Question 1. Name the following:
(i) Nervous system including brain and spinal cord.
(ii) Sympathetic and parasympathetic jointly forms.
(iii) Terminal end of spinal cord.
(iv) The third neuron that is involved in reflexes, other than simple reflex.
(v) Study of structure and functions of nervous system.
(vi) Nerve which carry impulse from sensory receptor to CNS.
(vii) The nerve which carry impulse from CNS to muscles.
(viii) The peripheral matter of spinal nerve.
(ix) The peripheral matter of the brain.
(x) Outermost meningial membrane of spinal cord.
(xi) Structural and metabolic unit of nervous tissue.
(xii) The biological term given to the protective membranes of the brain.
(xiii) Cavity in which brain is situated.
(xiv) The neobrain.
(xv) The important centre of emotion.
(xvi) Paired lobes of midbrain related to the vision.
(xvii) Paired lobes of the brain related to the sense of smell.
(xviii) Fissure between the cerebral hemispheres.
(xix) Inability to write.
(xx) The busiest organ of the body.
(xxi) Inability to speak.
(xxii) The longest cranial nerve.
(xxiii) Thoracolumber region of spinal cord form.
(xxiv) Highly branched axon’s end.
(xxv) Neuron only with axon.
(xxvi) White part of the eye.
(xxvii) Short sightedness.
(xxviii) Part of internal ear related to balance.
(xxix) The photosensitive pigment present in the rod cells of the retina.
Solution 1:
1. Nervous system including brain and spinal cord Central Nervous System
2. Sympathetic and parasympathetic jointly forms Autonomic Nervous System
3. Terminal end of spinal cord Conus medullaris/Medullary cone
4. The third neuron that is involved in reflexes, other than simple reflex Mixed neurons.
5. Study of structure and functions of nervous system Neuroscience
6. Nerve which carry impulse from sensory receptor to CNS Sensory neurons
7. The nerve which carry impulse from CNS to muscles Motor neurons
8. The peripheral matter of spinal nerve White matter
9. The peripheral matter of the brain White matter
10. Outermost meningial membrane of spinal cord Dura mater
11. Structural and metabolic unit of nervous tissue Neuron
12. The biological term given to the protective membranes of the brain Meninges
13. Cavity in which brain is situated Cranium
14. Paired lobes of midbrain related to the vision Neocortex /Neopallium
15. The important centre of emotion Limbic system
16. Paired lobes of midbrain related to the vision Corpora quadrigemina
17. Paired lobes of the brain related to the sense of smell Olfactory Lobes
18. Fissure between the cerebral hemispheres Median fissure
19. Inability to write Agraphia
20. The busiest organ of the body Brain
21. Inability to speak Aphasia
22. The longest cranial nerve Trigeminal nerve
23. Thoracolumber region of spinal cord form Sympathetic nervous system
24. Highly branched axon’s end Dendrites
25. Neuron only with axon Bipolar neuron
26. White part of the eye Sclera
27. Short sightedness Myopia
28. Part of internal ear related to balance Semicircular canal
29. The photosensitive pigment present in the rod cells of the retina Rhodopsin
Question 2. Define the following:
1. Ear pinna
2. External auditory
3. Cochlea
4. Semicircular canals
5. Lachrymal gland
6. Eyelids
7. Retina
8. Eye lens
9. Pupil
10. Olfactory lobe
11. Optic lobe
12. Medulla oblongata
Solution 2:
1. External ear pinna: The external ear pinna gathers sound waves from various directions and sends them to the middle ear.
2. External auditory meatus: The external auditory meatus connects the pinna to the ear drum.
3. Cochlea: This organ translates vibrations into nerve impulses, which aids hearing.
4. Semicircular canals: It maintains equilibrium by responding to changes in posture.
5. Lachrymal gland: This gland secretes a watery fluid that cleanses the eye’s surface.
6. Eyelids: It blinks to remove dust and grit from the cornea.
7. Retina: This is a photosensitive layer that receives images.
The image is focused on the retina by the eye lens.
9. Pupil: It controls how much light gets into the eye.
10. The olfactory lobe is responsible for the sense of smell.
11. Optic lobe: These are the parts of the brain that deal with vision.
12. Medulla oblongata: It regulates involuntary bodily functions such as coughing, swallowing, breathing, heartbeat, and so on.
Question 3. Select the odd one in the following series:
(i) Retina, Sclera, Ciliary body, Nephron.
(ii) Endolymph, Tympanic membrane, Semi-circular canal, Blind spot.
(iii) Prosencephalon, Mesencephalon, Rhombencephalon, Myelin.
(iv) Cerebellum, Medulla oblongata, Olfactory lobe.
(v) Parasympathetic, Sympathetic, Cranial nerve.
Solution 3:
1. Nephron
2. Blindspot
3. Myelin
4. Olfactorylobe
5. Cranialnerve
Question 4. Match the term of column I with those of column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Lens | (a) Adjustment of light rays |
| (ii) Lachrymal gland | (b) Vision |
| (iii) Olfactory epithelium | (c) Secretion of tear |
| (iv) Cochlea | (d) Balance of the body |
| (v) Semi-circular canal | (e) Hearing |
| (vi) Eyes | (f) Smell |
Solution 4:
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Lens | (a) Adjustment of light rays |
| (ii) Lachrymal gland | (c) Secretion of tear |
| (iii) Olfactory epithelium | (f) Smell |
| (iv) Cochlea | (e) Hearing |
| (v) Semi-circular canal | (d) Balance of the body |
| (vi) Eyes | (b) Vision |
Question 5. Define the following:
(i) Nerve impulse
(ii) Axon
(iii) Cyton
(iv) Action potential
(v) Reflex action
(vi) Yellow spot
(vii) Blind spot
(viii) Power of accommodation
Solution 5:
1. Nerve impulse:- A stimulation causes an electrochemical change in the membrane of a nerve fibre, which is known as a nerve impulse.
2. Axon:- The axon is a neuron’s fiber-like mechanism that transports impulses away from the cell body.
3. Cyton:- Cyton is a stellate body with a big central nucleus that is noval, angular, and polygonal.
4. Action potential:- When a cell, particularly a nerve or muscle cell, is stimulated, a transient change in electrical potential on the cell’s surface occurs, resulting in the transmission of an electrical impulse.
5. Reflexaction:-The entire process of response to a peripheral neural stimulation that occurs in voluntaries that is without conscious efforts or thought and required the involvement of a part of the central neural system is called a reflex action
6. Yellow spot:- at the posterior pole of the eye lateral at the blind spot there is a yellowish pigments what called macula lutea it is called yellow spot
7. Blind spot:- That area on the retina at which photoreceptor cells are absent is called the blind spot. The optic nerves leave the eye and retinal blood vessels enter the eye at the blind spot.
8. Power of accommodation – power of accommodation is ability of the lens to focus on the distant object.
Question 6. Distinguish between the following pairs of words:
(i) Nerve cell and neuroglia cell
(ii) Nervous system and hormonal system
(iii) Cranial nerve and spinal nerve
(iv) Cerebrum and cerebellum
(v) Adrenalin and acetylcholine
(vi) Motor and sensory nerve
(vii) Grey matter and white matter
(viii) Myopia and hypermetropia
Solution 6:
(i) Nerve cell and neuroglia cell
| Nerve Cell | Neuroglia Cell |
| These are the nerve cells that conduct impulses in the nervous system. | These are not conducting cells, but rather nerve cells or neurons’ helper cells. |
(ii) Nervous system and hormonal system
| Nervous system | Hormonal system |
| (i) It uses electrical impulses to coordinate the body. | (i) Hormones are secreted. |
| (ii) Muscle movement, sensation, heartbeat, respiration, digestion, memory, and speech are all controlled by the neurological system. | (ii) The endocrine system regulates blood glucose levels, hydration, heat generation, sexual maturity, sperm and egg production, and cell and tissue development. |
(iii) Cranial nerve and Spinal nerve
| Cranial Nerve | Spinal Nerve |
| (i) They are derived from the brain | (i) They originate in the spinal cord. |
| (ii) The cranial nerves are divided into 12 pairs. | (ii) The spine has 31 pairs of nerves. |
(iv) Cerebrum and Cerebellum
| Cerebrum | Cerebellum |
| Intelligence, memory, and voluntary actions are all part of it. | It is concerned with the body’s balance. |
(v) Adrenalin and acetylcholine
| Adrenalin | Acetylcholine |
| It’s a neurotransmitter that raises the heart rate at times of danger. | It is a neurotransmitter that causes the pulse to slow down. |
(vi) Motor and sensory nerve
| Motor Nerve | Sensory Nerve |
| Motor fibres carry brain signals from the brain or spinal cord to the effector organs of a motor nerve. | Sensory fibres carry impulses from the sense organs to the brain or spinal cord through a sensory nerve. |
(vii) Grey matter and White matter
| Grey Matter | White Matter |
| (i) It is made up of nerve cell cell bodies. | (i) It is made up of the axons of nerve cells. |
| (ii) It is located outside of the brain, but within the spinal cord. | (ii) It is located inside the brain but not within the spinal cord. |
(viii) Myopia and Hypermetropia
| Myopia | Hypermetropia |
| (i) The picture of a distant object is created in front of the eye rather than on the retina. | (i) Because the light rays are unable to converge on the retina, the picture is created outside of it. |
| (ii) It is caused by an unusually lengthy eyeball. | (ii) It is caused by an unusually small eyeball. |
| (iii) The flaw might be caused by the lens’s excessive convexity. | (iii) The flaw might be caused by the lens’s poor convexity. |
| (iv) It can be corrected by using concave-lens glasses. | (iv) It can be corrected by using convex-lens glasses. |
Question 7. Label the following diagram:

Solution 7:

Vertical section of Human eye

Longitudinal section of Human brain
Question 8. (i) Draw a well-labeled diagram of the vertical section of mammalian brain.
(ii) Which part of the brain is the seat of body temperature regulation?
(iii) Name the part of the brain responsible for sense of smell and mental function of intelligence and memory.
Solution 8:
(i)

(ii) Diencephalon is the seat of body temperature regulation
(iii) Cerebrum the part of the brain responsible for sense of smell and mental function of intelligence and memory.
Question 9. Draw a diagram of the side view of human brain and label the part which suits the following functions/ descriptions:
(i) It lies below and behind the cerebrum. It consists of three parts.
(ii) It is a cross-wise broad band of fibres which comments medulla oblongata, cerebellum and cerebrum.
(iii) It is the lower most and hinders part of the brain which continues below into spinal cord.
(iv) It is a small thick-walled area which lies hidden below the cerebrum.
(v) It is the largest part of the brain which constitutes more than 80% and possesses 6-7 billion neurons.
(vi) It takes part in relaying sensory impulses and regulation of smooth muscle activity?
Solution 9:
(i) Cerebellum lies below and behind the cerebrum. It consists of three parts.
(ii) Cerebral peduncles is a cross-wise broad band of fibres which comments medulla oblongata, cerebellum and cerebrum.
(iii) Medulla oblongata is the lower most and hinders part of the brain which continues below into spinal cord.
(iv) Olfactory lobes is a small thick-walled area which lies hidden below the cerebrum.
(v) Cerebrum is the largest part of the brain which constitutes more than 80% and possesses 6-7 billion neurons.
(vi) Diencephalon takes part in relaying sensory impulses and regulation of smooth muscle activity.

Question 10. Where are these located?
(i) Meninges
(ii) Ganglia
(iii) Cerebellum
(iv) Nodes of Ranvier
(v) Effector organs
Solution 10:
1. Meninges:- The meninges are the membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord.
2. Ganglia:- These are the nerve cells that are found outside of the brain and spinal cord.
3. Cerebellum:- The cerebellum is a structure in the brain that is placed behind the cerebrum and above the medulla oblongata.
4. Ranvier Nodes:- These are found on the axon’s unmyelinated regions.
5. Effector organs:- They can be found in every muscle, gland, or organ in the body.
Question 11. Draw a labeled diagram of the front view the human eye.
Solution 11:
Below is the front view of the human eye with label:-

Question 12. Differentiate between nerve and neuron.
Solution 12:
Below is the difference between nerve and neuron:-
| Nerve | Neuron |
| It’s a group of axons that connect the brain to the rest of the body. | A neuron is a nerve cell that has processes. |
Question 13. Name the respective organs in which the following are located and mention the main function of each:
(i) Iris
(ii) Semicircular canals
Solution 13:
1. Iris:- The iris is a part of the eye. Its purpose is to protect the eyeball and regulate the pupil size.
2. Semicircular canals:- The semicircular canals are found in the inner ear. These have to do with the body’s balance.
Question 14. Give two examples of reflex actions in our daily life.
Solution 14:
Below are the examples of the reflex action in our daily life:-
1. Sudden removing of the hand when is in contact with some hot object or sharp material.
2. Blinking of eyes when in contact with high intensity light.
Question 15. (i) What is a reflex action?
(ii) Give one example of a conditioned reflex in your own life.
Solution 15:
1. Reflex action:- the entire process of response to a peripheral neural stimulation that occurs in voluntaries that is without conscious efforts or thought and required the involvement of a part of the central neural system is called a reflex action..
2. Tying one’s shoe lace is the example of conditioned reflex in your own life.
Question 16. The diagram alongside represents the structure of the human ear.
(i) Write the names of the parts labeled a to g.
(ii) State briefly the functions of the parts b, d, and g.
(iii) Name the main division of the ear.
(iv) Which is the smallest bone in the human body?
(v) What is labyrinth?
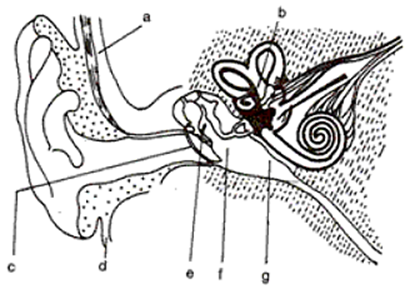
Solution 16:
(i)
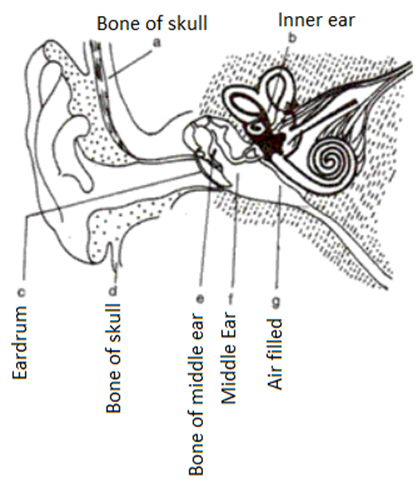
(ii) (b) The inner ear is responsible for transmitting the impulse to the brain.
(d) Skull bone – It aids in the fixation of the location of the ears, allowing the brain to employ auditory signals to estimate sound direction and distance.
(g) Air-filled – It balances the pressure in the middle ear with the outside pressure. The outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear are the three primary divisions of the ear
(iv) Stirrup is the smallest bone in the human body.
(v) The utriculus, sacculus, cochlea, and three semicircular canals make up the labyrinth, which is the inner.
Question 19. The diagram alongside represents the structure found in the inner ear. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
(i) Name the parts labeled A, B, C and D.
(ii) Name the parts of the ear responsible for transmitting impulses to the brain.
(iii) Name the part labeled above which is responsible for:
1. Static equilibrium. 2. Dynamic equilibrium. 3. Hearing.
(iv) Name the audio receptor cells which pick up vibrations.
(v) Name the fluid present in the inner ear.

Solution 19:
1.

(ii) Auditorynerve.
(iii) 1.Utriculusandsacculus
2. Semi-circularcanal
3. Cochlea
(iv) Sensory cells of organ of Corti
(v) Perilymph
Question 20. Give the main functions of each of the following:
(i) Cochlea
(ii) Fovea centralis
(iii) Three semicircular canals
(iv) Retina
(v) Lachrymal glands
Solution 20:
(i) Cochlea – It aids hearing by transferring impulses from the auditory nerves to the brain.
(ii) Fovea centralis – This is a spot on the retina where there are the most cone cells, resulting in the finest vision.
(iii) Three semicircular canals – This keeps the dynamic balance in place.
(iv) Retina – It inhibits light from refraction.
(v) Lachrymal glands – These glands generate tear to keep the eyeball lubricated.
Question 21. The arrangement of neurons in
Cerebrum: Cytons are present outside and axons are inside
Spinal cord: Cytons are present inside and axons are outside.
Solution 21:
The cerebrum has cytons on the surface and axons on the inside.
The cytons are inside the spinal cord, whereas the axons are on the outside.
Question 22. Describe briefly the functions of medulla oblongata.
Solution 22:
Below are the Functions of medulla oblongata:-
1. It controls the respiration and cardiovascular reflexes and gastric secretion.
2. It helps in the contraction and dilation of the blood vessels.
Question 23. What is meant by ‘reflex action’? Mention any two examples of reflex action occurring in day-to-day life.
Solution 23:
Reflex action:- The entire process of response to a peripheral neural stimulation that occurs in voluntaries that is without conscious efforts or thought and required the involvement of a part of the central neural system is called a reflex action. For example:-
1. blinking of eyes when amount of light enters in it.
2. Kneejerk.
Question 24. The diagram alongside represents a certain defect of vision of the human eye.
(i) Name the defect.
(ii) Describe briefly the condition in the eye responsible for the defect.
(iii) Redraw the figure by adding a suitable lens correcting the defect. Label the parts through which light-rays pass.
(iv) What special advantage do human beings derive in having both eyes facing forward?

Solution 24:
(i) The defect is Hypermetropia.
(ii) The two main conditions of eye defect:
a.) Shortening of the eyeball from front to back.
b.) The lens is less concave.
(iii)

(iv) Both the eyes facing forward help in judging the depth or relative distance. This is due to overlapping images formed in brain from both eyes which focus on an object together at one time.
Question 25. Name the cells of the retina that are sensitive to colors.
Solution 25: (i) Label the parts 1 to 5 of the diagram.
(ii) State the function of the parts labeled 4 and 5.
(iii) With the help of a diagram show the short sightedness.
(iv) Both the eyes facing forward help in judging the depth or relative distance. This is due to overlapping images formed in brain from both eyes which focus on an object together at one time.
Question 25. Name the cells of the retina that are sensitive to colors.
Solution 25:
Conecell’s is the cells of the retina that are sensitive to colors.
Question 26. The diagram alongside represents a section of a mammalian eye.
(i) Label the parts 1 to 5 of the diagram.
(ii) State the function of the parts labeled 4 and 5.
(iii) With the help of a diagram show the short sightedness.

Solution 26:
(i)

(ii) Optic Nerves:- It transmits the impulses to the brain.
Lens:- It focuses the image on the retina.
(iii)

Question 27. Given alongside is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye? Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
(i) Identify the defect.
(ii) Name the parts labeled 1, 2 and 3.
(iii) Give labeled two possible reasons for this eye defect.
(iv) Draw a labeled diagram to show how the above mentioned defect is rectified.

Solution 27:
(i) The name of defect is Myopia.
(ii) 1. Vitreous humor
2. Fovea
3. Optic nerve
(iii) 1. Lengthening of the eyeball from front to back.
2. Lens is too curved.
(iv)

Question 28. Fill in the blanks with the function in the following:
Cochlea: ______
Meninges: ______
Solution 28:
1. Cochlea:- It aids hearing by transferring signals from the auditory nerves to the brain.
2. Meninges:- The brain and spinal cord are protected by the meninges.
Question 29. Why does one feel blinded for a short while on coming out of a dark room?
Solution 29:
When exiting a dark room, one is temporarily dazzled. The term for this is “light adaptation of the eye.” The pupil is constricted to prevent light from entering the eye, and the pigment rhodopsin is bleached to lower the sensitivity of the rods.
Question 30. Name the following:
(i) The opening through which light enters the eyes.
(ii) The fluid that is present inside and outside the brain.
Solution 30:
(i) The opening through which light enters the eyes is iris
(ii) The fluid that is present inside and outside the brain is cerebrospinal fluid.
Question 31. Write whether the following are true or false:
(i) Axon of one neuron communicates with other nerve cell through synapse.
Solution :
True
(ii) Neurotransmitters are released on activation.
Solution :
True
(iii) Neurotransmitters are either broken down or reabsorbed after they have conducted an impulse.
Solution :
True
(iv) All voluntary actions are controlled by the cerebellum.
Solution :
True
(v) A convex lens is used for correcting myopia.
Solution :
False
(vi) Rods are the receptor cells in the retina of the eye sensitive to dimlight.
Solution :
True
(vii) The part of the ear associated with balance is the cochlea.
Solution :
False
(viii) Vitreous chamber is present in ear in humans.
Solution :
False
Q32. Choose the correct answer.
(i) More than one foot long cells of the body are:
(a) gland cell
(b) RBC
(c) bone cell
(d) nerve cell
Solution :
nerve cell
(ii) The largest part of the brain
(a) medulla
(b) cerebrum
(c) fornix
(d) optic lobe
Solution :
cerebrum
(iii) Number of spinal nerves in human beings:
(a) 31
(b) 10
(c) 21
(d) 12
Solution :
31
(iv) Number of cranial nerves:
(a) 10
(b) 12
(c) 14
(d) 20
Solution :
12
(v) Outermost covering of the brain is
(a) dura mater
(b) pia mater
(c) arachnoid
(d) pericardium
Solution :
duramater
(vi) Labyrinth is a part of
(a) ear
(b) brain
(c) nose
(d) eye
Solution :
ear
(vii) In the chemistry of vision, the photosensitive substance is
(a) melanin
(b) sclerotin
(c) rhodopsin
(d) none
Solution :
rhodopsin
(viii) Rods are receptor of
(a) twilight vision
(b) colour vision
(c) sound wave
(d) odour
Solution :
twilight vision
(ix) Which one is the photoreceptor
(a) organ of corti
(b) organ of sylvious
(c) cristae
(d) macula
Solution :
macula
(x) Synapse is a close proximity of
(a) two veins
(b) two arteries
(c) two muscles
(d) two nerves
Solution :
two nerves
(xi) Auditory nerve is responsible for
(a) smell
(b) sight
(c) hearing
(d) none
Solution :
hearing
(xii) Man has ______ pairs of spinal nerves.
(a)30
(b) 31
(c) 32
(d) 40
Solution :
31
(xiii) Canal joining middle ear to pharynx
(a) eustachian
(b) tympanic
(c) labyrinth
(d) none
Solution :
eustachian
(xiv) Aperture controlling passage to light into the eye is
(a) blind spot
(b) pupil
(c) iris
(d) cornea
Solution :
iris
(xv) Colour is detected by
(a) rods
(b) cones
(c) pigment
(d) choroids
Solution :
cones
(xvi) Organ of corti is found in
(a) eye
(b) Ear
(c) skin
(d) none
Solution :
Ear
(xvii) The cerebral hemispheres in mammals are connected by
(a) corpus luteum
(b) hypothalamus
(c) pons varolli
(d) corpus callosum
Solution :
corpuscallosum
(xviii) Presbyopia is a disease of
(a) ear
(b) nose
(c) mouth
(d) eye
Solution :
eye
(xix) The rods and cones of a vertebrate retina function is to
(a) focus light
(b) amplify light
(c) transduce light
(d) filter light
Solution :
filter light
(xx) In mammals the corpus callosum connects
(a) the two optic lobes
(b) the two cerebral hemispheres
(c) the cerebrum to the cerebellum
(d) the pons to the medulla oblongata
Solution :
the two cerebral hemi spheres







