Q) Multiple Choice Questions:-
1) A disease widely spread worldwide is known as
a) endemic
b) epidemic
c) pandemic
d) sporadic
Solution: (c) pandemic
2) The letter B in the name BCG vaccination stands for
a) Brief
b) Beri-beri
c) Bacteria
d) Bacillus
Solution: (d) Bacillus
3) Use of disposable syringes for injecting medicines, etc. is specially advised to prevent
a) Poliomyelitis
b) Mumps
c) Rabies
d) AIDS
Solution: (d) AIDS
4) The vector that transmits the malarial pathogen is:
a) Culex mosquito
b) Housefly
c) Anopheles mosquito
d) Entamoeba
Solution: (c) Anopheles mosquito
5) Amoebiasis is caused by the protozoan:
a) Amoeba proteus
b) Euglena
c) Plasmodium
d) Entamoeba
Solution: (d) Entamoeba
6) The expanded form of AIDS is
a) Active Immunity Deficiency Syndrome
b) Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome
c) Acquired Immuno Deficiency Status
d) Active Immuno Deficiency Syndrome
Solution: (b) Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome
Q) Mention whether the following statement is true (T) or false (F).
i) Filariasis is transmitted by the housefly.
a) True
b) False
Solution: F (False). Filariasis is transmitted by the Culex mosquito.
ii) Malaria is caused by protozoan.
a) True
b) False
Solution: T (True)
iii) BCG vaccine is used for chicken pox.
a) True
b) False
Solution: F (False). BCG vaccine is used for tuberculosis.
iv) Louis Pasteur discovered a cure for malaria.
a) True
b) False
Solution: F (False). Louis Pasteur discovered a cure for rabies.
v) AIDS is caused by a bacterium.
a) True
b) False
Solution: F (False). AIDS is caused by a virus.
vi) HIV is a serious disease, usually fatal.
a) True
b) False
Solution: T (True)
vii) AIDS is not transmitted by contact with a patient’s clothes.
a) True
b) False
Solution: T (True)
viii) Chicken pox and hepatitis are bacterial diseases.
a) True
b) False
Solution: F (False). Chicken pox and hepatitis are viral diseases.
ix) Goitre is endemic in sub-Himalayan regions of India.
a) True
b) False
Solution: T (True)
x) AIDS is caused by a fungus.
a) True
b) False
Solution: (F) False
xi) Hay fever and asthma are allergies.
a) True
b) False
Solution: T (True)
xii) Smallpox still occurs in India.
a) True
b) False
Solution: F (False). Smallpox has been eradicated from India.
xiii) The disease filariasis is caused by the bite of the female anopheles mosquito.
a) True
b) False
Solution: F (False). The disease filariasis is caused by the filarial worm Wuchereria bancrofti.
Q) Write the full form of the following as it occurs in biology: AIDS
Solution:
AIDS : Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome
Q) Name the Following:
i) Category of pathogen that causes diseases like common cold and mumps.
Solution: Viruses
ii) The vaccine for preventing tuberculosis.
Solution: BCG
iii) A disease that weakens the body’s defence system against infections.
Solution: Lungs
iv) Germ of germ-substance introduced into the body to prevent occurrence of an infectious disease.
Solution: AIDS
v) The vector responsible for transmission of sleeping sickness.
Solution: Vaccine
vi) The microorganism that requires a host to reproduce.
Solution: Tsetse fly
vii) The popular name of the disease filariasis.
Solution: Virus
Q) Short Answer Type:-
Question 1. Define the following:
1) Infection
2) Pathogen
3) Incubation period
4) Allergen
Solution:
(i) Infection: Infection refers to the spread of illness from one individual to another.
(ii) Pathogen: A pathogen is a microorganism that causes disease.
(iii) Incubation period: The incubation period is the time frame between the introduction of pathogens and the onset of the disease’s initial symptoms.
(iv) Allergen: An allergen is an antigenic material that can instantly cause hypersensitive allergy.
Question 2. What are the different ways in which infectious diseases can spread?
Solution:
The following list includes the many methods that infectious illnesses can spread:
1. Direct interaction: human-to-human, animal-to-human, and expectant mother-to-child.
2. Direct contact, such as a phone call or doorknob.
3. Sneezing, coughing, and other droplet-producing behaviors.
4. Airborne particle transmission: Contaminated air can spread infectious illnesses.
5. Stings and Bites: Ticks, lice, mosquitoes, etc.
6. Food Contamination: Eating substances, drinks, etc.
Question 3. Name any four non-infectious diseases and their causes.
Solution:
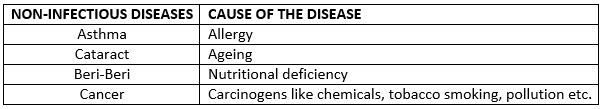
Question 4. Why is it important to know how the germs leave the body of a patient?
Solution:
Knowing how germs leave a patient’s body is crucial since various illnesses and infections can be spread by air, water, or even just direct touch. Knowing how germs exit the body of an infected individual is essential for taking preventative measures and shielding others from contracting the sickness.
Question 5. Name the causative germ of AIDS. How is this disease transmitted?
Solution:
Causative germ of AIDS: HIV (Human immunodeficiency virus)
AIDS Transmitted:
(a) Sexual intercourse
(b) Mother to child transmission
(c) Contaminated blood transfusions
Q) LONG ANSWER TYPE
Question 1. Write very briefly about the following:
(a) BCG
(b) Incubation period
(c) Chicken pox
(d) Hepatitis A
Solution:
(a) BCG: This vaccination protects against the bacterial illness tuberculosis (TB). It builds up TB immunity. Bacillus Calmette Guerin is referred to as BCG.
(b) Incubation period: This is the time frame between the introduction of pathogens and the onset of the disease’s initial symptoms. For instance, pneumonia takes 1-3 days to incubate.
(c) Chicken pox: This viral illness is brought on by the herpes zoster virus. By having direct touch with an infected individual, it spreads quickly. Children between the ages of 12 and 18 months receive an active vaccination with a live attenuated vaccine containing varicella.
(d) Hepatitis A: This virus infection results in liver inflammation and is brought on by the hepatitis A virus. It takes 14 to 45 days for incubation to occur. It is mostly spread by tainted food and water.
Question 2. What are the causes and symptoms of malaria, chicken pox and tuberculosis? How can these diseases be prevented?
Solution:
(i) Disease: Malaria
Causative agent: Protozoan, Plasmodium
Symptoms: Chills, high fever, profuse sweating, severe headache, nausea, vomiting, fatigue and body pain.
Prevention: Elimination of mosquitoes at all phases, including use of mosquito nets or repellents to prevent bites.
(ii) Disease: Chicken pox
Causative agent: Virus, Varicella zoster
Symptoms: Highly irritating rashes near the chest and back, gradually spreading to the arms, legs, face and head.
Prevention: Providing a live attenuated vaccine with varicella as an active immunization.
(iii) Disease: Tuberculosis
Causative agent: Bacterium, Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Symptoms: Persistent cough, afternoon fever, bloody mucus, loss of weight, fatigue and chest pain.
Prevention: BCG vaccination and isolation of the patient.



