Question 1. Multiple Type Question:-
Question 1. Bougainvillea flower is an example of:
a) incomplete flower
b) having a large nectary
c) water pollination
d) large colorful bracts
Answer
D
Question 2. A flower is said to be complete when:
a) It has the corolla and calyx
b) It has the corolla and gynoecium
c) It has the androecium and gynoecium
d) It has all the four whorls
Answer
D
Question 3. The part of the flower that gives rise to the fruit is:
a) Sepals
b) Petals
c) Ovary
d) Stamens
Answer
C
Question 4. The part of the flower that gives rise to the seed is:-
a) Ovary
b) Placenta
c) Ovule
d) Pollen grain
Answer
C
Question 5. The essential whorls of a flower are the:
a) Calyx and corolla
b) Stamen and ovary
c) Calyx and epicalyx
d) Androecium and gynoecium
Answer
D
Question 2. Match the parts in Column A with the flowers or parts of the flower in Column B.

Solution.

Question 3. Short Answer Type
Question 1. Explain the following term:
a) Incomplete flower
b) Staminate flower
c) Pistillate flower
d) Bisexual flower
Solution.
(a) Incomplete flower – An incomplete flower is one that lacks one or more sets of floral structures. Consider the American elm.
(b) Staminate flower – A male or staminate flower is a unisexual flower that comprises just the stamens, or male portions of the bloom. Consider the Eastern cottonwood.
(c) Pistillate flower – A female or pistillate flower is one that includes solely the carpels, or female portions of the flower. Consider the date palm.
(d) Bisexual flower – A bisexual or hermaphrodite flower is one that has both stamens and carpels. Consider Hibiscus.
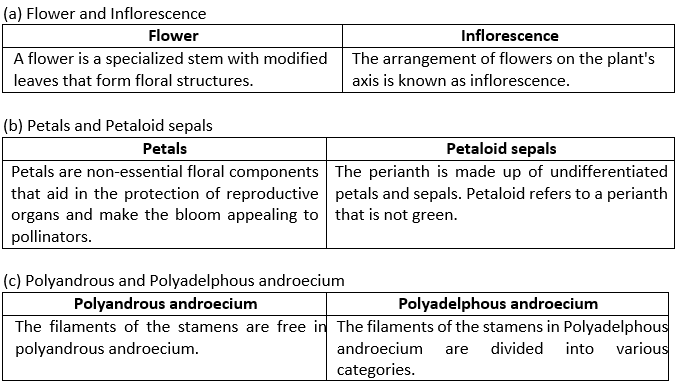
Question 2. Distinguish between the following pairs:
a) Flower and inflorescence
b) Petals and petaloid sepals
c) Polyandrous and polyadelphous androecium
Solution.
(a) Flower and Inflorescence
Question3. Where the following structures/parts located and what are their functions?
a) Placenta
b) Thalamus
c) Anther
d) Stigma
Solution.
(a) Placenta:
Location: In the ovary, there is a cushion or enlarged zone.
Function: Ovules get their start here.
(b) Thalamus:
Location: The flower stalk’s tip
Function: Supports all of the flower’s components.
(c) Anther:
Location: The stamen is located here.
Function: Male gametes or pollen grains are produced.
(d) Stigma:
Location: Terminal knob-like
Function: During pollination, it serves as a landing spot for pollen grains.
Question 4. Why are the following described as stated:
a) The androecium of pea flower is diadelphous
b) Ray florets of sunflower are neuters.
c) Salvia sepals are petaloid
Solution.
a) Because the filaments of the anther are joined in two bundles, the androecium of the pea flower is diadelphous. In the case of peas, nine stamens form a staminal tube, while one stamen is free.
b) Sunflower ray florets are neuters due to the absence of both male and female reproductive systems.
c) Salvia sepals are petaloid because the three sepals are joined together and have a red hue similar to petals. As a result, they are indistinguishable from the petals.
Question 4. Long answer type
Question 1. Name the different types of androecium found in flowers.
Solution.
Below are the types of androecium in flowers:
1. Polyandrous: When a flower’s stamens are free, the state is known as polyandrous.
2. Monadelphous: This phenomenon occurs when the filaments of anthers of a flower are united into one group.
3. Diadelphous: This phenomenon occurs when the filaments of anthers of a flower are united into two groups.
4. Polyadelphous: This phenomenon occurs when the filaments of anthers of a flower are united into more than two groups.
Question 2. Name the type of androecium found in:-
a) China rose
b) Bombax
c) Pea
Solution.
(a) China rose: Monadelphous
(b) Bombax: Polyadelphous
(c) Pea: Diadelphous
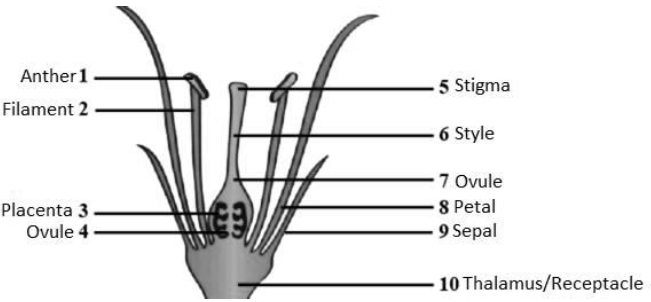
Question 3. The figure given alongside represents a generalized arrangement of the different parts of a bisexual flower. Name the parts numbered 1-10.

Solution.
Question 4. Given alongside are two figures (A & B) of a certain part of a flower. Study the figures carefully and answer the following questions:
(a) Which major organs of a flower does the figure A represent? What is the collective term for this organ?
(b) Are the contents of the pollen sacs in B male or female?
(c) Can you state how the contents of the pollen sacs would come out?

Solution.
(a) Figure A depicts the stamen. Androecium is made up of stamens.
(b) Male gametes are found in the pollen sacs in B.
(c) Pollen sac contents would be released by forces such as air, wind, and insects, resulting in flower pollination.
Question 5. What are bracts? State their function.
Solution.
The axil of a leaf-like structure where a flower emerges is known as the bract. Bracts are sometimes mistaken for petals since they are huge and brilliantly colored structures. This aids pollination by attracting insects.
Question 6. Explain the terms Monadelphous, Diadelphous and Polyadelphous. In each case name a flower possessing such an androecium.
Solution.
Condition of androecium:- Monadelphous
Explanation:- The filaments of a flower’s anthers are merged into a single bunch.
Example of flower:- Hibiscus
Condition of androecium:- Diadelphous
Explanation:- The anthers’ filaments are united into two groups in a flower.
Example of flower:- Pea
Condition of androecium:- Polyadelphous
Explanation:- The anthers’ filaments are united into more than two groups in a flower.
Example of flower:- Bombax




