Students can refer to Budgeting ICSE Class 10 notes and exam questions provided for ICSE students. This is an important chapter in ICSE commercial studies class 9. We have provided here questions and answers which are expected to come in the upcoming ICSE exams for class 10th. Prepared based on the latest examination pattern and guidelines issued by ICSE. You can also refer to ICSE Books in pdf available for the latest academic session.
ICSE Class 10 Commercial Studies Budgeting Important Questions
Students should learn the important questions and answers given below for Chapter Definitions From Topo Maps in Commercial Studies for ICSE Class 10. These board questions are expected to come in the upcoming exams. Students of ICSE Class 10th should go through the Important questions and answers ICSE Class 10 Commercial Studies which will help them to get more marks in exams.
Board Exam Questions Budgeting ICSE Class 10 Commercial Studies
Question: What is a master budget?
Ans. The master budget is a summary of all budgets. Therefore, it is also known as a summary budget. The Institute of Cost Management Accountants, England, has defined it as “the summary budgets, incorporating its component functional budgets, which is finally approved, adopted and employed.”
Question: Explain the main types of budgets used in business enterprises.
Ans. (i) Production Budget : Production budget contains an estimate of the total volume of production productwise and week or monthwise and a forecast of the closing inventory of finished product. Generally, production budget is based upon the sales budget. The production budget may be expressed in quantitative or financial units or in both.
(ii) Materials Budget : After deciding the volume of sales and the volume of production, it is necessary to estimate the cost of producing the budgeted output. Cost of production included materials, labour and overheads. A separate budget for each of these items is prepared. Materials may be direct or indirect.
(iii) Factory Overhead Budget: Factory or manufacturing overheads include the cost of indirect labour, indirect materials and indirect expenses. These overheads can be classified into three categories :
(a) Fixed, i.e., which tend to remain constant irrespective of changes in the volume of output,
(b) Variable, i.e., which tend to vary with changes in output, and
(c) Semi – variable, i.e., which are partly variable and partly fixed.
(iv) Administrative Overheads Budget : This budget contains the expenses of all administrative offices of the firm. A careful analysis of the needs of all administrative departments of the enterprise is necessary. These needs can be estimated on the basis of costs of prior years. The plans and responsibilities of different departments during the budget period should also be considered.
(v) Selling and distributive overheads Budget : This budget contains all the expenses relating to selling, advertising, delivery of goods to customers, etc. These costs should be analysed according to products, types of customers, territories and the sales outlets, etc. The sales manager is directly responsible for the prepartion and execution of this budget.
Question: Distinguish between Budgeting and Forecasting.
Ans.

Question: What is Purchase Budget ?
Ans. The purchase budget contains details about the quantity and quality of various thing which the firm needs to purchase during the coming year. The total amount to be spent on purchases as well as the amount of each item of purchase are also given. Purchase budget serves a guide in making purchases from time to time
Question: ‘Budgets are very useful in Management’. Justify.
OR
Briefly explain any five utilities of a budget.
OR
How can the management of an organisation use the budgetary control system for planning and controal ?
Ans. (i) Sound Planning : Budgets make planning purposeful and precise. Objectives and programmes are expressed in physical or monetary units in budgets. Budgets are prepared on the basis of forecasts.
(ii) Higher Efficiency : Budgets brings efficiency and economy to the working of a business firm. They help management in obtaining the most profitable combination of different factors of production.
(iii) Sense of Responsibility : Budgets helps to establish divisional departmental responsibility. They prevent “buckpassing” and create a sense of responsibility among managers.
(iv) Source of Motivation : Budgets represent the ‘milestones’ to be reached. They tell people what is expected. Budgets become the goals or targets to be attained. The budget is an impersonal policeman that maintains ordered efforts in the organisation.
(v) Coordination : Budgets force executives to think as a group. Budgets are prepared in consultation with one another. Therefore, they help in achieving co-ordination between different departments of the enterprise. The interaction between persons working in different departments that takes place during the process of budgeting facilitates uniformity of policies and united actions.
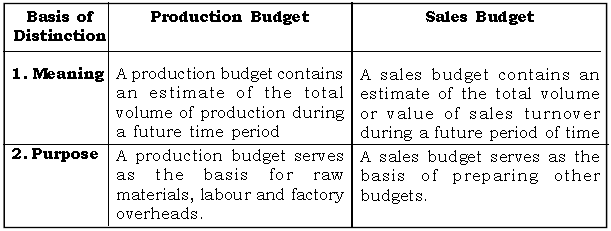
Question: Distinguish between Production Budget and Sales Budget.
Ans.
Question: Define the term ‘budget’.
Ans. A budget is a detailed plan of operations for some specific future period. It is an estimate of needs and expected results prepared in advance of the period to which it relates. A budget is formal expression of plans and policies laid down by the management for the concern as a whole and for each of its sub-divisions.
Question: What is Cash Budget ?
Ans. This budget is a summary statement of the firm’s expected inflows and outflows of cash over a future time period. It involves a projection of future cash receipts and cash payments over different time intervals.
We hope you like the above provided Budgeting ICSE Class 10 notes and questions with solutions. In case you are searching for more study material then you can send us your comments in the box below. Our team of ICSE teachers will work to provide you the ICSE study material for free.



