Multiple Choice Questions:-
Question 1. In potato starch is stored in:
a) Sclerenchyma
b) Collenchyma
c) Parenchyma
d) Chlorenchyma
Answer
C
Question 2. Tendons and ligaments are examples of:
a) Fibrous connective tissue
b) Cartilage
c) Muscular tissue
d) Adipose tissue
Answer
A
Question 3. Which one of the following pairs is correctly matched?
a) Meristem – Actively dividing cells
b) Xylem – Transport of food
c) Phloem – Transport of water
d) Sclerenchyma – Storage of starch
Answer
A
Question 4. Parenchyma containing chloroplasts is known as :
a) Parenchyma
b) Aerenchyma
c) Collenchyma
d) Chlorenchyma
Answer
D
Question 5. Annual rings are the number of:
a) Internodes in a stem
b) Rings of vascular bundles in a monocot stem.
c) Barks layers in a woody stem.
d) Layers of Xylem in a stem.
Answer
B
Question 6. Which of the following cells in plants are said to be nonliving?
a) Meristem
b) Parenchyma
c) Collenchyma
d) Sclerenchyma
Answer
D
Question 7. Which of the following connects a muscle to a bone?
a) Cartilage
b) Ligament
c) Tendon
d) Interstitial fluid
Answer
C
Question 8. Cardiac muscle is:
a) Involuntary
b) Smooth
c) Striated
d) Involuntary and Striated
Answer
A
Very short answer type:-
Question 1. Name the kind of tissue found at the tip of plant roots.
Solution.
Apical or terminal meristematic tissue found at the tip of plant roots.
Question 2. Name the kind of tissue found at the lower surface of the leaf.
Solution.
Protective tissue found at the lower surface of the leaf.
Question 3. Name the kind of tissue found in the inner lining of the intestine.
Solution.
Columnar epithelium (Epithelial tissue) found in the inner lining of the intestine.
Question 4. Name the kind of tissue found at the joint between two long bones.
Solution.
Ligament (Connective tissue) found at the joint between two long bones.
Question 5. Name the kind of tissue found in the walls of the veins of the leaves.
Solution.
Conducting tissue found in the walls of the veins of the leaves.
Question 6. Name the kind of tissue found as gritty masses in the pulp of pears.
Solution.
Sclerenchyma (Supporting tissue) found as gritty masses in the pulp of pears.
Question 7. Where is the least specialized tissue located in plants?
Solution.
Sclerenchyma is the least specialized tissue in plants, consisting of long, thin, and thick cells that have died. This tissue offers strength to tissue plant components by forming the walls and borders of plant cells.
Write one word in the following:-
Question 1. A group of similar cells performing a specific function.
Solution.
Tissue
Question 2. Cells least specialized in plant.
Solution.
Permanent tissue cells
Question 3. Cells responsible for the increase in diameter of the stem and root of dicot plants.
Solution.
Cambium
Very short answer type:-
Question 1. Name one place in living organisms where the following tissue is located:
(a) Meristematic tissue
(b) Cartilage
(c) Squamous epithelium
(d) Sclerenchyma
(e) Ciliated epithelium
(f) Ligament
Solution.
(a) Tips of roots
(b) Nose
(c) Lining of mouth
(d) Veins of leaves
(e) Lining of trachea
(f) Bones
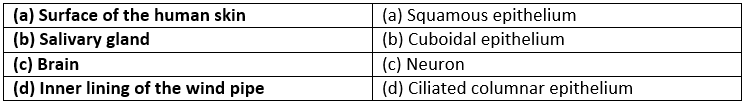
Question 2. Name the kind of cells found in the following place:
(a) Surface of the human skin
(b) Salivary gland
(c) Brain
(d) Inner lining of the wind pipe
Short answer type:-
Question 1. Name any one body part where ciliated epithelium is found in humans. What is its function?
Solution.
The trachea is the portion of the body that includes the ciliated epithelium. Ciliated epithelial structures are epithelial cells with cilia, which are short projections. Cilia are tiny hair-like projections on the cell surface. The general purpose of epithelium is to protect the underlying tissues or cells. The ciliated epithelium also includes hairs that push harmful particles away. They are found in the trachea to protect the respiratory system from infections.
Question 2. What is the difference between the nervous tissue and nervous system?
Solution.
Neurons, or nervous tissue, are a specialized type of cells. Animal perception and reactions are the focus of this tissue.
The nervous system, which is an organ system, is made up of nerve tissue. All of the body’s systems are controlled and coordinated by it.
Question 3. List the tissues found in the human heart.
Solution.
Below are the tissues found in the human heart:-
(1) Muscular tissue (Cardiac muscles)
(2) Epithelial tissue (Lining of blood vessels of the heart)
(3) Connective tissue (Fluid connective tissue in the form of red blood corpuscles)
Question 4. Can you consider a cluster of eggs as a tissue? Why?
Solution.
A tissue is a collection of comparable cells from the same origin that perform a single function. A zygote or a cell is an egg, but a cluster of eggs is not a tissue because it does not create an organ like a tissue. Instead, if fertilized, it produces a new individual creature.
Question 5. Name the three kinds of muscles found in the human body. In each case, name one region in the body where they are found.
Solution.
(1) Striated muscles: These muscles provide the force for locomotion and all voluntary bodily motions. The limbs contain these muscles.
(2) Unstriated muscles: These muscles allow food to travel through the intestines. These muscles can be found in the iris of the eye, blood vessel linings, the urine bladder, and other places.
(3) Cardiac muscles: These muscles contract and relax in a cyclic pattern. Only the heart contains these muscles.
Long Answer Type:-
Question 1. What is the difference between cells and tissue?
Solution.

Question 2. What is the difference between organ and organism?
Solution.

Question 3. What is the difference between organ and organelle?
Solution.

Question 4. What is the difference between organ and organ system?
Solution.

Long Answer Type:-
Question 1. Differentiate between cells of Parenchyma and Collenchyma:-
(a) Parenchyma and Collenchyma
(b) Meristematic tissue and Permanent tissue
(c) Sclerenchyma and Parenchyma
(d) Cells of involuntary muscle and voluntary muscle
(e) Fibres of voluntary muscle and cardiac muscle
Solution.

Structured/Application Questions
Question 1. Study the diagram given below and then answer the question that follows:
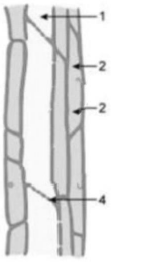
Solution.
(a) The figure depicts phloem tissue because the cells have cellular contents, as opposed to xylem tissue, which has hollow cells with no cellular contents.
(b)

(c) Phloem is a food-conducting tissue found in the leaves and stems of plants that
transports the food produced in the leaves to other sections of the plant.
(d)
1. Sieve cells: Assist in the movement of food from the leaves to the plant’s storage organs
and other sections.
2. Phloem parenchyma cells: Starch, fat, and other organic food materials are stored in
these cells.
3. Companion cells: These cells assist the sieve tube cells in their activity.
4. Sieve plate perforations allow water and dissolved organic solutes to pass through the
sieve tube.
Question 2. Study the diagram given below and then answer the question that follows:
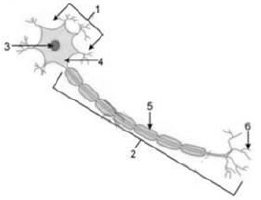
(a) Identify the cell.
(b) Name the parts labelled 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6.
(c) Where is this cell likely to be found in the human body and what is its function?
Solution.
(a) Nerve cell or neuron
(b)
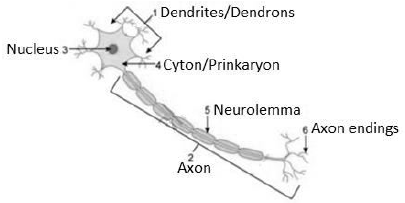
(c) The nerve cell is most likely to be discovered in the human nervous system. The nerve cell’s job is to convey information from one region of the body to another. It has to do with animal perception and reactions.




