Students of ICSE Class 10 should refer to Agriculture I And II ICSE Class 10 Geography previous year questions and solutions. below which have come in past board exams. You should always go through questions that have come in previous years. This will help you to understand the pattern of questions in ICSE Class 10 Geography and prepare accordingly. This will help you to get better marks in ICSE Class 10 Board Exams
ICSE Class 10 Geography Agriculture I And II Last Year Questions
Students should learn the important questions and answers given below for Chapter Agriculture I And II in Geography for ICSE Class 10. These board questions are expected to come in the upcoming exams. Students of ICSE Class 10th should go through the board exams questions and answers for ICSE Class 10 Geography which will help them to get more marks in exams.
Board Exam Questions Agriculture I And II ICSE Class 10 Geography
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question: Give two reasons, why the yield of Indian agriculture is low as compared to world standards?
Answer: (i) Inadequate use of manures and fertilizers, negligence of crop rotation, use of poor quality seeds, inadequate water supply, etc. leads to low productivity.
(ii) Use of simple and old agricultural tools, use of no or less machines for ploughing, sowing, irrigating, pruning, harvesting and threshing results in low yield.
Question: How has the consolidation of land holdings helped the farming community?
Answer: The consolidation of landholdings helped the famers in the following ways-
(i) It saved time, energy and money in moving from one farm to another.
(ii) Farmers feel encouraged to spend money on
the improvement of his land.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question: Mention any two reasons for the importance of agriculture in India.
OR
What is the importance of agriculture in India? Mention two factors.
Answer: – Provides food for our growing population
– Provides fodder for livestock
– Provides employment
– Supplies raw material for agro-based industries
– Gives rise to industries related to agriculture, like pesticides, fertilizers, farming tools
– Earns foreign exchange through export.
Question: How has the poverty and fragmentation of land become problems of agricultural India?
Answer: Farm fragmentation reduces the size of the farm on which it is not possible to use harvesters or
other farm machinery and modern methods of agriculture. Because of poverty the farmers cannot
afford good quality seeds, fertilizers or pesticides or farm implements and so the yield is low.
Question: Mention any two problems of agriculture in India.
Answer: Problems of Agriculture in India-
(i) Lack of adequate irrigation facilities and dependence on monsoon.
(ii) The land holdings are uneconomic due to their small size and as such the yields are low.
(iii) Agriculture is becoming mechanized and requires huge capital investments to purchase machineries, fertilizers, pesticides and high yielding variety seeds. The Indian farmers are poor to buy all these materials.
(iv) A majority of Indian farmers are still dependent on the primitive and poor techniques of producing crops.
Types of Farming in India
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question: Explain the term Plantation Farming.
Answer: (i) Plantation farming is an extensive system of agriculture in which single cash crop is cultivated on a large scale in an estate.
(ii) Crops like tea, coffee, rubber, spices, etc. are grown under plantation farming mainly for profit.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question: Differentiate between subsistence farming and commercial farming
Answer:

Question: What is Mixed Farming? Mention any one benefit of Mixed Farming.
Answer: Mixed Farming is a combination of growing crops and rearing of cattle simultaneously. The main benefit of this type of farming is that it ensures a steady income for the farmers because if any one business or farming fails, the other means can support.
Question: Explain briefly the following terms:
(i) Shifting cultivation
(ii) Bud grafting
Answer: (i) Shifting cultivation involves a patch of forest which is cleared, trees are cut down and the stumps set on fire. The patch is then cultivated for a few years and when the soil becomes infertile, the cultivator moves to a fresh piece of land and repeats the same procedure.
(ii) The bud from a good rubber tree is grafted on the seedling of a new rubber tree, Once the bud starts sprouting the shoot from the seedling is cut down and the bud then grows into a tree with all of the traits of the mother tree.
Question: Mention any two features of plantation farming stating two examples.
Answer: Any two of the following:
Huge capital investment Large land holding Labour intensive Single crop or monoculture Crop grown usually for export Crops grown as plantation crops are tea, coffee, rubber and spices.
Question: Distinguish between Intensive Commercial Farming and Extensive Commercial Farming.
Answer:

Question: Explain two important characteristics of plantation farming. Name one important plantation crop.
Answer: Characteristics of plantation farming-
(i) Plantation farming is an extensive system of agriculture in which single cash crop is cultivated on a large scale in an estate.
(ii) Crops like tea, coffee, rubber, spices, etc. are grown under plantation farming mainly for profit.
(iii) This type of farming is practiced in vast lands extending from a few hectares to thousands of hectares.
(iv) Modern methods, techniques and machineries are used for growing crops.
(v) Huge capital is invested in buying machineries, fertilizers, pesticides and building factories for processing of crops. One important plantation crop- Tea.
Question: Mention two differences between shifting agriculture and plantation agriculture.
Answer:

Question: Describe any two main features of Subsistence Agriculture.
Answer: Two main features of Subsistence Agriculture-
(i) Subsistence farming is a self-sufficient farming in which the farmers grow enough food to feed himself and his family.
(ii) The farmers have small land and do not use fertilizers and thus the yield is low.
(iii) The output is mostly for local requirements with little or no surplus trade.
(iv) The land holdings are small and scattered.
(v) The farmer uses simple and primitive tools with traditional method of agriculture.
Agricultural Seasons and Food Crops
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question: State the method of cultivation of growing wheat.
Answer: Sowing and harvesting are the two methods of growing wheat.
Question: Millets are known as dry crops. Give a geographical reason.
OR
Millets are referred to as dry crops. Explain why?
Answer: Millets are known as dry crops because they can grow in areas of low rainfall ranging from 50-100 cms.
Question: Pulses are important food crops. Give a geographical reason.
Answer: Pulses are high in protein and are an important vegetarian diet.
Question: Explain the term Broadcasting.
Answer: In this method after ploughing, the seeds are scattered all over the field by hand before the onset of monsoon.
Question:. Explain the propagation of paddy by transplantation.
Answer: (i) Transplantation is the process in which seedlings are first grown in nurseries and after 4 to 5 weeks when the saplings attain a height of 25 to 30 cm they are transplanted to prepared rice fields.
(ii) Transplantation enables to select only healthy seedlings for the plants.
question: Explain the term Drilling.
Answer: Drilling- In this method the seeds are sown in the furrows with the help of a drill made of a bamboo.
Question: Pulses are grown as rotation crops. Explain why?
Answer: Pulses are grown as rotation crops as they are leguminous crops that fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil and increase the natural fertility of the soil.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question: What are the main crop seasons of India? Explain giving one example of each.
Answer: Kharif Season and Rabi Season are the two main crop seasons in India.
Kharif Crops- Rice, jowar, sugarcane, bajra, ragi, maize, cotton and jute. Rabi Crops- Wheat, barley, rapeseed, linseed, gram, peas, mustard.
Question: With reference to Rice cultivation, answer the following:
(i) Why does rice grow well in a soil with clay like subsoil?
(ii) What is the advantage of growing rice in nurseries before it is transplanted?
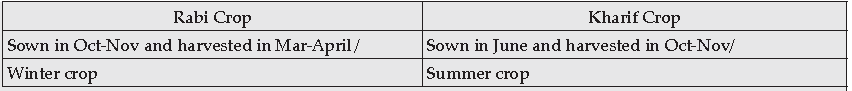
Question: Differentiate between a Rabi crop and a Kharif crop.
Answer:
Question: With reference to rice cultivation, answer the following:
(i) Name two leading states in the production of rice.
(ii) Give two advantages of growing rice in nurseries.
Answer: (i) West Bengal, Punjab, Uttar Pradesh and Andhra Pradesh.
(ii) Advantages of growing rice in nurseries:
1. It enables deeper penetration of the roots in the soil.
2. Less wastage of seeds.
3. It minimizes weed pressure by resowing.
4. It gives higher yield.
Question: State two geographical requirements for the growth of wheat in India.
Answer: Temperature required- 10°C-15°C. Rainfall- 50 cm to 100 cm Soil- well-drained loams and clay loams.
Question:

Study the picture given above and answer the following questions:
(i) Name the crop which is being planted. Give one benefit of this method of planting this crop.
(ii) Mention the climatic conditions which favour the cultivation of the crop being planted.
Answer: (i) Rice. It enables deeper penetration of the roots in the soil and gives higher yield.
(ii) 1. Temperature- 18°C – 32°C
2. Rainfall- 150 cm – 300 cm
3. Soil- Deep fertile clayey or loamy soils.
Question: (i) When are Kharif crops (1) sown and (2) harvested?
(ii) Name a cash crop which is also a Kharif crop.
Answer: (i) (1) Kharif crops are sown in the months of June and July and (2) harvested in September and October.
(ii) Cotton.
Question: In which season is wheat grown in northern India?
What are the rainfall and soil requirements of this crop?
Answer: Wheat is grown in the Rabi season in northern India.
Rainfall- 50 cm to 100 cm Soil- Alluvial soil or well-drained loams and clay loams soil.
Question: Explain why wheat is grown as a Rabi crop?
Answer: Wheat is a Rabi crop because-
1. Sown in October- November and harvested in January in south, by March-April in north.
2. Temperature of 10°C-15°C is suitable for sowing and 20°C-25°C during harvest and rainfall
between 50 cm to 100 cms.
Question: Mention the climate and the soil conditions needed for the cultivation of rice.
Answer: 1. Temperature- 18°C – 32°C
2. Rainfall- 150 cm – 300 cm
3. Soil- Deep fertile clayey or loamy soils.
Question: Explain the terms:
(i) Transplantation
(ii) Broadcasting
Answer: (i) Transplantation: In transplantation, seedlings are first grown in nurseries and after 4 to 5 weeks when the saplings attain a height of 25 to 30 cm they are transplanted to prepared rice fields.
(ii) Broadcasting: In this method after ploughing, the seeds are scattered all over the field by hand before
the onset of monsoon.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question: Mention three differences in the geographical conditions and cultivation of rice and wheat.
Answer:

Question: State three important aspects of the Japanese method of rice cultivation.
Answer: Three aspects of Japanese method of cultivation-
(i) Use of High Yielding Variety (HYV) of seeds.
(ii) Saplings are sown in the nursery and raised in the nursery beds for 4-5 weeks.
(iii) Manure is extensively used to enhance the yield.
Question: Give the importance of Pulses.
Answer: Importance of Pulses-
(i) Pulses form an important part of the Indian diets because they are full of protein.
(ii) Pulses are grown as rotation crops as they are leguminous crops that fix atmospheric nitrogen
in the soil and increase the natural fertility of the soil.
(iii) Pulses are good cattle fodder too
Question: Name the major crop seasons along with their months and crops.
Answer: Major crop seasons are-
(i) Kharif Crops- The cropping season is from July to October during the south west monsoon. Rice, jowar, sugarcane, bajra, ragi, maize, cotton and jute are some of the important kharif crops.
(ii) Rabi Season- The cropping season is from October to March. Crops like wheat, barley, rapeseed, linseed, gram, peas, mustard, potatoes, etc. are grown as Rabi crops.
Question: What are the advantages of transplantation method?
Answer: (i) It enables to select only healthy seedlings for the plants.
(ii) Less wastage of seeds.
(iii) It minimizes weed pressure by resowing.
(iv) It gives higher yield.
Question. What kind of soil is needed for the cultivation of wheat ?
Answer: Wheat requires well drained loams and clay loam.
Question. What are the main features of shifting cultivation ?
Answer: The special features are :
(i) A patch of forest is cleared by cutting and burning of the stumps and the same ash is used as fertilizer.
(ii) Seeds are sown on the ground without ploughing or following any other steps of agriculture.
(iii) After 2-3 years when the soil has lost its nutrients, the field is abandoned and the same practice is repeated on another patch of forest.
(iv) Shifting cultivation is extremely harmful to the environment both by means of forest destruction as well has acceleration of soil erosion.
Question. What are the special features of intensive (commercial) farming ?
Answer: The special features of Intensive commercial farming are :
(i) It is practiced on smaller farms in thickly populated region
(ii) More than one crop is cultivated on the same field
(iii) Optimum use of land is made.
(iv) It is more of labour intensive method of cultivation.
(v) Per acre production is more but total production is less due to smaller landholding.
(vi) To increase the output, rich manure and fertilisers good quality seeds and irrigation facilities are used.
Question. What is ‘National Agricultural Policy’ ?
Answer: (i) The Union Government announced the National Agricultural Policy (NAP) envisaging over 4 cent growth rate per annum in the next decades, in July 28, 2000.
(ii) The policy seeks to promote technically sound, economically viable, environmentally non-degrading, and socially acceptable use of country’s natural resources – land, water and genetic endowment to promote substainable development of agriculture.
Question. Name the state that produces the highest quantity of rice in India.
Answer: West Bengal produces the highest quantity of rice in India.
Question. State the use of growing rice on lowlands.
Answer: Rice produced in lowland is used for local consumption and supplied to other regions. Suppling water through irrigation is also possible.
Question. What are the disadvantages of Shifting cultivation?
Answer: Disadvantage of shifting agriculture are :
(i) It accelerates soil erosion and causes floods and silting in lower reaches of riverine flood plains.
(ii) The yield per hectare is low as the farmers do not use fertilizers.
Question. How is the ‘Threshing’ done ?
Answer: Threshing is done by beating the sheaves against the wooden bars. The grains are separated from the stalks.
Question. How do the monsoons affect agriculture in India ?
Answer: (i) Indian agriculture is dependent to a large extent on the monsoons, which are uncertain, irregular and unequally distributed.
(ii) Nearly 55% of the net sown area continues to depend on rainfall rather than irrigation.
(iii) The irrigation facilities in India are very low.
Question. What are the special features of Extensive farming ?
Answer: The special features are :
(i) Farms are of large size.
(ii) More of mechanical plower (machines) are used.
(iii) Farmers are specialized in one or two major commercial crops.
(iv) It is highly capital intensive method of cultivation.
(v) Total production is high with large surplus for sale.
Question. Explain the ‘Winnowing and Milling’.
Answer: (i) Winnowing is the process of removing the unwanted husk from the grains.
(ii) Milling is done to remove the yellowish husk from the grains.
Question. Shifting cultivation is a great menace to environment.
Answer: (i) In shifting cultivation a patch of forest is cleared and cleared patch is then cultivated for a few years until the fertility of the soil is seriously reduced.
(ii) This results in acceleration of soil erosion and causes floods and silting in the lower reaches of rivers.
Question. Explain the role of ‘National Agricultural Policy’ as a remedy to boost agricultural production.
Answer: The policy seeks to promote technically sound, economically viable, nvironmentally non-degrading, and socially acceptable use of country’s
natural resources – land, water and genetic endowment to promote sustainable development of agriculture.
The salient features of this policy are :
(i) Annual growth rate of over 4 per cent envisaged.
(ii) Private sector participation to be promoted through contract farming and land leasing.
(iii) Wider coverage of future markets to minimise fluctuations in price and other risks.
(iv) Plant varieties to be promoted through legislation.
(v) Animal husbandry, poultry, dairy and aquaculture to receive high priority to diversify agriculture.
(vi) New location-specific and economically viable improved varieties of agriculture and horticulture crops to be developed.
(vii) Restrictions on movement of agricultural commodities will be removed.
(viii) Review of tax structure.
(ix) Institutionalisation of farm credit.
(x) Priority to rural electrification.
(xi) National Agriculture Insurance Scheme to cover every aspect of agriculture.
Question. What is bajra also known as ? What are its requirements with regard to temperature, rainfall and soil ?
Answer: Bajra is also known as Cumbu. The requirements are :
Rain : 40 cms to 50 cms
Temperature : 25ºC to 30ºC
Soil : Red soil, sandy loams or black soil.
Question. Give two advantages of growing rice in nurseries.
Answer: (i) If the rice is grown in nurseries only healthy plants are picked up for resowing in the field unhealthy plants are discarded.
(ii) Weeds are removed while resowing.
Question. State two geographical requirements for the growth of wheat in India.
Answer: Geographical conditions for wheat :
(i) Temperature : Wheat being a rabi crop, is sown just before winter. Ideally, temperature in the range of 10ºC-15ºC is suitable for sowing and 20º-25ºC during harvest.
(ii) Rainfall : 80 cm of annual rainfall is ideal for wheat cultivation.
(iii) Soils : Well drained loams and clay loams.
Question. What is ragi also known as ? What are its requirements with regard to rainfall and soil ?
Answer: Ragi is also known as Nachni or Buck wheat. The requirements are :
Rain : 50 cms to 100 cms
Temperature : 20ºC to 30ºC
Soil : Red soil, black soil, sandy loams.
Question. What is meant by “transplantation”? State its advantages.
Answer: In transplantation seedlings of rice are first grown in nurseries and after 4 to 5 weeks when saplings attain 25 to 30 cm of height they are ‘transplanted’ into prepared rice fields in groups of four to six at a distance of 30-45 cm.
Advantage of transplatation :
(i) Only healthy plants are picked for resowing in the field and unhealthy plants are discarded.
(ii) Weeds are removed while resowing.
(iii) This method gives higher yield.
(iv) There is less wastage of seeds as compared to broadcasting method.
Question. What are the main features of mixed farming?
Answer: The special features of mixed farming are :
(i) Crop cultivation and animal rearing is done simultaneously.
(ii) Two or more crops are grown together.
(iii) It ensures steady income to the farmers.
(iv) Rotation of crops is practiced.
Question. What solutions are offered against irregular monsoons as far as farming is concerned ?
Answer: (i) The government has given importance to optimum utilisation of irrigation infrastructure.
(ii) Programmes have been started to ensure completion of irrigation projects.
(iii) Sprinklers and drip irrigation system has been installed.
Question. In which state in South India rice is grown extensively? Why?
Answer: Tamil Nadu, as it receives good amount of rainfall as well as temperature ranges from 25ºC to 30ºC in Tamil Nadu which is required for rice cultivation.
Question. State the climatic conditions suitable for the cultivation of pulses.
Answer: Climatic conditions for pulses :
Temperature : 20ºC to 25ºC
Rainfall : 50 cm to 75 cm.
Question. Explain Zaid Kharif crops and Zaid Rabi crops. Give example for each.
Answer: (i) Zaid Kharif Crops : These crops are sown in August and September and are harvested in December and January. Most of the oilseeds like
mustard are grown in this season.
(ii) Zaid Rabi Crops : These crops are sown at the beginning of the hot season in February and March and are harvested in the months of
April and May. Summer vegetables, jowar, maize, watermelons, cucumbers, etc., are important among these crops.
Question. Expain two methods of rice cultivation in India.
Answer: In India, rice is cultivated by two methods (i) the dry method; and (b) the puddled method.
(i) The dry method : The dry system of cultivation is mainly confined to areas which depend on rains and do not have supplementary irrigation
facilities. In this method, the seeds are sown in rows with the help of drills in heavy rainfall areas and scattered with hands in areas of moderate rainfall.
(ii) The puddled method : The puddled or wet method of cultivation is practised in areas which have assured and adequate supply of water. In this method, the land is ploughed thoroughly and filled with three to five centimetres of standing water in the field. This water is maintained in the fields up to a depth of two to three centimetres till the seedlings are well established.
Question. How is Ragi cultivated in India ?
Answer: (i) Ragi is Kharif crop, sown between May and August and harvested between September and January.
(ii) In many parts of South India it is cultivated throughout the year with the help of irrigation.
(iii) The seeds are sown by broadcast method or with the help of drills and even transplanted on well-prepared friable beds.
(iv) The crop requires 3 to 5 months to mature.
Question. Rice is not the main crop in the Deccan Plateau.
Answer: Rice is not the main crop in the Deccan Plateau because Deccan plateau receives rainfall less than 100 cm which is not suitable for rice, as rice requires rainfall between 150 to 300 cm.
Question. What is the impact of the globalisation on Indian agriculture ?
Answer: Globalisation has thrown open Indian markets to the world. Now foreign products including agricultural products can easily be imported to India and
India can export its products to other countries. Consequently, Indian farmers are facing a big challenge from international competition. This is because :
(i) The yields per hectare of major crops in the developed countries are much higher than that of India.
(ii) The prices of most farm products in the international markets are declining whereas in the Indian markets these are increasing. The prices are declining in the international market due to :
(a) Use of sophisticated farm machinery which has led to the reduction in the cost of production;
(b) Rapid progress in the field of biotechnology, which has made available highly productive seeds to the farmers.
(c) Heavy subsidies given to the farmers in the developed countries, which result in low production cost.
(iii) Reduction in import duties on agricultural products have proved detrimental to agriculture in India.
Question. What are the special features of subsistence farming?
Answer: The special features of subsistence farming are
(i) Landholdings are small and scattered.
(ii) The farmers use traditional methods of agriculture.
(iii) The agricultural output depends on monsoon, natural fertility of soil & organic fertilizers used by the farmer.
(iv) Per acre output is low and is consumed within the family. There is no surplus for sale.
(v) Food crops are the main crops grown.
Question. What is known as ‘Shifting Agriculture’? OR How is shifting cultivation carried out ?
Answer: (i) Shifting Agriculture is a primitive agricultural practice in which a patch of forest is cleared, trees are cut and stumps are set on fire.
(ii) The cleared land is then cultivated for a few years until fertility of the soil is seriously reduced.
(iii) Then the farmer moves to a fresh piece of land and the same process is repeated.
Question. Explain the methods of cultivation of wheat.
Answer: Sowing :
(i) The fields are ploughed and pulverized several times before the seed is sown.
(ii) The seeds can be sown by using drilling or the broadcasting method.
(iii) The seeds germinate in about three or four days.
(iv) The plant needs three or four times irrigation during the growing period.
Harvesting :
(i) The wheat crop starts ripening in the month of March (temperature about 21ºC) and is harvested in April when the temperature is 2Question.5ºC.
(ii) Wheat is mostly harvested using a sickle.
(iii) However, machines have replaced the sickles in Punjab, Haryana and western Uttar Pradesh.
(iv) The traditional method of threshing (to get the crop trampled under the bullock’s feet) is used to separate the grain from husk.
(v) But this work is now done by threshers as the traditional method is time-consuming.
Question. What are the special features of commercial farming?
Answer: The special features are :
(i) It is generally practiced on large farms.
(ii) Crops are grown mainly for sale as there is large surplus for sale.
(iii) Farming activities are highly mechanized.
(iv) It is a capital intensive method of cultivation and it is prevalent in the areas where farms are large and market economy is well developed.
Question. Compare the climatic conditions for wheat cultivation with those for rice cultivation.
Answer: (i) Rice is a Kharif crop whereas Wheat is a Rabi crop.
(ii) Rice needs temperature ranges between 18º to 32º whereas wheat needs temperature 10ºC to 15ºC for sowing and 20ºC to 25ºC during harvest.
(iii) Rice needs rainfall 180 to 300 cm and incase of wheat 80 cm annual rainfall is ideal.
Question. What are millets? Why are millets referred to as ‘foodgrains of the poor?’
Answer: The term ‘millets’ refers to a number of inferior grains. They are cheaper in rate and can be afforded by poor people.
Question. In which region is ragi grown in India ? Why ?
Answer: (i) Ragi is grown in Karnataka and Tamil Nadu as well as in Uttarakhand, Jharkhand, Gujarat.
(ii) These areas receive less rainfall as ragi requires average annual rainfall between 50 cm to 100 cm therefore cultivation of ragi is possible in above regions.
Question. Mention the climatic conditions necessary for the growth of Jowar.
Answer: Temperature : Jowar grows well at a temperature between 27ºC and 32ºC at the time of germination, but it cannot be grown when temperature is
below 16ºC.
Rainfall : Jowar can be grown in arid and semi-arid areas having rainfall under 45 cm.
Question. Millets are called dry crops.
Answer: Millets are called dry crops because :
(i) They can be grown in regions of low rainfall where rice and wheat can not be grown.
(ii) It is a hardy plant and drought resistant crop. It has no special soil requirements. It is a short duration crop.
Question. What is jowar also known as ? What are its requirements with regard to rainfall, temperature and soil ?
Answer: Jowar is also known as Sorghum. The requirements are :
Rain : 50 cms to 100 cms
Temperature : 27ºC to 32ºC
Soil : Black clayey loamy dry soil is ideal.
Question. What are the main features of plantation farming?
Answer: The main features of Plantation farming are :
(i) Commerical crops such as tea, coffee, rubber etc are grown where the same plants give yield for more than one year.
(ii) Single crop is grown on a large tracts of land, using modern machinery.
(iii) Cultivation is highly scientific with the latest technology and modern methods of agriculture being used.
(iv) Large amount of capital investment is made to meet the daily expenses involved.
(v) Chemical fertilisers, herbicides and insecticides are used extensively.
Question. Mention any two problems of agriculture in India.
Answer: (i) Unreliable Rainfall : Indian agriculture is dependent to a large extent on the monsoons which are uncertain and irregular & unequally distributed that is why when rains fail agricultural production is badly affected resulting in scarcity of food grains.
(ii) Soil Erosion : Indiscriminate cutting of trees, overgrazing, faulty landuse result in ‘soil erosion’ and ‘soil degradation’. Loss of fertility is responsible for the low crop yields.
(iii) Lack of Irrigation Facilities : A large percent of the net cropped area lacks irrigation facilities and is dependent on monsoon. The failure of monsoon is the failure of agriculture.
Question. In what way are the millets different from rice ?
Answer: Difference between millets and rice are as follows :
(i) Rice is the most important crop of India and supports half of the India’s population whereas millets provide food for the poor, stalk and stem are used as fodder for the cattle.
(ii) Deep fertile clayey or friable loams are ideal for the cultivation of rice. Even black lava soil is suitable for its cultivation whereas millets do not have any special requirements as far as soil is concerned it can grow in soils which are rather interfile.
(iii) Rice requires an average temperature of about 24ºC while millets require temperature ranging from 26ºC to 33ºC.
(iv) Rice requires 150 cm to 200 cm rainfall whereas millets require 50 cm to 100 cm rainfall.
Question. Ragi is one of hardiest crops.
Answer: Ragi is one of the hardiest crops as it can grow under conditions of very low rainfall and can withstand very severe drought.
Question. Mention any three remedial steps taken by the government to boost agricultural production.
Answer: Three remedial steps taken by government :
(i) The Government announces minimum support prices for various agricultural commodities from time to time to ensure adequate returns to the farmers.
(ii) The government of India provides subsidy on fertilisers to ensure adequate availability of fertilizer to farmers at reasonable rates.
(iii) The Government started Kisan call centres. These are working in 25 different locations covering almost all the states of the country.
Question. Name two states that grow wheat extensively. What climatic features have helped these states in this respect?
Answer: Punjab and Haryana have continental type of climate for wheat cultivation. i.e. they have temperature around 7ºC to 10ºC in winter season as well
as they receive rainfall less than 100 cm. which is favorable climate for wheat cultivation
Question. Pulses are usually rotated with other crops.
Answer: Being leguminous crops, pulses fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil and increase the natural fertility of soil. Hence, pulses are usually rotated with other crops to maintain or restore soil fertility.
Question. Explain the methods of cultivation of Jowar.
Answer: (i) Jowar requires less preparation of the fields as compared to rice or wheat.
(ii) However, the soil management before sowing plays an important role in the dry farming areas.
(iii) The seeds are mostly sown using the broadcast method.
(iv) But they are also dibbled in some areas.
(v) The crop matures in about four to five months.
Question. Why is agriculture said to be the backbone of the Indian economy?
Answer: (i) It provides food for our expanding population and fodder for our livestock.
(ii) It generates working capital for non-agricultural development, supplies raw materials for agro-based industries like textile, sugar, food processing, vanaspati, etc.
(iii) It provides a large part of the market for industrial goods, especially the farm inputs like fertilisers, pesticides, implements, machinery, etc.
(iv) It accounts for a substantial portion of India’s exports.
(v) It provides employment to millions of people.
Question. Wheat is a winter crop in India.
Answer: Wheat is a winter crop in India because, wheat is mostly confined to the regions of cool winter. It grows best in cool moist climate and ripens in
warm dry climate. It requires temperature 10º to 15ºC during sowing and 20º to 25º during harvest.
Question. What is the difference between the Upland rice and the Lowland rice?
Answer: (i) Upland rice is grown on mountainous regions where as lowland rice is grown on low lying region.
(ii) Upland rice depends on the distribution of rainfall.
(iii) Lowland Rice requires plenty of water during sowing and harvesting.
(iv) Upland rice is consumed by local people where as lowland rice is used for local consumption as well as supplied to other regions.
Question. What are the two main agricultural seasons in India ?
Answer: Kharif : Kharif crops associated with southwest monsoon or rainy season.
Rabi : It begins with onset of winter in October and November.



