Question 1. Multiple Type Question:-
Question 1. Which one of the following is one of the characteristics of self-pollinated flowers?
a) Flowers are large and showy
b) Flowers remain closed and do not open
c) Stigma and anthers mature at the same time
d) Pollen is produced in very large quantities
Answer
C
Question 2. Exine and intine are the parts of:
a) Embryo sac
b) Pollen grain
c) Stigma
d) Seed
Answer
B
Question 3. State the name of the chief pollinating agent against the corresponding plant by choosing from those given in brackets.
1) Dahlia_______ .
a) crow
b) butterflies
c) mosquito
Answer
B
Question 4. Maize_______ .
a) bees
b) locusts
c) rain
d) wind
Answer
D
Question 5. Vallisneria ______
a) wind
b) water
c) ants
d) rabbits
Answer
B
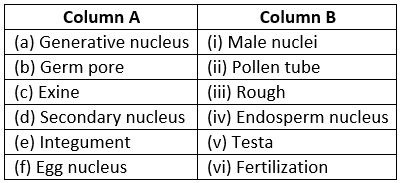
Question 2. Match the items in Column A with those in Column B.

Solution.
Question 3. Fill in the blank with suitable words
Question 1. Transference of pollen grains from anthers to stigma of the same flower is called ________.
Answer
autogamy.
Question 2. Different timings for the maturation of gynoecium and androecium is called ________.
Answer
dichogamy
Question 3. _______ is a water-pollinated flower.
Answer
Vallisneria
Question 4. Fill in the blank with suitable words:-
Question 1. Name of the part of the ovary which gives rise to:
Seed ______
Fruit ______
Fruit wall ______
Answer
Seed – Ovules
Fruit – Ovary
Fruit wall – Ovarian wall
Question 5. Give one word/term for the following:
Question 1. A flower containing both male and female parts.
Answer
Bisexual flower
Question 2. Arrangement of flowers on a twig/stem.
Answer
Inflorescence
Question 3. When pollen grains of a flower reach the stigma of the same flower.
Answer
Self-pollination/Autogamy
Question 4. When maturation time of reproductive parts in a flower is different.
Answer
Dichogamy
Question 5. When stigma and anthers do not grow up to the same height, which favors only cross-pollination.
Answer
Heterostyly
Question 6. Pollination of flowers by insects.
Answer
Entomophily
Question 7. Pollination of flowers by birds.
Answer
Ornithophily
Question 6. Short answer type:-
Question 1. Explain the Following Term:
a) Ornithophily
b) Elephophily
c) Artificial pollination
Solution.
(a) Ornithophily – Pollination by birds is known as ornithophily.
(b) Elephophily – Elephophily is when elephants pollinate plants.
(c) Artificial pollination – Men-made Pollination aided by artificial methods.
Question 2. What happens to the following after fertilization?
a) Ovules
b) Calyx
c) Petals
d) Stamens
Solution.
(a) Ovules – Ovule develops into seed. Inside the seed present a small under-developed plant called embryo.
(b) Calyx – Calyx is the part of a plat which supports the flower. It has sepals that whorl around the flower. After fertilization, calyx falls off the plant.
(c) Petals – Petals of the flower fall off and the ovary containing the seeds forms a fruit.
(d) Stamens – Dries up.
Question 3. Mention any two contrivances in flowers which favour cross – pollination
Solution.
Below are the contrivances in flowers which favour cross-pollination:-
1. Unisexuality
2. Different timings of maturation of androecium and gynoecium
3. Self-sterility
4. Structural barriers
Question 7. Long answer type question:-
Question 1. What are the advantages of the following in the flower to the plant concerned?
a) Long and feathery stigma
b) Brightly coloured petals
c) Smooth and light pollen
d) Protruding and easily movable anthers
e) Fragrant nectar
Solution.
(a) Long and feathery stigma: Plants benefit from long and feathery stigmas because they catch more pollen.
(b) Vividly colored petals: The brightly colored petals are used to attract various pollen-attracting agents.
(c) Pollen that is smooth and light: Pollen that is smooth and light may readily disperse in the air and pollinate the stigma.
(d) Protruding and readily moveable anthers: They can be moved by even the smallest breeze.
(e) Fragrant nectar: Attracts pollinating insects.
Question 2. Describe the advantages and disadvantages of cross-pollination to the plant.
Solution.
Cross-pollination has the following benefits:
1. The progeny are healthier.
2. The seeds that are generated are plentiful and viable.
3. Cross-pollination of two distinct kinds of the same species can result in new variants.
Disadvantages of cross-pollination:
1. Pollination isn’t always guaranteed.
2. A huge amount of pollen must be generated.
3. The procedure is inefficient for the plant since the blooms must be huge, colorful, fragrant, and generate nectar to attract pollinators.
Question 8. Diagram question:-
Question 1. What is the function of the pollen tube? Explain it with the help of a diagram.
Solution.

By breaking through its exine, the pollen tube emerges from the pollen grains. The pollen tube expands by dissolving the stigma and style with enzymes until it reaches the ovary, where it enters the ovule through a tiny orifice known as the micropyle.
Question 2. Given ahead is a diagrammatic sketch of the sectional view of a germinating pollen grain. Study the same and then answer the question that follows:
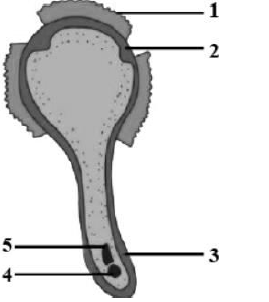
(a) Name the parts labelled 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5.
(b) Where does the germination of the pollen grain take place and how?
(c) What is the function of the part labeled ‘4’?
(d) What happens to the part labeled ‘5’ during the process?
Solution.
(a)

(b) Pollen grains germinate only when they come into contact with the stigma of the same plant species. Because the stigma secretes carbohydrates, the pollen grain is encouraged to germinate.
(c) The purpose of portion ‘4’ (tube nucleus) is to direct the pollen tube’s development towards the ovary.
(d) During pollen grain germination, portion ‘5’ (generative nucleus) near the pollen tube’s tip separates into two sperm nuclei. One of the synergids accepts the pollen tube, which releases its two sperm nuclei. One sperm nucleus penetrates the egg cell and unites with its nucleus, while the other sperm nucleus travels to the central cell’s two polar nuclei and merges with them.
Question 3. Given ahead is a diagrammatic representation of the process of fertilization. Study the same and then answer the question that follows:
(a) Name the parts labeled 1,2,3,4, 5 and 6.
(b) What happens to (i) Ovary (ii) Ovule after fertilization?
(c) What is the function of the synergids?
(d) What part does the stigma play in the process of fertilization?

Solution.
(a)

(b) Following fertilization, the following modifications occur:
(i) Ovary – It expands to allow fruit to develop. The fruit wall is formed from the ovarian wall.
(ii) Ovule – The ovule develops into the seed.
(c) Synergid Function –
1. It feeds the egg cell, allowing the pollen tube to get to the egg.
2. Makes sure the pollen tube is working properly.
3. Is in charge of the sperm nuclei’s release.
(d) Stigma Function –
Pollen grains are transported to the stigma during pollination. Pollen grains only germinate when they fall on the stigma. After germination, the pollen tube grows past the stigma and into the ovary, where it fertilizes the egg cell.




