Q) Multiple Choice Questions:-
1) If for some reason the sebaceous glands fail to function
a) the body will not be able to regulate the body temperature
b) the skin will turn darker with more melanin
c) the hairs will fail to grow
d) the skin will turn dry and rough
Solution: (d) the skin will turn dry and rough
2) Which one pair of two conditions includes both as abnormal conditions of skin pigmentation?
a) Leucoderma, Ringworm
b) Albinism, Leucoderma
c) Baldness, Albinism
d) Rickets, Baldness
Solution: (b) Albinism, Leucoderma
3) Which one out of the organs listed below, most actively functions in regulating our body temperature?
a) Heart
b) Lungs
c) Skin
d) Stomach
Solution: (c) Skin
4) Sweat glands are situated in:
a) Epidermis
b) Dermis
c) Both
d) None of the above
Solution: (b) Dermis
5) The epidermis is highly thickened in:
a) Eyelid
b) Thigh
c) Lip
d) Palm
Solution: (d) Palm
Q) Very Short Answer Type:-
Question 1) Name the principal body heat-regulating centre in our brain.
Solution:
Our brain’s primary center for controlling body temperature is the hypothalamus, a region of the forebrain.
Question 2) Name any one modified sweat gland and anyone modified sebaceous gland.
Solution:
Modified sweat gland: Mammary gland
Modified sebaceous gland: Ceruminous gland
Question 3) Name the skin glands which when inflamed cause acne.
Solution:
Sebaceous glands
Q) Short Answer Type:-
Question 1) State any two functions of the mammalian skin other than those concerned with heat regulation.
Solution:
Other functions of mammalian skin besides regulating body temperature
(i) Food storage: The hypodermis of the skin serves as an energy reserve by storing food in the form of fat.
(ii) Vitamin D Synthesis: In the presence of sunshine, skin has the capacity to manufacture a tiny amount of vitamin D.
Question 2) What is “goose-flesh”? How is it brought about?
Solution:
Goose flesh is a distinctive roughness of the skin brought on by cold or fright, in which the hair follicles stand up and form bumps on the skin.
Goose flesh results from the contraction of the erector or arrector muscles at the root of the hair. Between the hair follicle and the outer layer of the dermis, the erector muscles are positioned obliquely. Smooth muscles are required in order to move the hair. Goose flesh is produced when the erector muscle contracts, pulling the hair vertical and depressing the skin.
Question 3) What is the difference between leucoderma and albinism?
Solution:
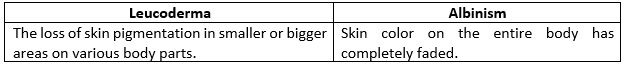
Question 4) Name any two glands found in the human skin. State their functions.
Solution:
In the skin of a human, there are two glands:
1. Ceruminous gland: Located in the auditory canal, it is a modified sebaceous gland. It secretes ear wax, a material that resembles wax.
2. A modified sweat gland, the mammary gland. Pregnancy and reproductive hormones are connected to it.
Question 5) An otherwise normal healthy young man started perspiring while it was intensely cold outside. What could have been one reason for it?
Solution:
Even when it’s chilly outdoors, sweat might result from a fever, a disease, or any form of strenuous exercise.
Q) Long Answer Type:-
Question 1) Enumerate in a tabular form the different structures found in the epidermis and dermis of the human skin respectively.
Solution:

Question 2) Explain the terms “vasodilation” and “vasoconstriction”. How do these processes contribute in temperature regulation of the body?
Solution:
Vasodilation: Widening of skin-area blood vessels that increases the flow of blood.
Vasoconstriction: The narrowing of blood vessels that lowers the amount of blood reaching the skin.
Temperature control in frigid climates:
1. The blood arteries become constricted or restricted at cold temperatures. The skin’s blood supply is decreased as a result.
2. Heat loss through convection, conduction, and radiation is reduced. Due to decreased blood flow, sweat glands produce less sweat, which results in less heat loss through vaporization.
Regulating temperature in hot weather
1. Vasodilation, or the dilatation of skin blood vessels, occurs at high temperatures to enhance the blood flow to the skin.
2. As a result, convection, conduction, and radiation lose more heat. Due to the increased sweat production brought on by the increased blood flow to the skin, there is a greater loss of heat through vaporization.

Q) Long answer type:-
Question 1) How does our skin provide protection to our body against the following?
1. Entry of germs ____________.
2. Excessive loss of heat in severe cold ____________.
3. Entry of harmful ultra-violet rays ____________.
Solution:
(a) Germ entry: Skin serves as a barrier to dangerous chemicals and infectious organisms entering the body.
(b) Excessive heat loss in extreme cold: Skin stops the body from losing energy. In cold temperatures, it helps maintain body heat, whereas in hot weather, it aids in heat loss.
(c) The presence of dangerous UV rays: The skin shields the body from ultraviolet radiation.
Q) Structure Application Question:-
Question 1) Draw a labelled diagram of the generalized vertical section of the mammalian skin.
Solution:

Vertical section of the mammalian skin
Question 2) Given below is a diagrammatic sketch of the vertical section of the human skin.

a) Label the parts numbered from 1 to 9.
b) State one main function of each of the following parts :
Part 2___________
Part 3___________
Part 4___________
Part 9___________
Name any one of the above parts which has at least three functions.
c) Part 4 may add to one’s good appearance or the “figure”. State one example of this function which may be common to both men and women.
Solution:
a) 1. Sweat pore
2. Sebaceous gland
3. Sweat gland
4. Fat
5. Dermis
6. Stratum malpighian
7. Stratum corneum
8. Epidermis
9. Hair
b) The sebaceous gland, which makes the oil known as sebum, plays a function in maintaining the moisture of our skin.
The skin stores food as a layer of fat. This is the purpose of component 4 (Fat).
The third component, the sweat gland, has the function of secreting a clear liquid, known as perspiration, from the body to control body temperature.
The purpose of component 9 (Hair) is to create a tactile experience and to aid forensic investigations.
The sebaceous gland is a part that serves at least three purposes.
Skin protection, lubrication of animals’ hair and skin through the secretion of an oily material known as sebum, and the ability to feel moist even when we haven’t taken a bath in days are all benefits of sebum.
c) The one function of fat that may be shared by both men and women is that it acts as a shock absorber, food store, and heat insulating layer.


