Multiple Choice Questions:-
1) During inspiration, the diaphragm
a) relaxes
b) contracts
c) expands
d) gets folded
Solution: (b) contracts
2) The ultimate end parts of the respiratory system in humans are known as
a) alveoli
b) bronchioles
c) tracheoles
d) bronchi
Solution: (a) alveoli
3) During respiration there is
a) gain in dry weight
b) loss in dry weight
c) no change in dry weight
d) increase in the overall weight
Solution: (b) loss in dry weight
Choose the odd one out in the following groups of four items each:
1) Trachea, Bronchus, Alveolus, Diaphragm
2) Ethyl alcohol, Carbon dioxide, Starch, Oxygen
3) Diffusion, Respiratory gases, Alveoli, Capillary network
4) Trachea, Ciliated epithelium, Mucous, Diffusion
5) Oxyhaemoglobin, Carbaminohaemoglobin, Hypoxia, Carboxyhaemoglobin
6) Hairy, Moist, Nostril, Vocal cord
Solution::-
(a) Diaphragm
(b) Ethyl alcohol
(c) Diffusion
(c) Diffusion
(e) Hypoxia
(j) Vocal cord
Name the body structure concerned with the given functional activity:
1) Prevents food from entering the trachea during swallowing.
2) Transports oxygen to the body cells.
3) Helps to increase the volume of the chest cavity lengthwise.
4) Combines with the oxygen in the lungs.
5) Protects the lungs from mechanical injury
6) Provides actual diffusion of respiratory gases in the lungs.
Solution::-
1) Prevents food from entering the trachea during swallowing. :- Epiglottis
2) Transports oxygen to the body cells. :- Capillaries
3) Helps to increase the volume of the chest cavity lengthwise. :- Diaphragm
4) Combines with the oxygen in the lungs. :- Bronchioles
5) Protects the lungs from mechanical injury. :- Ribs
6) Provides actual diffusion of respiratory gases in the lungs. :- Alveoli or air sacs
Very Short Answer Type:-
Question 1) What is the normal percentage composition of gases in inspired and expired air respectively?
Solution:
Component Inspired Air Expired air
1. Oxygen 20.96% 16.40%
2. Carbon dioxide 0.04% 4.00%
3. Nitrogen 79.00% 79.60%
Question 2) Which chemical compound inside a cell can be termed “Currency of Energy”?
Solution:
The “Currency of Energy” of the cell is ATP, or adenosine triphosphate.
Match the items in Column I with the ones most appropriate in Column II. Rewrite the matching pairs.

Solution:

Short Answer Type:-
Q1) Fill in the blanks on a similar pattern.
a) Alveoli and _____________.
b) Mitochondria and _____________.
c) Epiglottis and _____________.
d) Pleura and _____________.
e) Diaphragm and _____________.
f) ‘C’ shaped cartilage rings and ____________.
Solution:
(a) Alveoli and gaseous diffusion
(b) Mitochondria and power house (respiration)
(c) Epiglottis and guard of entrance to trachea
(d) Pleura and lung covering
(e) Diaphragm and differentiate thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity
(f) ‘C’ shaped cartilage rings and support
Q2) State one function of the following:
1) Ciliated epithelium lining the respiratory tract
2) Mitochondria
3) Diaphragm
4) Intercostal muscles
5) Pleural fluid
Solution:
1) The respiratory tract’s ciliated epithelium: This is the inner, protective lining of the respiratory route. Driving whatever fluid that is on them, it aids in motion.
2) Mitochondria: In the presence of oxygen, pyruvic acid is further broken down in mitochondria in a step-by-step, cyclic way.
3) Diaphragm: The diaphragm aids in the lengthening of the chest cavity.
4) Intercostal muscles: These muscles assist in rib inward and outward motion, which enlarges the chest cavity all around.
5) Pleural fluid: It lubricates the free movement of the lungs as they expand and collapse.
Q3) Match the items in Column A with those in Column B.
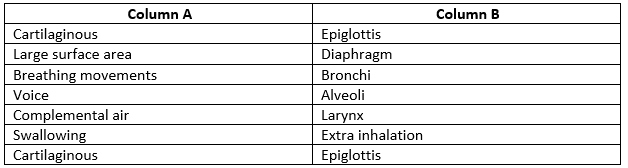
Solution:

Short Answer Type:-
Question 1) Under what conditions would the breathing rate increase?
Solution:
After a strenuous workout, breathing becomes more rapid. Additionally, a buildup of CO2 in the blood quickens breathing.
Question 2) How would you prove that air you breathe out is warmer?
Solution:
The air that is released when breathing is always warmer or body temperature. By exhaling onto our own palm, we can feel it. The warm air that is exhaled during breathing may be felt.
Question 3) How is the respiratory passage kept free of dust particles?
Solution:
Mucous glands and ciliated epithelium line the nasal cavity. Mucous is produced by the mucous glands. The whole lining of the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles is made up of the ciliated epithelium. Dust, microorganisms, pollen, and other minute airborne particles are captured by the cilia and mucus that are constantly moving. In this method, dust particles are kept out of the respiratory tract.
Question 4) What is wrong in the statement “We breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide”.
Solution:
We breathe in air that is higher in oxygen and lower in carbon dioxide. We exhale air that has less oxygen and more carbon dioxide. Therefore, it is incorrect to say that we breathe in oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide.
Long Answer Type:-
Question 1. Differentiate between the following pairs on the basis of the aspect given in the brackets.
a) Aerobic and Anaerobic respiration (End products of the process)
b) Respiration and Photosynthesis (Gas released)
c) Photosynthesis and Respiration (Reactants)
d) Inspired air and Alveolar air (CO2 content)
e) Respiration and Breathing (Organs involved)
f) Tidal volume and Residual volume (Quantity of air)
Solution:
(a) Aerobic respiration:- CO2, H2O, ATP, Heat energy
Anaerobic respiration:- Lactic acid, ATP, Heat energy
(b) Respiration:- CO2
Photosynthesis:- O2
(c) Photosynthesis:- CO2 + sunlight + H2O
Respiration:- Glucose (with or without oxygen)
(d) Inspired air:- 004%
Alveolar air:- 4.00%
(e) Respiration:- lungs, bronchi, alveoli
Breathing:- nasal cavity, trachea, diaphragm
(f) Tidal volume:- 1500 ml
Residual volume:- 500 ml
Question 2. Breathing through the nose is said to be healthier than through the mouth.
Solution:
The hair in the nostrils prevents big dust particles from entering the respiratory system, making breathing via the nose healthier than breathing through the mouth.
Question 3. Why does gaseous exchange continue in the lungs even during expiration?
Solution:
Because expiration is the consequence of the ribs and diaphragm moving backwards, gas exchange occurs in the lungs even during expiration. The thoracic cavity is reduced and the lungs are squeezed as a result of the motions of the ribs and diaphragm, pushing the air out into the environment.
Question 4. Why does a person feel breathlessness at higher altitudes?
Solution:
Low oxygen levels are present in the air at greater altitudes. Therefore, breathing becomes difficult at greater elevations.
Question 5. Why do you shiver and why do your teeth chatter when it is very cold in winter?
Solution:
Heat generation is raised by accelerated metabolic rate and increased muscle activity in order to maintain the body temperature constant under severely cold winter circumstances. There is a lot of muscle action involved in trembling and teeth chattering. In order to boost the body’s ability to produce heat, this is why we shiver and grind our teeth during the cold.
With regard to the respiratory system and the process of respiration in man, answer the following questions:
Question 1. Name the two muscles that help in breathing.
Solution:
(i) Abdominal muscles
(ii) Intercostal muscles
Question 2. Briefly describe how the above mentioned muscles help in the inspiration of air.
Solution:
(i) The chest cavity is made larger by the ribs being forced inward and outward by the intercostal muscles that are stretched between them.
(ii) The diaphragm flattens and squeezes the abdominal organs. The abdominal wall expands when the abdominal muscles are relaxed.
Question 3. Give the overall chemical equation to represent the process of respiration in humans.
Solution:
The general chemical formula for how humans breathe is as follows:
C6H12 O6 + 6O2 Enzymes→ 6CO2 + 6H2O + 38ATP + 420kcal
Question 4. What is meant by:
(i) Residual air and
(ii) Dead air space
Solution:
1. Residual air: Even after forcing air out of the lungs, some air is always left behind. This is the air that is still present. 1500 ml make up this amount.
2. Dead air space: Some tidal air is left in the trachea and bronchi, respiratory passageways where gas diffusion cannot take place. Dead air gap is the name given to this area. Its volume is 150 ml.
Question 5. Starting from the nostrils, trace the path in sequence which the inspired air takes until it reaches the air sacs.
Solution:
The inspired air’s motion:
Nose → Pharynx → Larynx → Trachea → Bronchi
Long answer type:-
Question 1) What are the functions of the following in breathing?
a) Ribs
b) Diaphragm
c) Abdominal muscles
Solution:
a) Ribs: The muscles stretched between the ribs cause the ribs to shift inward and outward, increasing the chest cavity all around.
b) Diaphragm: During contraction, the diaphragm flattens down or descends from its dome-shaped contour to virtually a horizontal plane, which helps to lengthen the chest cavity.
c) Abdominal muscles: By moving the diaphragm, abdominal muscles help to expand the thoracic cavity, which facilitates inspiration.
Structure Application question:-
Question 1) Given alongside is a diagrammatic sketch of a kind of part in human lungs. Name the parts numbered 1-4.

Solution:

Question 2) Given below are chemical reactions (1 to 5) involving glucose and five other chemical products (A-E).

A. Write the reaction number of the following:
(i) Anaerobic respiration in plants _
(ii) End products in aerobic respiration ___
(iii) Reaction occurring in liver
(iv) Anaerobic respiration in animals
(v) Storage in the liver __
Solution:
(i) Anaerobic respiration in plants: 5
(ii) End products in aerobic respiration: 4
(iii) Reaction occurring in liver: 2
(iv) Anaerobic respiration in animals: 1
(v) Storage in the liver: 3
B. Which reactions (1-5) in the above correspond to the following (write the corresponding number of reaction next to them).
(i) Aerobic respiration
(ii) Change taking place in the liver
(iii) Anaerobic respiration in yeast
(iv) Change taking place in a plant storage organ, e.g., potato
(v) Anaerobic respiration in animals
Solution:
(i) Aerobic respiration: 4
(ii) Change taking place in the liver: 3
(iii) Anaerobic respiration in yeast: 5
(iv) Change taking place in a plant storage organ, e.g., potato: 2
(v) Anaerobic respiration in animals: 1
Question 3) The volume of air in the lungs and the rate at which it is exchanged during inspiration and expiration was measured. The following diagram shows a group of lung volumes and capacities.
Study the diagram carefully and explain briefly the following:
(a) Tidal volume (TV)
(b) Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
(c) Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
(d) Vital capacity (VC)
(e) Residual volume (RV)

Solution:
(a) Tidal volume (TV): Air breathed in and out, in normal quiet breathing is called tidal volume. It is 500 ml.
(b) Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV): Air that can be drawn in forcibly over and above the tidal air is called inspiratory reserve volume. It is also known as complemental air. It is 3000 ml.
(c) Expiratory reserve volume (ERV): Air that can be forcibly expelled out after a normal expiration is called expiratory reserve volume. It is also called supplemental air. It is 1000 ml.
(d) Vital capacity (VC): Volume of air that can be taken in and expelled out by maximum inspiration and expiration is called vital capacity. It is 4500 ml.
(e) Residual volume (RV): Air left in the lungs, even after forcible expiration is called residual volume. It is 1500 ml

