Students should refer to The Nervous System ICSE Class 10 Biology Board Exam Questions provided below with solutions. These will help the students to understand the type of questions which have been asked in previous year examinations and the type of solutions which the student should give to get good marks. You should also refer to ICSE Class 10 Biology Sample papers for more practice
ICSE Class 10 Biology The Nervous System Important Questions
Students should learn the important questions and answers given below for Chapter The Nervous System in Biology for ICSE Class 10. These board questions are expected to come in the upcoming exams. Students of ICSE Class 10th should go through the Important questions and answers ICSE Class 10 Biology which will help them to get more marks in exams.
The Nervous System ICSE Class 10 Biology Board Exam Questions
The Nervous System ICSE Class 10 Biology
Question. Explain electrochemical mechanism of transfer of nerve impulses.
Ans. Between the tip of each of the axon’s terminal fibres and the dendrites of another neuron– the junction
point known as synapse – is a tiny synaptic gap or cleft. The message of one neuron crosses to another
neuron by means of a complicated event. An electrical impulse travelling down the axon releases into this gap molecules of the neurotransmitter.
These molecules cross the gap and excite activity in the second neuron. The neuron then fires an electrical impulse along its own axon. The strength of the impulse depends upon the total impact it receives from the incoming messages at the synapses. Meanwhile at each synapse, the neurotransmitter chemicals are either absorbed by
other neurons or chemically destroyed.
Q.5. The following diagram represents the human brain as seen in an external view. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow :
(i) Name the parts labelled 1, 2, 3 and 4
(ii) Mention the difference in the arrangement of the nerve cells in the parts marked ‘1’ and ‘4’.
(iii) What is the main function of the parts marked ‘3’ and ‘4’?
(iv) Name the sheet of nerve fibres that connect the two halves of the part labelled ‘1’

Ans. (i) 1 – Cerebrum ; 2 – Cerebellum
3 – Pons varolli 4 – Medulla oblongata and Spinal cord.
(ii) Part – 1 Part –4
outer cyton inner cyton
inner axon outer axon
(iii) Functions Part ‘3’ acts as a bridge between mid–brain and medulla oblongata.
(iv) Corpus callosum
Question. What is gray matter?
Ans. Gray matter is a collection of unmyelinated cell bodies (neurons) and dendrites .
Question. State whether the following actions are’ voluntary actions’ ‘simple reflex’ or ‘conditional reflex’
a) Blinking b) Cleaning the table
c) Playing on the keyboard d) Salivating when food is put in the mouth
Ans. a) Blinking – Simple reflex
b) Cleaning the table – Voluntary action
c) Playing on key board – Conditional reflex
d) Salivation when food is put in – Simple reflex
Question. Describe the structure of spinal cord.
Ans. The spinal cord is a cylindrical structure located in the spinal canal of veretebral column. It begins as a continuation of the medulla oblongata. In cross section, the spinal cord shows an inner gray matter lying within a white matter. The gray matter forms a H–shaped area. Located in the centre of cross bar of the H of the gray matter in small space called the central canal. The canal runs to the length of the spinal cord and contains the cerebrospinal fluid. A major function of the spinal cord is to convey nerve impulses from the periphery to the brain and to conduct motor impulses from the brain to the periphery. It also serves as reflex centre.
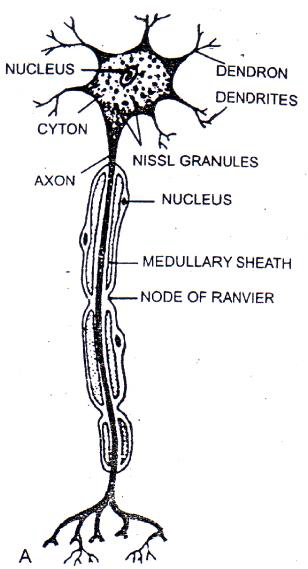
Question. Describe the structure of neuron.
Ans. (i) Neuron is made up of a cell body and cell processes.
(ii) Cell body consists of a mass of cyton surrounded by a cell membrane.
(iii)The cell body gives off many processes – Dendrites.
(iv) The neuroplasm shows the presence of granular material – Nissl’s granules of RNA granules
(v) The axon could be as long as 1 meter.
(vi) The axon may be covered by myelin sheath.
(vii)At some points the myelin sheath does not cover the axon. These are called Nodes of Ranvier.
(viii) The myelin sheath consists of Schwann cells.
(ix) The dendrites carry impulses towards the neuron while axon carries it away from neuron.
Question. Define synapse.
Ans. The junction between two neurons, axon of one neuron and dendron of another neuron is called a synapse.
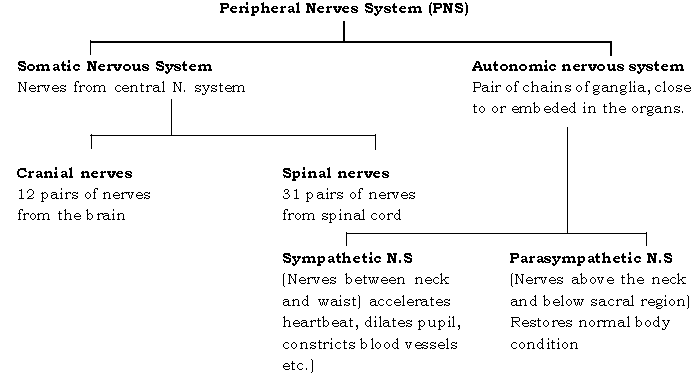
Question. Give the divisions of the nervous system and explain peripheral nervous system.
Ans. The nervous system may be divided into two principal divisions – the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system.
(i) Peripheral nervous system : The peripheral nervous system is composed of the cranial nerves processes that connect the brain and spinal cord with receptor muscles and glands.
• Cranial nerves : Out of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves 10 originate from the brain stem. Some cranial nerves contain only sensory fibres and are called sensory nerves. The others contain both sensory and motor fibres and are referred to as mixed nerves.
• Spinal nerves : The 31 pairs of spinal nerves are named and numbered according to the region and level of the spinal cord from which they emerge. Thus there are 8 pairs : Cervical nerves (neck regions), 12 pairs : Thoracic nerves, 5 pairs : Lumbar nerves, 5 pairs : sacral, 1 pair : Coccygeal nerves.
• Afferent system : The sensory nerves of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) form the afferent system which conveys information from the periphery of the body to the CNS.
• Efferent system : The motor nerves of the PNS form the efferent system which conveys information from the CNS to the muscles and glands. Somatic nervous system : Nervous system conveying impulses to the skeletal muscles constitutes the somatic nervous system.
Question. Name the part of the human brain that controls body temperature.
Ans. Hypothalamus.
Question. Name the lobes of cerebrum giving the function of each lobe.
Ans. Each cerebral hemisphere is divided into 4 lobes –
The frontal lobe, the parietal lobe, the temporal lobe and the occipital lobe.

Functions :
Frontal lobe : is associated with reasoning, planning, emotions etc.
Parietal lobe : is associated with movement, recognition, perception of stimuli.
Occipital lobe : is associated with vision.
Temporal lobe : is associated with auditory stimulus, memory and speech.
Question. Draw neat and labelled diagram of Human cerebrum
Ans.

Question. Complete the following sentence using the correct word from the alternatives given :
(a) The seat of memory and intelligence in human brain is _________________
(cerebrum, cerebellum, hypothalamus)
(b) The dorsal root ganglion of the spinal cord contains cell bodies of _________________
neurons. (motor / sensory / intermediate)
Ans. (a) The seat of memory and intelligence in human brain is cerebrum.
(b) The dorsal root ganglion of the spinal cord contains cell bodies of motor neurons.
Question. What is white matter?
Ans. White matter is an aggregate of myelinated axon.
Question. (a) Give short explanation of the following statement :
Your mouth begins to water (salvation) at the sight of tasty food.
Ans. (a) An acquired reflex is, for example, what you experience, simply at the sight or by the smell of tasty food resulting in watering (salvation) of your mouth. This means that if you have not eaten that food earlier the response would not occur. In natural reflex salivation occurs when you chew or eat food. But in the above example, the
sight of food was enough for the response. Here the brain actually remembers the taste of the food and works in an unconscious way. Such actions are called conditioned reflexes.
Question. The diagram below represents the spinal cord of a mammal seen in a transverse section together with the nerves. Study the same and then answers the questions that follow
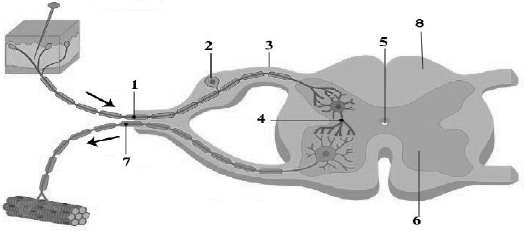
(a) Label the parts1 – 8 indicated by guide–lines.
(b) What do the arrows indicate? What is the pathway indicated termed as?
(c) What type of nerve is shown in the diagram?
Ans. 1. Sensory nerve 2. Dorsal ganglion
3. Dorsal root 4. Association neuron
5. Central Canal 6. Gray matter
7. Motor nerve 8. White matter
(b) Arrows indicate the direction of the impulse, pathways indicated is termed as nervous pathway.
(c) Spinal nerve
Question. Write a note on unconditioned and conditioned reflex.
Ans. Unconditioned reflex : These reflexes are inborn and inherited. Response to the stimulus requires no previous experience, learning or judgement. Swallowing blushing, blinking when some object passes close to the eyes, withdrawal of hand on touching a hot object are some common examples.
Conditioned reflexes : These reflexes are temporary nervous connections of the body with environmental or internal stimuli. Conditioned reflexes are learned in response to stimuli acquired individually during the life of an organism. These vary in different individuals of a species. Conditioned reflexes are changeable and easily induced or lost depending on the environment conditions. Conditioned reflexes are dominated by the cerebral cortex. Two stimuli are required to induce a conditioned reflex.
(i) A stimulus which is neutral under the given circumstances, but which is destined to become a conditioned reflex
(ii) A stimulus which evokes an unconditioned reflex.
Question. Give appropriate terms for the following :
(a) Protective covering of the brain and spinal cord.
Ans. (a) Meninges
Question. The diagram alongside is that of the human brain. Guidelines 1 to 5 indicate different parts of the surface of the brain and these are as follows :
(1) Frontal lobe as cerebrum
(2) Temporal lobe of cerebrum
(3) Occipital lobe of cerebrum
(4) Cerebellum and
(5) Medulla oblongata

Study the diagram and answer the following questions :
(i) What handicaps would result from :
(a) damage to part numbered 3?
(b) damage to part numbered 4?
(ii) Mention one main function of each of the parts numbered 1, 2 and 5
Ans. (i) (a) Visual sensation and hearing can be affected.
(b) An individual can lose the balance of the body and co-ordination of muscular activities.
(ii) (1) It is concerned with the thinking.
(2) Temporal lobe of cerebrum is concerned with auditory stimulus.
(3) Medulla oblongata controls heart beat, respiration and blood pressure
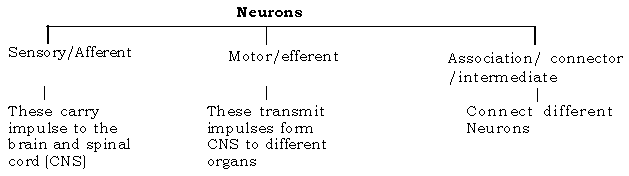
Question. How are neurons classified?
Ans. Classification of neurons : According to their functions, neurons are divided into three categories – sensory (afferent) neurons, motor (efferent) neurons and association (connecting) neurons.
Sensory neurons : These carry nerve impulses to the brain and spinal cord, i.e. to the central nervous system. Their processes are called afferent fibres.
Motor neurons : These transmit impulses from the central nervous system through the efferent fibres to various organs and alter the state and functions of the organs
Connecting neurons : These connect different neurons.
Question. Describe the structure of a multipolar or myelinated neuron?
Ans. The cell body or Cyton contains nucleus with granular cyptoplasm surrounding it.
The Dendrities or dendrons – are branched cyptoplasmic processes of the cyton, reaching the finest part of the body and their function is to conduct nerve impulses to the cyton. The Axon – Axon is one very long process from the cyton. It varies in size, covered on the outer side by a white insulating sheath called neurilemma. Axon surrounded by white layer is called myelinated neuron and axon without the myelin is called unmyelinated neuron or non-myelinated neuron. Between the segments of myelin the is called myelinated gaps called Nodes of Ranvier.
Question. What is a nerve ?
Ans. A bundle of axons enclosed in a tubular sheath is called a nerve.
Question. Give the three types of neurons according to the functions ?
Ans. According to the functions of neurons, they are of three types.
Question. Define the following :
(a) Natural reflex (b) Nerve (c) Stimulus (d) Excitability (e) Ganglion (f) Electroncephalogram
Ans. (a) Natural reflex : It is a repsonse to a stimulus performed without conscious control, e.g., blinking of the eye when dust particle enters into the eye.
(b) Nerve : Nerves are the thread like glistening white structures which emerge from the brain and spinal cord and branch out to almost all parts of the body. e.g. sensory nerve, motor nerve, mixed nerve.
(c) Stimulus : Change of external or internal environment that results in a change in the activities of the organisms. e.g. blinking of the eye.
(d) Excitability : It is the ability of nerve cell to respond to stimuli and convert them into nerve impulses.
(e) Ganglion : It is an aggregation of nerve cell bodies and the proximal portion of their processes.
(f) Electroncephalogram (EEG) : EEG is a graph made by an instrument (encephalograph) that records the waves of the brain. The minute electrical waves produced by the nerve cell of the brain are transmitted to the instrument, which amplifies and records them on a strip of paper.
Question. What is synapse? Give its function?
Ans. Synapse is a tiny gap between the tip of axon fibre and dendrites of another neuron. Through these synapse, the neurotransmitters chemicals are either absorbed by other neuron or chemically destroyed. (Acetylcholine is an important neurotransmitter)
Question. Select the correct alternatives :
(i) Cerebellum is the part of the brain which is responsible for :
(a) Interpreting sensations
(b) Conducting reflexes in the body.
(c) Maintaining posture and equilibrium
(d) Controlling thinking, memory and reasoning.
(ii) The parts of the human ear concerned with hearing are :
(a) ear ossicles and tympanum
(b) semicircular canals, utricules and sacculus
(c) eustachian tube, tympanum and utriculus.
(d) perilymph, ear ossicles and semicircular canals
Ans. (i) Cerebellum is the part of the brain which is responsible for maintaining posture and equilibrium.
(ii) The parts of the human ear concerened with hearing are ear ossicles and tympanum.
Question. Draw and label only a myelinated neuron ?
Ans.

Question. What is very special about neuron?
Ans. Unlike other body cells, neurons are incapable of cell division, thus once formed – they can only be destroyed
Question. Select the correct answer out of 4 available choices In mammals, the corpus callosum connects :
(a) the two optic lobes.
(b) the two cerebral hemispheres
(c) the cerebrum to the cerebellum
(d) the pons to the medulla oblongata
Ans. In mammals, the corpus callosum connects the two cerebral hemispheres
Question. Give the classification of nerves according to their function and structure.
Ans. Accordingly there are three types of nerves

Question. Mention one major function of the following :
(a) Cerebellum (b) Medulla obologata
Ans. (a) Cerebellum : Cerebellum co-ordinates the muscular movements during walking and running. It also plays an important role in maintaining the posture and equilibrium of the body.
(b) Medulla oblongata : Controls the involuntary muscles of lungs and heart

Question and Answer :
Question. What is the weight of an adult brain?
Ans. The adult brain weighs about 1.35kg
Question. What is the main function of Cerebellum?
Ans. Cerebellum maintains ‘balance’ of the body and co-ordinate muscular activities.
Question. How many membranes protect the brain? Give their names and situation.
Ans. Three membranes called meninges protect the brain. The outermost tough fibrous membrane is dura mater, the middle thin is the arachnoid and the innermost vascular membrane is called the pia mater.
Question. What connects these two cerebral hemispheres?
Ans. A sheet of fibres connecting the two cerebral hemispheres is called corpus callosum.
Question. What is the hollow parts of the brain called?
Ans. The hollow parts of the brain are called ventricles
Question. What is the function of Pons?
Ans. (i) Pons is a bridge of nerve fibres connecting the two lobes of the cerebellum.
(ii) Transmit impulses and co-ordination of muscular movements on both sides of the body.
Question. What does the outer region Cerebrum contain?
Ans. The outer portion of cerebrum is called Cortex and is made up of cell bodies (cytons) of the neurons and it is grayish in colour called the gray matter.
Question. What is pons varoli?
Ans. (i) Pons is a part of hind brain, located in the centre of the brain below the cerebellum.
Question. How does gyri and sulci make a difference to a person?
Ans. The gyri and sulci increase surface area of the brain to accomodate more nerve cells and hence more the convolutions, greater the intelligence.
Question. Where is the brain situated?
Ans. The brain is situated inside the skull
Question. What does inner portion of cerebrum consists of?
Ans. The inner portion of the cerebrum consists of “white matter”, which mainly contains the axons (nerve fibres) of the neurons.
Question. What are the functions of spinal cord?
Ans. Functions of the spinal cord :- The spinal cord is concerned with –
i) Reflexes below the neck. The brain comes to know few seconds later.
ii) Conducts sensory impulses from the skin and muscles to the brain and
iii) Conducts motor responses from the brain to muscles of the trunk and limbs.
Question. What is the function of cerebrospinal fluid?
Ans. The cerebrospinal fluid :
i) protects the brain from shock.
ii) acts like a cushion for the brain.
Question. Which is the largest part of the brain?
Ans. Cerebrum is the largest part of the brain.
Question. What is the function of corpus callosum?
Ans. Functions are –
a) Transfers information from one hemisphere to the other
b) Connects the two cerebral hemispheres of Cerebrum.
Question. What forms convolutions in the gray matter and what are they called?
Ans. The gray matter in the cortex region forms folds and grooves, known as gyri(folds) and sulci (depression) – (singular gyrus and sulcus)
Question. Where is medulla oblongata situated?
Ans. Medulla oblongata is the lowest part of the brain and is located at the base of the skull.
Question. Name the three parts of the brain visible externally.
Ans. They are –
i) Cerebrum ii) Cerebellum iii) Medulla oblongata
Question. How much oxygen is consumed by human brain?
Ans. The human brain consumes 20% (one-fifth) of the total O2 taken into the body.
Question. What are the parts of Diencephalon?
Ans. Diencephalon consists mainly of Thalamus and hypothalamus on which is pituitary gland.
Question. What are the function of Cerebrum?
Ans. i) The highly developed cortex – enable us to think, reason out, invent, plan and memorise.
ii) Cerebrum is the seat of intelligence, consciousness and will power.
iii) Cerebrum controls all voluntary actions.
Question. What are cerebral hemispheres?
Ans. Cerebrum is divided mid-dorsally into two cerebral hemispheres, left and right.
Question. What is spinal cord? Give its location.
Ans. • Spinal cord is a cylindrical structure, located inside the vertebral column.
• The spinal cord extends from the medulla oblongata of the brain down almost the whole length of backbone. In the centre is the central canal filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
Question. What is the function of Medulla oblongata?
Ans. Medulla oblongata controls involuntary activities of internal organs, heart beat, breathing etc., and coordinates reflexes such as swallowing, vomiting, coughing, sneezing, hiccuping etc.
Question. Where is “Small brain” situated?
Ans. The cerebellum (small brain) is located just at the base and under the large cerebrum.
Question. What are the functions of Thalamus and Hypothalamus?
Ans. Thalamus is the centre for interpretation of sensory impulsory impulses such as pain, temperature, light, touch and pressure.
Hypothalamus controls normal body temperature, food intake and thirst. It also controls the functioning or pituitary gland.
Question. Put the order in sequence :
1. Dorsal root ganglion, Motor neuron, effector, Sensory nerve, Connector neuron.
Ans. Sensory nerve → Dorsal root ganglion → connector neuron, → motor neuron → effector
2. Dorsal root ganglion, Receptor, effector, ventral root ganglion, associated neuron
Ans. Receptor → Dorsal root ganglion → association neuron → ventral root ganglion → effector.
Question. Fill in the blanks :
(a) The spinal cord is the centre of _______________ action.
Ans.
reflex
(b) There are _______________ pairs of cranial nerves
Ans.
twelve
(c) The central nervous system consists of _______________ and _______________
Ans.
Brain and spinal cord
(d The association of two nerves is called _______________
Ans.
synapse
Question. Write scientific terms for each of the following :
(a) A collection of several nerves _______________
Ans.
Nerve fibres
(b) The very fine processes of a neuron _______________
Ans.
Dendrites
(c) The nerve arising from the brain _______________
Ans.
Motor nerve
(d) The liquid that protects the brain from shocks _______________
Ans.
Cerebrospinal fluid
Question. Match the pairs
Column – I Column – II
1) Neurotransmitters (a) Cell body
2) Spinal cord (b) Acetylcholine
3) Perikaryon (c) Reflex action
4) Cerebellum (d) Forebrain
5) Cerebrum (e) Hindbrain
Ans. Column – I Column – II
1) Neurotransmitters (b) Acetylcholine
2) Spinal cord (c) Reflex action
3) Perikaryon (a) Cell body
4) Cerebellum (e) Hindbrain
5) Cerebrum (d) Forebrain
Question. Name the following :
(a) The part of the human brain which is concerned with memory and intelligence in the body.
Ans.
Cerebrum
(b) The part of the human brain which is concerned with muscular co-ordination in the body.
Ans.
Cerebellum
(c) Convolusion in the brain that increases its surface area.
Ans.
Sulci and gyri
(d) Sudden and spontaneous responses of the body not involving brain.
Ans.
Involuntary
(e) Nerve that carry the message from brain towards a motor organ.
Ans.
Motor nerves
(f) The nerves that arise from brain.
Ans.
Motor nerves
(g) Cavity of the skull in which brain is present
Ans.
Sphenoid cavity
(h) Nerve that carry the message from a sensory organ towards the brain.
Ans.
Sensory nerves
Question. Odd one out :
1. Myelin sheath, Node of Ranvier, Melanin, Neurilemma
Ans.
Melanin
2. Cerebrum, Cerebral hemispheres, Temporal lobe, Cerebellum
Ans.
Cerebellum
3. Sneezing, Coughing, Typing, Blinking.
Ans.
Typing
4. Pericardium, Meninges, Pleura, Peritonium, Spinal cord.
Ans.
Spinal cord
5. Corpus luteum, Corpus Callosum, Pons, Cerebellum.
Ans.
Corpus luteum
6. Pons, Cerebellum, Medulla oblongata, Cerebrum
Ans.
Cerebrum
Question. Choose the correct alternative :
1. Dilation of blood vessels and slowing of heart beat is caused through……………….
nervous system. (Sympathetic/ Parasympathetic/ Central)
Ans.
parasympathetic
2. ……………..is the largest part of the brain.
(Cerebellum/ Cerebrum/ Medulla oblongata)
Ans.
Cerebrum
3. The fluid present inside and outside the brain is …………………
(pericardial fluid/ Cerebrospinal fluid/ Endolymph)
Ans.
cerebrospinal fluid
4. In all there are ……………. pairs of cranial nerves and …………….. pairs of spinal nerves in human.
(10/ 12/ 20/ 21/ 31)
Ans.
12,31
5. Brain and spinal cord are the parts of………………….Nervous system.
(Central/ peripheral/autonomous)
Ans.
central
6. The dorsal root ganglion of the spinal cord contains cell bodies of………………
(motor/ sensory intermediate) neurons.
Ans.
sensory
7. White matter consists of mainly .
(Axon/ Cytons/ dendrites)
Ans.
axon
Question. Name the following :
.1. The aggregate of the nerve cells (cell bodies) form which nerve fibres may arise or enter into
Ans.
Ganglia.
2. The outermost covering of the brain
Ans.
dura mater.
3. The fluid that is present inside and outside the brain
Ans.
cerebrospinal fluid.
4. The fluid that is present inside and outside the brain
Ans.
cerebrospinal fluid.
5. A spontaneous, quick and involuntary response to a stimulus
Ans.
reflex action.
6. Long thread like part of the nerve cell
Ans.
Axon.
7. Outer protective membrane of the brain
Ans.
dura mater.
8. Point of contact between two nerve cells
Ans.
synapse.
9. Cell body of the neuron
Ans.
cyton.
10. Performs reflex action below neck without the involvement of the brain
Ans.
spinal cord.
11. The kind of nerve carrying impulses from the brain to a gland or muscle
Ans.
motor nerve.
12. Branched protplasmic extensions of the cell body
Ans.
dendrons or dendrites.
13. The part of the human brain which controls body temperature
Ans.
hypothalamus.
14. Part of the brain that co-ordinates muscular activities
Ans.
cerebellum.
15. The structural and functional unit of nervous system
Ans.
Neuron.
16. The part of the brain which is concerned with memory
Ans.
cerebrum (frontal lobe).
17. Part of the brain co-ordinates involuntary action
Ans.
medulla oblongata.
18. Chemicals responsible for passing the impulse from one neuron to another
Ans.
neurohormone (acetylcholine).
19. The sheet of nerve fibres that connect the two halves of cerebral hemispheres
Ans.
corpus callosum.
20. Gaps in the insulating layer enclosing the axon
Ans.
Nodes of Ranvier.
21. Carries impulses towards the brain and spinal cord
Ans.
afferent neuron
22. The outer layer of the brain
Ans.
cortex.
23. Wave of electrical disturbance that sweeps over the nerve cell
Ans.
Impulse.
24. A bundle of axons enclosed in a tubular sheath
Ans.
nerve







