Students should refer to The Endocrine System ICSE Class 10 Biology Board Exam Questions provided below with solutions. These will help the students to understand the type of questions which have been asked in previous year examinations and the type of solutions which the student should give to get good marks. You should also refer to ICSE Class 10 Biology Sample papers for more practice
ICSE Class 10 Biology The Endocrine System Important Questions
Students should learn the important questions and answers given below for Chapter The Endocrine System in Biology for ICSE Class 10. These board questions are expected to come in the upcoming exams. Students of ICSE Class 10th should go through the Important questions and answers ICSE Class 10 Biology which will help them to get more marks in exams.
The Endocrine System ICSE Class 10 Biology Board Exam Questions
The Endocrine System ICSE Class 10 Biology
Question. Give symptoms of cretinism?
Ans. It occurs in children.
(a) Dwarfism: The person shows retarded growth.
(b) Mental retardation : Due to failure of the brain to develop fully.
(c) Body metabolism is lowered resulting in low body temperature and slow heart rate.
Question. Give the function of Glucocorticoids?
Ans. It helps in regulation of carbohydrates, proteins and fat metabolism.
Question. Give structure, location and function of pancreas?
Ans. The pancreas has a flat leaf like structure, it is located slightly inferior to the stomach. It is made up of cells that are clustered together forming Islets of Langerhans
(a) Alpha cells secrete the hormone glucagon. Glucagon increases the blood sugar by breaking glycogen into glucose.
(b) Beta cells secrete the hormone insulin. It promotes glucose utilisation by the body cells. It stimulates deposition of extra glucose of the blood as glycogen in liver.
Question. Give symptoms of simple goitre.
Ans. Simple goitre results in swelling of neck.
Question. Mention the role of Adrenaline.
Ans. The hormone prepares the body to meet any emergency situation i.e., fight (to face danger) or flight (run away).
Question. What are the effects of hypersecretion of thyroid gland.
Ans. Hyperthyroidism in adults leads to exophthalmic goitre.
Question. Describe the Hormones secreted by anterior lobe (Adenohypophysis).
Ans. GH or STH : (Growth Hormone or Somatotropic Hormone) : It stimulates body growth, helps in growth of bones, muscles and regulation of fat and carbohydrates metabolism.
TSH : (Thyroid stimulating hormone) : The hormone stimulates the uptake of iodine and controls physiological state of thyroid gland including the synthesis and release of thyroxine.
ACTH : (Adrenocorticotropic hormone) : The hormone controls the development and hormonal secretion of adrenal cortex, it maintains organic balance.
Gonadotropins :
(a) FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone) : This hormone acts on the gonads in both male and female. In male the hormone controls spermatogenesis. In females it stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles and secretion of female sex hormones.
(b) LH (Luteinising hormone) : It is only secreted in females which brings about development of corpus luteum and secretion of progesterone.
(c) ICSH (Interstitial Cell stimulating hormone): In males the hormone promotes the activity of interstitial cells (Leydig cells) to secrete male hormone testosterone.
(d) Prolactin : It is a female hormone which is functional in females after the child birth. It promotes the development of mammary glands and secretion of milk.
Question. How does thyroid hormone act on body?
Ans. • Regulation of organic metabolism and energy balance : All protein, fat and carbohydrates metabolism is influenced by thyroxine.
• Regulation of growth and development. They regulate tissue growth, particularly in children.
• Help in regulation of calcium ions (calcitonin).
Question. Give the exact location of parathyroid gland.
Ans. The two pairs of parathyroid gland is embedded on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland.
Question. Name the hormone secreted by the adrenal medulla.
Ans. The hormone secreted by adrenal medulla is adrenaline or epinephrine.
Question. What is MSH? What is its functions?
Ans. MSH stands for melanocyte stimulating hormone. It is produced by the intermediate lobe of pituitary gland.
The hormone takes part in both synthesis and dispersal of pigment melanin in the skin. It is important in controlling skin pigmentation in fishes, amphibians and some reptiles. In human beings it is vestigial.
Question. What are the effects of undersecretion of thyroxine?
Ans. Undersecretion of thyroxine is known as hyposecretion.
Hyposecretion in children leads to cretinism.
Hyposecretion in adults leads to myxoedema.
Question. Government has made it compulsory to sell iodised salt?
Ans. Thyroid requires supply of iodine through blood for synthesis of thyroxine. Thyroxine is needed for normal BMR, growth, activity of CNS etc. Its deficiency can lead to goitre. Hence to prevent severe disorder due to Iodine deficiency the government has made compulsory.
Question. Give symptoms of myxoedema?
Ans. It occur in adults.
(a) Disorder is characterised by oedema retention of fluids
(b) It causes swelling in facial muscles and looks puffy.
(c) It also leads to slow heart rate and low body temperature.
Question. What is insulin shock?
Ans. If a diabetic person is given an overdose of insulin, his blood sugar level may fall drastically (hypoglycemia) and patient may become unconscious. This is called ‘insulin shock’.
Question. State the symptoms of diabetes mellitus.
Ans. A diabetic person has –
a) Hyperglycemia – more sugar in the blood.
b) Frequent urination and excessive thirst.
c) Excretes glucose in the urine.
d) Loses weight
Question. State the effect produced by glucagon.
Ans. Glucagon converts the glycogen in the liver to glucose which is released into the blood, thus it raises sugar level in the blood.
Question. “Pituitary is called the master gland.” Say why?
Ans. The hormones of pituitary gland regulate so many body activities and also control the secretion of other endocrine glands, thus it is referred to as a master gland. The anterior lobe secretes ‘Tropic hormone’ which control the production of other endocrine glands, e.g., TSH secreted by pituitary controls the production of thyroxine by the thyroid gland.
Question. Give the location of adrenal gland?
Ans. Adrenal glands are triangular in shape stituated above both the kidneys.
Question. What is Addison’s disease?
Ans. It is caused due to undersecretion of adrenal cortex (glucocorticoids). Symptoms are dark pigmentation of skin, loss of energy and nausea.
Question. What is the result of insufficient insulin?
Ans Undersecretion of insulin results in diabetes mellitus.
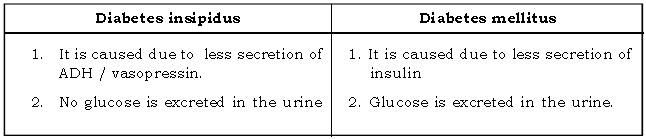
Question. Differentiate between diabetes insipidus and diabetes mellitus.
Ans.
Question. Give structure and location of pituitary gland?
Ans. Structure : Pituitary gland or hypophysis is a small pea sized (weight 0.5 – 0.6 gms) endocrine gland. Anterior lobe (Adenohypophysis),posterior lobe ( Neurohypophysis) and intermediate lobe.
Location : It is located inferior to hypothalamus, the gland is connected to the hypothalamus by the means of a stalk or infundibulum.
Question. What is the functions of insulin?
Ans. It maintains proper sugar level in the blood by:
a) Promoting utilization of glucose by the body cells.
b) Accelerating conversion of extra glucose to glycogen in liver and muscles.
Question. Give the functions of mineralocorticoids?
Ans. It influences mineral metabolism. It also stimulates kidney to retain sodium and excrete potassium.
Question. What are antagonistic hormones ? Give an example.
Ans. Hormones which have the opposite action at the same point are called antagonistic e.g., Insulin which lowers blood sugar level and Glucagon which raises blood sugar level.
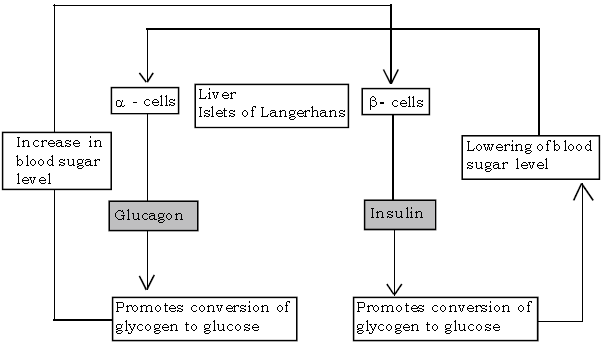
A diagrammatic sketch to show the role of antagonistic hormones of the Pancreas.
Question. What is simple goitre?
Ans. Simple goitre is caused due to hyposecretion of thyroxine by the thyroid gland. It is generally caused due to deficiency of iodine in the diet. Iodine is required for proper formation and production of thyroxine. If iodine intake is less then thyroxine secretion reduces leading to simple goitre.
Question. A diabetic person is administered insulin by injection and not orally. Why?
Ans Insulin is chemically a protein. Thus if admistered orally it would be digested like a dietary protein and not reach the target cells. Thus insulin is given by injections.
Question. Give a brief summary of the hormones of the Anterior lobe of Pituitary and their function.
Ans. Hormones of Anterior lobe and their action.

Question. Mention the hormones secreted by posterior pituitary (Neurohypophysis).
Ans. (a) ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone) : It is also known as vasopressin. Its function is reabsorption of water from glomerular filtrate making the urine concentrated and preventing excessive loss of water.
(b) Oxytocin : It is a female hormone that stimuates uterine contractions during child birth. It also helps in ejection of milk from the mammary glands.
Question. What is Cushing’s syndrome?
Ans. It is caused due to hypersecretion of glucocorticoids, leads to development of moon face, buffalo lump, hypertension, hyperglycemia, weakness etc.
Question. Give the hormone secreted by adrenal cortex?
Ans. The hormones secreted by adrenal cortex are called cortisones; they are glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, adrenocorticoids.
Question. Differentiate between the following pairs :
(a) Simple goitre and exophthalmic goitre
(b) Cretinism and dwarfism
Ans.

Question. What is the effect of hypersecretion of insulin?
Ans. It results in hypoglycemia i.e., sugar level in the blood is lowered. Person may enter into coma if sugar level falls drastically.
Question. Adrenaline is called an ‘emergency hormone’ say why?
OR
Adrenaline is called a ‘fight or flight’ hormone. Explain.
Ans. Adrenaline prepares the body to cope with an abnormal/emergency situation by –
a) Increasing contractability of skeletal muscles for immediate action.
b) Converting glycogen to glucose, thus increasing energy level of the body.
c) Increasing heart beat so that more oxygen and glucose is sent to the muscles for action.
Question. Give symptoms of exophthalmic goitre?
Ans. (a) The thyroid is enlarged by 2 to 3 times its original size.
(b) Fluid is retained behind the eye which causes the eye to protrude.
(c) Appetite increases but the person looses weight.


Question. State the exact location of the following endocrine glands.
a) Pituitary b) Thyroid c) Adrenal f) Pancreas
Ans.

Question. Name the hormone produced by each.
a) Stomach b) Intestine c) Placenta
Ans.

Question. Name the hormone that :
1. Is secreted by adrenal medulla. _________
Ans.
Adrenaline
2. Deficiency of which hormone in childhood causes dwarfism. ____________
Ans.
GH (Growth Hormone)
3. Is called the fight or flight hormone. ___________
Ans.
Adrenaline
4. Is produced by corpus luteum to maintain the state of pregnancy. ________
Ans.
Progesterone
5. Regulates calcium and phosphorus metabolism in the body. __________
Ans.
Calcitonin
6. Controls the amount of water excreted in the urine. __________
Ans.
Antidiuretic hormone
7. Is secreted by β-cells of Islets of Langerhans. _________
Ans.
Insulin
8. Controls the secretions of thyroid gland. ________
Ans.
TSH (Thyroid
9. Oversecretion of which causes bulging eyeballs and high metabolism. _________
Ans.
Thyroxine
10. Accelerates the conversion of glycogen to glucose. ________
Ans.
Glucagon
11. Is secreted by the placenta. ___________
Ans.
Progesterone / Oestrogen
12. Promotes the conversion to glucose to glycogen for storage. __________
Ans
.Insulin stimulating hormone)
13. Is secreted by pituitary that stimulates contraction of uterus. ________
Ans.
Oxytocin
14. Oversecretion of which in adulthood causes acromegaly. ___________
Ans.
GH (Growth Hormone)
15. Is secreted by β- cells of islets of Langerhans. __________
Ans.
Glucagon
Question. Give one word for each of the following :
1 A fluid, directly into which the homones are released and transported _____________
Ans.
Blood
2. Chemical regulators that are secreted into the blood stream. ___________
Ans.
Hormones
3. Hormones that stimulate other endocrine glands to produce their specific hormones. ________
Ans.
Tropic homuoues
4. Hormones which have opposite effect at the same place. ___________
Ans.
Antagonistic hormones
5. A ductless gland which pours its secretion into the blood directly. _____________
Ans.
Endocrine gland
6. The cells / tissue which responds to a particular hormone. ____________
Ans.
Target cells / tissues
7. A gland which pours its secretion into a particular location with the help of a duct.________
Ans.
Exocrine gland
8. A group of male hormones. ___________
Ans.
Androgens
9. A physical and mental dwarf produced due to early atrophy of thyroid ____________
Ans.
Cretin
10. A condition of mantaining a steady internal environment ___________
Ans.
Homeostasis
Question Give the full form of each of the following :

Question. Name the disease / disordered produced by :
1. Hypersecretion of glucocorticoids. __________
Ans.
Cushing’s syndrome
2. Hyposecretion of thyroxine in childhood. ___________
Ans.
Cretinism
3. Oversecretion of growth hormone during growing years. __________
Ans.
Gigantism
4. Oversecretion of ACTH from pituitary to compensate reduced production of glucocorticoids. __________
Ans.
Adrenal virilism
5. Undersecretion of vasopressin. ___________
Ans.
Diabetes insipidus
6. Oversecretion of thyroxine. __________
Ans.
Exophthalmic goitre
7. Inadequate insulin secretion. ___________
Ans.
Diabetes mellitus
8. Deficiency of iodine in the diet. ___________
Ans.
Simple goitre
9. Increased insulin secretion. ____________
Ans.
Insulin shock/hypoglycemia
10. Undersecretion of glucocorticoid from adrenal cortex. _________
Ans.
Addison’s disease
11. Undersecretion of thyroxine in adulthood. ___________
Ans.
Myxoedema
12. Early atrophy of thyroid gland. ____________
Ans.
Cretinism
13. Deficiency of iodine in the diet. __________
Ans.
Simple goitre
14. Hypersecretion of growth hormone during adulthood. __________
Ans.
Acromegaly
15. Hyposecretion of growth hormone in childhood. ___________
Ans.
Dwarfism
Question. Fill in the blanks with correct word / words : –
(i) A child who is physically and mentally a dwarf is called a _____________.
Ans.
Cretin.
(ii) Oversecretion of thyroxine causes ________________.
Ans.
Exophthalmic goitre
(iii) Mineral element found in thyroxine is ___________________.
Ans.
lodine
(iv) Thyroid is a lobular gland with _____________ lobes.
Ans.
two
(v) An abnormal swelling in the neck due to hypothyroidism is due to _____________.
Ans.
Simple goitre
Question. Study the relationship and complete the following :
(i) Vasopressin : controls urine output :: __________ : uterine contraction
Ans.
Vasopressin : controls urine output :: Oxytocin : uterine contraction
(ii) Hypothyroidism : simple goitre :: __________ : exophthalmic goitre
Ans.
Hypothyroidism : simple goitre :: hyperthyroidism : exophthalmic goitre
(iii) Pituitary (anterior lobe) : GH :: __________ : ADH / Vassopressin.
Ans.
Pituitary (anterior lobe) : GH :: Pituitary (posterior lobe) : ADH / Vassopressin.
(iv) Endocrine gland : thyroid :: __________ : salivary glands.
Ans.
Endocrine gland : thyroid :: exocrine gland : salivary glands.
(v) Pituitary: brain region :: thyroid : __________
Ans.
Pituitary: brain region :: thyroid : neck region
Question. Name the following :
(i) Special group of cells that produce hormones in Pancreas
Ans.
Islets of Langerhans
(ii) A hormone secreted by α-cells
Ans.
Glucagon
(iii) A condition caused due to hyposecretion of insulin
Ans.
Diabetes mellitus
(iv) A gland which is both exocrine and endocrine
Ans.
Pancreas
(iii)A hormone which lowers blood sugar level
Ans.
Insulin
Question. Choose the most appropriate answer :
1. Master gland of the human body is :
a) Pancreas
b) Liver
c) Pituitary
d) Thyroid.
Ans.
Pituitary
2. Pituitary gland regulates the urine formation through : ___________
a) Oxygen
b) TSH
c) ACTH
d) ADH
Ans.
ADH
3. Gigantism and acromegaly are due to : _______________
a) Hyposecretion of thyroxine
b) Hyposecretion of growth hormone
c) Hypersecretion of thyroxine
d) Hypersecretion of growth hormone.
Ans.
Hypersecretion of growth hormone.
4. Which of the following is not a endocrine gland : _________
a) Pancreas
b) Lacrimal gland
c) Adrenal
d) Pituitary
Ans.
Lacrimal gland
5. Which of the following is not a hormone : __________
a) Insulin
b) Oxytocin
c) Glucagon
d) Glucose
Ans.
Glucose
6. Development of secondary sexual characteristics in human males is promoted by :__________
a) Oesterogen
b) Testosterone
c) ADH
d) ACTH.
Ans.
Testosterone
7. Fight or flight hormone is : _________
a) Thyroxine
b) Progesterone
c) Adrenaline
d) Insulin
Ans.
Adrenaline
8. Contraction of uterus during child birth is caused by : ___________
a) TSH
b) Oxytocin
c) Salivary gland
d) Adrenal
Ans.
Oxytocin
9. Secretion of endocrine glands are called : __________
a) hormones
b) Enzymes
c) Amino acid
d) Saliva
Ans.
hormones
10. ACTH is secreted by : __________
a) Adrenal
b) Pituitary
c) Pancreas
d) Thyroid.
Ans.
Pituitary







