Students should read the Meaning and Scope of Public Finance ICSE Economics Class 10 notes provided below. These revision notes have been prepared based on the latest ICSE Economics Books for Class 10 issued for the current academic year. Our teachers have designed thee notes for the students are able to understand all topics given in Economics in standard 10 and get good marks in exams
ICSE Class 10 Economics Meaning and Scope of Public Finance Revision Notes
Students can refer to the quick revision notes prepared for Chapter Economics Meaning and Scope of Public Finance in Class 10 ICSE. These notes will be really helpful for the students giving the Economics exam in ICSE Class 10. Our teachers have prepared these concept notes based on the latest ICSE syllabus and ICSE books issued for the current academic year. Please refer to Chapter wise notes for ICSE Class 10 Economics provided on our website.
Meaning of Public Finance
Professor Dalton defined public finance as being connected with the income and expenditure of public authorities, with the adjustment of one to another. Tax revenue and non-tax revenue are the two sources of income.
Scope of Public Finance
Public finance is concerned with the methods of raising and allocating of funds between various activities of the government. Important branches of public finance:

- Public revenue: It refers to the income or earnings of the government of any country. Public revenue consists of tax and non-tax revenue.
- Public expenditure: It deals with various types of expenditures required for the proper functioning of the government.
- Public debt: When the planned expenditure of the government of a country exceeds its total revenue, the government has to borrow money from various organisations and individuals. This is called public debt.
- Budgetary policy: It deals with the type of financial statement made by the government with respect to its anticipated revenue and expenditure during any particular year. If the government expenditure exceeds its revenue, there arises a deficit in the budget.
- Fiscal policy: The fiscal policy affects the revenue and expenditure of the government. Fiscal policy instruments are government expenditure, imposition of taxes, subsidy provision and public debt.
Nature of Public Finance
Positive and normative are the two aspects of modern finance. Classical economists believed the market mechanism and they dealt with the theory of public finance only with public revenue, public expenditure and public debt without considering their impact on welfare. This aspect is called the positive aspect of public finance.
Welfare economists strongly believed in the welfare aspects of public revenue and public expenditure. No government can afford to tax the people without ensuring economic welfare. Hence, they try to transfer incomes from the rich to the poor through fiscal operations. This aspect is called the normative aspect of public finance.
Comparison between Public and Private Finance
- Differences between public and private finance
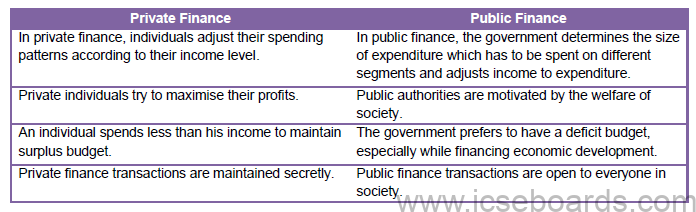
- Similarities between public finance and private finance
o Public and private finance have almost the same objectives. Private finance aims to satisfy individual wants, whereas public finance tries to satisfy the wants of all members of society.
o Limited resources are available to satisfy wants. Both private and public sectors’ primary aim is to maximise the use of limited resources.
o Both private and public finance have to look into the income and expenditure statements. According to priorities, both public and private finance have to raise the sources of income and allocate funds among different heads of expenditure.
o Both public and private finance have to borrow to bridge the gap between expenditure and income.
Significant Role of Public Finance
Public finance plays a dynamic role in the economy. It is very significant for the allocation of productive resources to maximise the national output. The public sector makes certain provisions for social wants such as defence, railways, park, law and order. Apart from the process of revenue and expenditure of the government, it is used to allocate the total resources of the community among private and social goods.
- Measures to secure equal distribution of income and wealth
o Progressive taxation of direct taxes ensures equality in the distribution of income and wealth.
o Government expenditure on welfare projects for the poor.
o Levying high taxes on goods mostly purchased by the rich income groups and providing subsidies on the goods purchased by the poor income groups.
Relation of Public Finance with Other Social Sciences
- Public finance is considered a branch of economics. In the economy, public finance involves raising and spending of funds by government authorities. The principles of economics are considered in the formulation of policies for public revenue and public expenditure. Hence, public finance and economics are interrelated.
- Public finance is the study of finances of the government or public bodies. It has no existence without political finance.
- Policy of public finance is always formulated by looking into its history. Statistical data of the past guide the government and helps it to follow the right track.
- While determining the taxation policy, the government ensures that the burden of tax does not fall on the poor sections of society.



