.out.println(“Sum of Prime Numbers:”+s);
}
}
12. Create a class with the following methods:
a. boolean is Armstrong(int n), which returns true if n is Armstrong number otherwise returns false.
Armstrong numbers are those numbers, whose sum of the cube of its digits is equal to the number.
Eg. 153 = 13 + 53 + 33
b. void call() to input 10 integers using scanner and find largest Armstrong number if any.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol12
{
static boolean isArmstrong(int n)
{
int i,s=0,d;
for(i=n;i>0;i=i/10)
{
d=i%10;
s+=d*d*d;
}
if(s==n)
return true;
else
return false;
}
static void call()
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int i,n,max=0;
System.out.println(“Enter 10 numbers:”);
for(i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
n=sc.nextInt();
if(isArmstrong(i)==true)
{
if(max==0)
max=n;
if(n>max)
max=n;
}
}
if(max>0)
System.out.println(“Largest armstrong number:”+max);
else
System.out.println(“No armstrong number present”);
}
}
13. Create a class with the following methods:
a. boolean prime(int n), which returns true if n is prime otherwise returns false.
b. void call() to input 2 integers using scanner and print only the prime numbers between the given integers.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol13
{
static boolean prime(int n)
{
int i,c=0;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(n%i==0)
c++;
}
if(c==2)
return true;
else
return false;
}
static void call()
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int i,a,b,s,l;
System.out.println(“Enter 2 numbers:”);
a=sc.nextInt();
b=sc.nextInt();
if(a>b)
{
l=a;
s=b;
}
else
{
l=b;
s=a;
}
for(i=s+1;i<l;i++)
{
if(prime(i)==true)
System.out.println(“Prime number:”+i);
}
}
}
14. Create a class with the following methods:
a. boolean prime(int n), which returns true if n is prime otherwise returns false.
b. int sum(int n), which finds the sum of the digits in n and returns it.
c. void call() to display all such three digit numbers, whose sum of the digits is a prime number.
Ans.
class Sol14
{
static boolean prime(int n)
{
int i,c=0;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(n%i==0)
c++;
}
if(c==2)
return true;
else
return false;
}
static int sum(int n)
{
int i,d,s=0;
for(i=n;i>0;i=i/10)
{
d=i%10;
s+=d;
}
return s;
}
static void call()
{
int i,s;
for(i=100;i<=999;i++)
{
s=sum(i);
if(prime(s)==true)
System.out.println(“Prime number:”+i);
}
}
}
15. Create a class with the following methods:
a. boolean prime(int n), which returns true if n is prime otherwise returns false.
b. boolean palindrome(int n), which returns true if n is palindrome otherwise returns false.
c. void call() to display all three digit pal-prime numbers. Pal-prime numbers are those numbers which are both palindrome as well as prime.
Ans.
class Sol15
{
static boolean prime(int n)
{
int i,c=0;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(n%i==0)
c++;
}
if(c==2)
return true;
else
return false;
}
static boolean palindrome(int n)
{
int i,r=0,d;
for(i=n;i>0;i=i/10)
{
d=i%10;
r=r*10+d;
}
if(r==n)
return true;
else
return false;
}
static void call()
{
int i,s;
for(i=100;i<=999;i++)
{
if(prime(i)==true && palindrome(i)==true)
System.out.println(“Pal-Prime number:”+i);
}
}
}
16. Create a class with the following methods:
a. boolean prime(int n), which returns true if n is prime otherwise returns false.
b. void call() to display all two digit twin-prime numbers. Twin-prime numbers are those pair of numbers which are both prime as well as whose difference is 2. For example, 11 and 13, 17 and 19, etc.
Ans.
class Sol16
{
static boolean prime(int n)
{
int i,c=0;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(n%i==0)
c++;
}
if(c==2)
return true;
else
return false;
}
static void call()
{
int i,s;
for(i=10;i<=98;i++)
{
if(prime(i)==true && prime(i+2)==true)
System.out.println(“Twin-Prime number:”+i+“ ”+(i+2));
}
}
}
17. Create a class with the following methods:
a. boolean prime(int n), which returns true if n is prime otherwise returns false.
b. int sumPrime(int n), which returns the sum of prime digits present in integer n.
c. void call() to input an integer and check whether the sum of prime digits is also a prime number or not.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol17
{
static boolean prime(int n)
{
int i,c=0;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(n%i==0)
c++;
}
if(c==2)
return true;
else
return false;
}
static int sumPrime(int n)
{
int i,s=0,d;
for(i=n;i>0;i=i/10)
{
d=i%10;
if(prime(d)==true)
s=s+d;
}
return s;
}
static void call()
{
int i,s,n;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(“Enter a number:”);
n=sc.nextInt();
s=sumPrime(n);
if(prime(s)==true)
System.out.println(“Sum of the prime digits is also a prime number”);
else
System.out.println(“Sum of the prime digits is not a prime number”);
}
}
18. Create a class with the following methods:
a. int largest(int a,int b), which returns largest among the two integers a and b and return it.
b. void call() to input 10 integers and using the above function find the largest among the 10 integers.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol18
{
static int largest(int a,int b)
{
if(a>b)
return a;
else
return b;
}
static void call()
{
int i,max=0,n;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(“Enter 10 numbers:”);
for(i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
n=sc.nextInt();
if(max==0)
max=n;
else
max=largest(max,n);
}
System.out.println(“Largest:”+max);
}
}
19. Create a class with the following methods:
a. int LCM(int a,int b), which returns the least common multiple(LCM) among the two integers a and b and return it.
b. void call() to input 10 integers and using the above function find the LCM among the 10 intgers.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol19
{
static int LCM(int a,int b)
{
int i;
for(i=a;i<=a*b;i++)
{
if(i%a==0 && i%b==0)
break;
}
return i;
}
static void call()
{
int i,lcm=0,n;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(“Enter 10 numbers:”);
for(i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
n=sc.nextInt();
if(lcm==0)
lcm=n;
else
lcm=LCM(lcm,n);
}
System.out.println(“Largest:”+lcm);
}
}
20. Create a class with the following methods:
a. int HCF(int a,int b), which returns the highest common factor(HCF) among the two integers a and b and return it.
b. void call() to input 10 integers and using the above function find the HCF among the 10 intgers.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol20
{
static int HCF(int a,int b)
{
int i;
for(i=a;i<=a*b;i++)
{
if(i%a==0 && i%b==0)
break;
}
return (a*b)/i;
}
static void call()
{
int i,hcf=0,n;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(“Enter 10 numbers:”);
for(i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
n=sc.nextInt();
if(hcf==0)
hcf=n;
else
hcf=HCF(hcf,n);
}
System.out.println(“Largest:”+hcf);
}
}
21. Create a class called GeneratePrime which will be used to generate n number of prime numbers. The class should have the following methods:
(i) Method called isPrime() which accepts an integer as a parameter and return true if it is a prime number otherwise return false.
(ii) Method called display() which accepts an integer n as Scanner input and display the first n prime number by calling the above function.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class GeneratePrime
{
static boolean isPrime(int n)
{
int i,c=0;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(n%i==0)
c++;
}
if(c==2)
return true;
else
return false;
}
static void display()
{
int i=0,n,p=2;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(“Enter a number:”);
n=sc.nextInt();
while(i<n)
{
if(isPrime(p)==true)
{
System.out.println(p);
i++;
}
p++;
}
}
}
22. Create a class with the following Member Functions:
(i) Method called isPrime() which accepts an integer as a parameter and return true if it is a prime number otherwise return false.
(ii) Method called sumOfPrimeDigits() which accepts an integer as a parameter and return the sum of prime digits only.
(iii) Method called check() which accepts 10 integers and checks whether the sum of the prime numbers is also a prime number or not.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol22
{
static boolean isPrime(int n)
{
int i,c=0;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(n%i==0)
c++;
}
if(c==2)
return true;
else
return false;
}
static int sumOfPrimeDigits(int n)
{
int i,s=0,d;
for(i=n;i>0;i=i/10)
{
d=i%10;
if(isPrime(d)==true)
s=s+d;
}
return s;
}
static void check()
{
int i,s=0,n;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(“Enter 10 numbers:”);
for(i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
n=sc.nextInt();
if(isPrime(n)==true)
s+=n;
}
if(isPrime(s)==true)
System.out.println(“Sum of the prime numbers is also a prime number”);
else
System.out.println(“Sum of the prime numbers is not a prime number”);
}
}
23. Create a class called Series which will contain the following members function:
(i) long fact(int f) to find the factorial of f and return it.
(ii) void sumSeries1(int x,int n) to calculate and print the sum of the following series:
x+x/2!+x/3!+x/4!+…+x/n!
(iii) void sumSeries2(int x,int n) to calculate and print the sum of the following series:
x/2!+x2/3!+x3/4!+x4/5!+… +xn/(n+1)!
(iv) void sumSeries3(int x,int n) to calculate and print the sum of the following series:
x/2! -x2/3!+x3/4! -x4/5!+…±xn/(n+1)!
Where the symbol ! stands for factorial eg. 5!=5*4*3*2*1, 3!=3*2*1
Ans.
class Series
{
static long fact(int f)
{
long i,p=1;
for(i=1;i<=f;i++)
{
p=p*i;
}
return p;
}
static void sumSeries1(int x,int n)
{
double s=0;
int i;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
s=s+(double)x/fact(i);
}
System.out.println(“Sum=”+s);
}
static void sumSeries2(int x,int n)
{
double s=0;
int i;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
s=s+Math.pow(x,i)/fact(i+1);
}
System.out.println(“Sum=”+s);
}
static void sumSeries3(int x,int n)
{
double s=0;
int i;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(i%2==0)
s=s-Math.pow(x,i)/fact(i+1);
else
s=s+Math.pow(x,i)/fact(i+1);
}
System.out.println(“Sum=”+s);
}
}
24. Using overloading technique, write methods to:
• accept two int type data as parameters and return their sum.
• accept three int type data as parameters and return their sum.
• accept two double type data as parameter and return their sum.
• accept a double type and int type as parameter and return their sum.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol24
{
static int overload(int a,int b)
{
int s;
s=a+b;
return s;
}
static int overload(int a,int b,int c)
{
int s;
s=a+b+c;
return s;
}
static double overload(double a,double b)
{
double s;
s=a+b;
return s;
}
static double overload(double a,double b,double c)
{
double s;
s=a+b+c;
return s;
}
}
25. Create a function which accepts an integer as parameter and return true if it is a prime number otherwise return false. Create another function which accepts an integer as parameter and return true if it is palindrome otherwise return false. In the main() method display all three digit pal-prime number. Palprime numbers are such numbers which are both palindrome as well as prime numbers.For example, 101,131,151,181,191,313,353,373,383,727,757,787,797,919 and 929 are all three digit pal-prime numbers.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol25
{
static boolean prime(int n)
{
int i,c=0;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(n%i==0)
c++;
}
if(c==2)
return true;
else
return false;
}
static boolean palindrome(int n)
{
int i,r=0,d;
for(i=n;i>0;i=i/10)
{
d=i%10;
r=r*10+d;
}
if(r==n)
return true;
else
return false;
}
static void main()
{
int i,s;
for(i=100;i<=999;i++)
{
if(prime(i)==true && palindrome(i)==true)
System.out.println(“Pal-Prime number:”+i);
}
}
}
26. Create a function which accepts an integer as parameter and return the sum of its digits. Create another function which accepts an integer as parameter and return true if it is magic number otherwise return false. In the main input an integer and check whether it is a magic number or not.
If you iterate the process of summing the decimal digits of a number and if this process terminates in 1, then the original number is called a magic number. For example 55=> (5+5)=10=>(1+0)=1.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol26
{
static int sum(int a)
{
int i,d,s=0;
for(i=a;i>0;i=i/10)
{
d=i%10;
s=s+d;
}
return s;
}
static boolean isMagic(int n)
{
do
{
n=sum(n);
}while(n>9);
if(n==1)
return true;
else
return false;
}
static void main()
{
int n;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(“Enter a number:”);
n=sc.nextInt();
if(isMagic(n)==true)
System.out.println(“Magic Number”);
else
System.out.println(“Not a Magic Number”);
}
}
27. Create a function which accepts an integer as parameter and return the sum of the square of its digits. Create another function which accepts an integer as parameter and return true if it is happy number otherwise return false. In the main input an integer and check whether it is a happy number or not.. For example 7=> (72)=49=> (42+92)=97=>(92 +72)=130 =>(12 +32+02)=10 =>(12+02)= 1.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol27
{
static int sum(int a)
{
int i,d,s=0;
for(i=a;i>0;i=i/10)
{
d=i%10;
s=s+d*d;
}
return s;
}
static boolean isHappy(int n)
{
do
{
n=sum(n);
}while(n>9);
if(n==1)
return true;
else
return false;
}
static void main()
{
int n;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(“Enter a number:”);
n=sc.nextInt();
if(isHappy(n)==true)
System.out.println(“Happy Number”);
else
System.out.println(“Not a Happy Number”);
}
}
28. Create a class with the following functions:
(i) boolean isBinary() which accepts a binary number as parameter and return true if it is a valid binary number or not. A binary number consists of only two digits 0 and 1.
(ii) int binToDecimal(int b) which accepts a binary number as parameter and return its decimal equivalent.
(iii) int deciToBinary(int d) which accepts a decimal number as parameter and return its binary equivalent.
(iv) void sum() where you input two binary numbers and if they are valid binary numbers find their sum.
Sample input and output when the sum() function is executed:
INPUT
Enter two valid binary numbers: 1011 11011
OUTPUT
Sum of the two given binary numbers is: 100110
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol28
{
static boolean isBinary(int b)
{
int i,d,f=0;
for(i=b;i>0;i=i/10)
{
d=i%10;
if(!(d==1 ||d==0))
f=1;
}
if(f==0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
static int binToDecimal(int b)
{
int i,d,s=0,c=0;
for(i=b;i>0;i=i/10)
{
d=i%10;
s=s+d*(int)Math.pow(2,c++);
}
return s;
}
static int decToBinary(int d)
{
int i,r,s=0,c=0;
for(i=d;i>0;i=i/2)
{
r=i%2;
s=s+r*(int)Math.pow(10,c++);
}
return s;
}
static void sum()
{
int a,b,s;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(“Enter 2 valid binary numbers:”);
a=sc.nextInt();
b=sc.nextInt();
if (isBinary(a)==false || isBinary(b)==false)
System.out.println(“Both should be valid binary numbers”);
else
{
s=binToDecimal(a)+binToDecimal(b);
s=decToBinary(s);
System.out.println(“Sum of the 2 given binary number is:”+s);
}
}
}
29. Write a class with the name volume using function overloading that computes the volume of a cube, a sphere and a cuboid.
Formula:
volume of a cube (vc) = s*s*s
volume of a sphere (vs) = 4/3 * pi * r * r * r (where pi = 3.14 or 22/7)
Volume of a cuboid (vcd) = l * b * h
Ans.
class volume
{
static void overload(int s)//cube
{
int vc;
vc=s*s;
System.out.println(“Volume of the cube:”+vc);
}
static void overload(float r)//sphere
{
float vs;
vs=4/3f*3.14f*r*r*r;
System.out.println(“Volume of the sphere:”+vs);
}
static void overload(int l,int b,int h)//cuboid
{
int vcd;
vcd=l*b*h;
System.out.println(“Volume of the cuboid:”+vcd);
}
}
30. Design a class to overload a function num_calc( ) as follows:
a. void num_calc(int num,char ch) with one integer argument and one character argument, computes the square of integer argument if choice ch is ‘s’ otherwise find its cube.
b. void num_calc(int a, int b,char ch) with two integer arguments if ch is ‘p’ else adds the integers.
c. void num_calc(String s1,String s2) with two String arguments, which prints whether the strings are equal or not.
Ans.
class Overload
{
static void num_calc(int num,char ch)
{
if(ch==’s’)
System.out.println(“Square:”+(num*num));
else
System.out.println(“Cube:”+(num*num*num));
}
static void num_calc(int a,int b,char ch)
{
if(ch==’p’)
System.out.println(“Product:”+(a*b));
else
System.out.println(“Sum:”+(a+b));
}
static void num_calc(String s1,String s2)
{
if(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2))
System.out.println(“Equal”);
else
System.out.println(“Not Equal”);
}
}
31. Design a class to overload a function compare() as follows:
a. void compare(int,int) – to compare two integer values and print the greater of the two integers.
b. void compare(char,char) – to compare the numeric values of two characters and print the character with higher numeric value.
c. void compare(String, String) – to compare the length of the two strings and print the longer of the two.
Ans.
class Sol31
{
static void compare(int a,int b)
{
if(a>b)
System.out.println(a);
else
System.out.println(b);
}
static void compare(char a,char b)
{
if((int)a>(int)b)
System.out.println(a);
else
System.out.println(b);
}
static void compare(String s1,String s2)
{
if(s1.length()>s2.length())
System.out.println(“First string is greater”);
else
System.out.println(“second string is greater”);
}
}
32. Design a class to overload a function polygon() as follows:
(i) void polygon(int n, char ch): with one integer argument and one character type argument that draws a filled square of side n using the character stored in ch.
(ii) void polygon(int x, int y): with two integer arguments that draws a filled rectangle of length x and breadth y, using the symbol ‘@’
(iii) void polygon(): with no argument that draws a filled triangle shown below:
*
* *
* * *
Ans.
class Sol32
{
static void polygon(int n,char ch)
{
int i,j;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
System.out.print(ch);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
static void polygon(int x,int y)
{
int i,j;
for(i=1;i<=y;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=x;j++)
{
System.out.print(“@”);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
static void polygon()
{
int i,j;
for(i=1;i<=3;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=i;j++)
{
System.out.print(“*”);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
33. Design a class to overload a function compute() as follows:
(i) void compute(int,char): to compute the square of the integer argument if the given character argument is ‘s’ otherwise find its cube.
(ii) void compute(double char): to compute voume of a cube if the given character argument is ‘v’ otherwise find its diagonal.
(iii) void compute(int,int,char): to compute area of a rectangle if the given character argument is ‘a’ otherwise finds its perimeter.
Volume of cube=side3 Area of rectangle=length*breadth
Diagonal of cube=a√3 Perimeter of rectangle=2*(length+breadth)
Ans.
class Sol33
{
static void compute(int num,char ch)
{
if(ch==’s’)
System.out.println(“Square:”+(num*num));
else
System.out.println(“Cube:”+(num*num*num));
}
static void compute(double s,char ch)
{
if(ch==’v’)
System.out.println(“Volume:”+(s*s*s));
else
System.out.println(“Diagonal:”+(s*Math.sqrt(s)));
}
static void num_calc(int l,int b,char ch)
{
if(ch==’a’)
System.out.println(“Area:”+(l*b));
else
System.out.println(“Perimeter:”+(2*(l+b)));
}
}
34. Design a class to overload a function series() as follows:
(i) double series(double n) with one double argument and returns the sum of the series. sum = 1/1 + 1/2 + 1/3 + ….. 1/n
(ii) double series(double a, double n) with two double arguments and returns the sum of the series. sum
= 1/a2 + 4/a5 + 7/a8 + 10/a11 ….. to n terms
Ans.
class Sol34
{
static double series(double n)
{
double s=0,i;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
s+=1/i;
}
return s;
}
static double series(double a,double n)
{
double s=0,i,c=1;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
s+=c/Math.pow(a,c+1);
c+=3;
}
return s;
}
}
35. Design a class to overload a function series( ) as follows:
(i) double series(double n) with one double argument and returns the sum of the series:
S = X + 1/2! + 1/3! + 1/4! +…… 1/n!
(ii) double series(double x,double n) with two double arguments and returns the sum of the series
S = x + x2/2! + x3/3! + x4/x! +…… 1n/n!
Ans.
class Sol35
{
static double series(double n)
{
double s=0,i,j,f;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
f=1;
for(j=1;i<=i;j++)
{
f=f*j;
}
s+=1/f;
}
return s;
}
static double series(double x,double n)
{
double s=0,i,j,f;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
f=1;
for(j=1;i<=i;j++)
{
f=f*j;
}
s+=Math.pow(x,i)/f;
}
return s;
}
}
36. Write a menu driven program to accept a number from the user and check whether is a ‘BUZZ’ number or to accept any two numbers and print ‘GCD’ of them.
a. A BUZZ number is the number which either ends with 7 or divisible by 7.
b. GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) of two integers is calculated by continued division method. Divide the larger number by the smaller, the remainder then divides the previous devisor. The process is repeated till the remainder is zero. The divisor then results the GCD.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol36
{
static void main()
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int i,n,r,ch,d;
System.out.println(“M E N U”);
System.out.println(“1. Buzz Number”);
System.out.println(“2. GCD”);
System.out.println(“Enter your choice:”);
ch=sc.nextInt();
switch(ch)
{
case 1:
System.out.println(“Enter a number:”);
n=sc.nextInt();
if(n%10==7 || n%7==0)
System.out.println(“Buzz Number”);
else
System.out.println(“Not a Buxx number”);
break;
case 2:
System.out.println(“Enter 2 numbers:”);
n=sc.nextInt();
d=sc.nextInt();
do
{
r=n%d;
if(r!=0)
{
n=d;
d=r;
}
}while(r!=0);
System.out.println(“GCD:”+d);
break;
default:
System.out.println(“Invalid choice!”);
}
}
}
37. Write a menu driven program to accept a number and check and display whether it is a Prime Number or not OR an Automorphic Number or not. (Use switch-case statement).
a. Prime number: A number is said to be a prime number if it is divisible only by 1 and itself and not by any other number. Example : 3,5,7,11,13, etc.
b. Automorphic number: An automorphic number is the number which is contained in the last digit(s) of its square. Example: 25 is an automorphic number as its square is 625 and 25 is present as the last two digits.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol37
{
static boolean isPrime(int n)
{
int i,c=0;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(n%i==0)
c++;
}
if(c==2)
return true;
else
return false;
}
static boolean isAutomorphic(int n)
{
int i,c=0;
for(i=n;i>0;i=i/10)
{
c++;
}
if(n==(n*n)%(int)Math.pow(10,c))
return true;
else
return false;
}
static void main()
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int i,n,r,ch,d;
System.out.println(“M E N U”);
System.out.println(“1. Prime Number”);
System.out.println(“2. Automorphic”);
System.out.println(“Enter your choice:”);
ch=sc.nextInt();
switch(ch)
{
case 1:
System.out.println(“Enter a number:”);
n=sc.nextInt();
if(isPrime(n)==true)
System.out.println(“Prime Number”);
else
System.out.println(“Not a prime number”);
break;
case 2:
System.out.println(“Enter a number:”);
n=sc.nextInt();
if(isAutomorphic(n)==true)
System.out.println(“Automorphic Number”);
else
System.out.println(“Not an Automorphic number”);
break;
default:
System.out.println(“Invalid choice!”);
}
}
}
38. Write a menu driven program to perform the following: (Use switch case statement)
a. To print the series 0,3,8,15,24… n terms(value of ‘n’ is to be an input by the user).
b. To find the sum of the series given below:
S= 1/2 + 3/4 + 5/6 + 7/8 …. 19/20.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol38
{
static void series(int n)
{
int i,s=0,c=3;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
System.out.print(s+” “);
s=s+c;
c=c+2;
}
}
static void sumSeries()
{
int i;
float s=0;
for(i=1;i<=19;i+=2)
{
s+=(float)i/(i+1);
}
System.out.print(“Sum:”+s);
}
static void main()
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int ch,n;
System.out.println(“M E N U”);
System.out.println(“1. Display series”);
System.out.println(“2. sum of the series”);
System.out.println(“Enter your choice:”);
ch=sc.nextInt();
switch(ch)
{
case 1:
System.out.println(“Enter a number:”);
n=sc.nextInt();
series(n);
break;
case 2:
sumSeries();
break;
default:
System.out.println(“Invalid choice!”);
}
}
}
39. Using the switch statement, write a menu-driven program to:
(i) Generate and display the first 10 terms of the Fibonacci series 0,1,1,2,3,5,….
(ii) find the sum of the digits of an integer that is input. Eg 15390=18
For an incorrect choice, appropriate error message should be displayed.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol39
{
static void fibo()
{
int i,f=1,s=0,t=0;
System.out.print(t+” “);
for(i=1;i<=9;i++)
{
t=f+s;
System.out.print(t+” “);
f=s;
s=t;
}
}
static void sum(int n)
{
int i,d,s=0;
for(i=n;i>0;i/=10)
{
d=i%10;
s+=d;
}
System.out.print(“Sum:”+s);
}
static void main()
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int ch,n;
System.out.println(“M E N U”);
System.out.println(“1. Fibonacci series”);
System.out.println(“2. Sum of the digits in a number”);
System.out.println(“Enter your choice:”);
ch=sc.nextInt();
switch(ch)
{
case 1:
fibo();
break;
case 2:
System.out.println(“Enter a number:”);
n=sc.nextInt();
sum(n);
break;
default:
System.out.println(“Invalid choice!”);
}
}
}
40. Using the switch statement, write a menu driven program:
(i) To check and display whether a number input by the user is a composite number or not
(A number is said to be a composite, if it has one or more then one factors excluding 1 and the number itself).
Example: 4, 6, 8, 9…
(ii) To find the smallest digit of an integer that is input:
Sample input: 6524
Sample output: Smallest digit is 2
For an incorrect choice, an appropriate error message should be displayed.
Ans.
import java.util.*;
class Sol40
{
static void isComposite(int n)
{
int i,c=0;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(n%i==0)
c++;
}
if(c>2)
System.out.println(“Composite number”);
else
System.out.println(“Not a Composite number”);
}
static void smallest(int n)
{
int i,d,min=0;
for(i=n;i>0;i=i/10)
{
d=i%10;
if(min==0)
min=d;
if(d<min)
min=d;
}
System.out.println(“Smallest digit:”+min);
}
static void main()
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int i,n,r,ch,d;
System.out.println(“M E N U”);
System.out.println(“1. Composite Number”);
System.out.println(“2. Smallest digit in a number”);
System.out.println(“Enter your choice:”);
ch=sc.nextInt();
switch(ch)
{
case 1:
System.out.println(“Enter a number:”);
n=sc.nextInt();
isComposite(n);
break;
case 2:
System.out.println(“Enter a number:”);
n=sc.nextInt();
smallest(n);
break;
default:
System.out.println(“Invalid choice!”);
}
}
}

We believe that every student can get good marks by solving User defined Methods Solutions. So, let’s start to learn User defined Methods Solutions class 10 for your exam.
You can also learn revision note for class 10 computer application prepared by our expert teachers at icseboards.com


